Difference between revisions of "Setaria corrugata"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | Populations of ''Setaria corrugata'' have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.<ref> | + | Populations of ''Setaria corrugata'' have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.<ref>Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, R. E. Masters, K. M. Robertson and S. M. Hermann 2012. Fire-frequency effects on vegetation in north Florida pinelands: Another look at the long-term Stoddard Fire Research Plots at Tall Timbers Research Station. Forest Ecology and Management 264: 197-209.</ref> |
<!--===Pollination and use by animals===--> | <!--===Pollination and use by animals===--> | ||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
Revision as of 12:18, 23 July 2021
Common name: coastal bristlegrass[1]
| Setaria corrugata | |
|---|---|
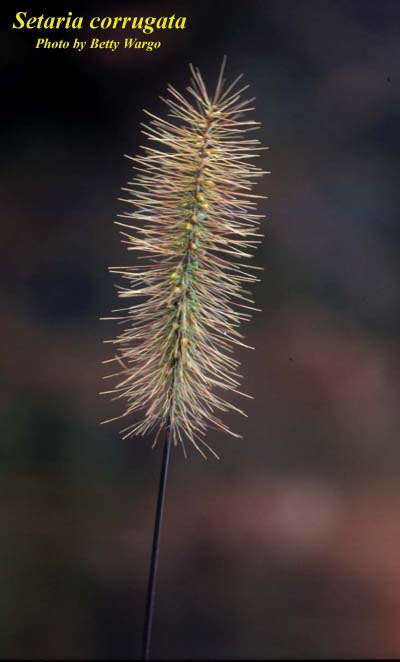

| |
| Photo by Betty Wargo hosted at Atlas of Florida Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Setaria |
| Species: | S. corrugata |
| Binomial name | |
| Setaria corrugata (Elliott) Schult. | |
| |
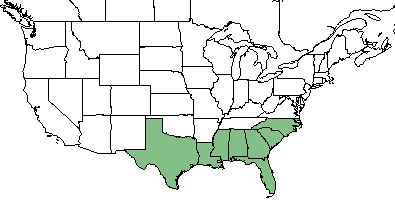
| Natural range of Setaria corrugata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Chaetochloa corrugata (Elliott) Scribner
Varieties: none
Description
S. corrugata is an annual graminoid of the Poaceae family native to North America.[1]
Distribution
S. corrugata is found along the southeastern coast of the United States from Texas to North Carolina[1] with disjunct populations in western Cuba.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
S. corrugata proliferates in pinelands and disturbed areas.[3] Specimens have been collected from open pineland, coastal hammocks, roadsides, banks of holding ponds, wooded old dune, sandy hardwood clearing, mixed forest, oak woods, longleaf pine sand ridge, wiregrass savanna, bluff by river, mangrove swamp, and open field.[4]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by wind.[5]
Fire ecology
Populations of Setaria corrugata have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.[6]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=SECO4
- ↑ Sorrie, B. A. and A. S. Weakley 2001. Coastal Plain valcular plant endemics: Phytogeographic patterns. Castanea 66: 50-82.
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R.K. Godfrey, Loran Anderson, C. Jackson, R. Kral, R. E. Perdue, Richard Houk, R. Kral, A.F. Clewell, D.L. Martin, S. T. Cooper, Gwynn Ramsey, R.S. Mitchell, J. P. Gillespie, D.B. Ward, J. Hunter, F. S. Ward, D. Burch. States and counties: Florida (Leon, Wakulla, Franklin, Santa Rosa, Gadsden, Levy, Brevard, Madison, Citrus, Sarasota, Dixie, Suwannee, Hamilton, Walton, Monroe) Georgia (Thomas)
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, R. E. Masters, K. M. Robertson and S. M. Hermann 2012. Fire-frequency effects on vegetation in north Florida pinelands: Another look at the long-term Stoddard Fire Research Plots at Tall Timbers Research Station. Forest Ecology and Management 264: 197-209.