Difference between revisions of "Buchnera floridana"
(→Description) |
|||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| + | |||
===Fire ecology===<!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology===<!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
Thrives in fire-maintained pine graminoid ecosystems in strongly acidic soils.<ref name="flora"/> | Thrives in fire-maintained pine graminoid ecosystems in strongly acidic soils.<ref name="flora"/> | ||
Revision as of 15:10, 23 June 2021
| Buchnera floridana | |
|---|---|

| |
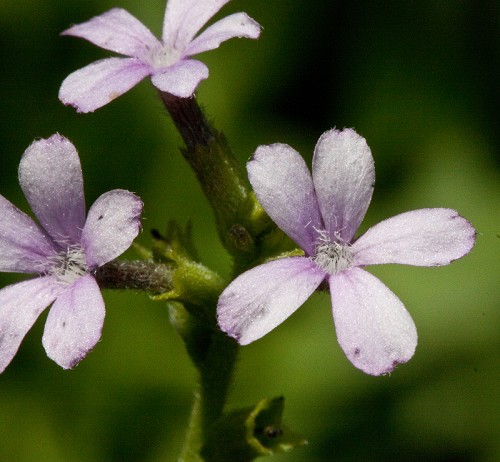
| Photo by John R. Gwaltney, Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Scrophulariales |
| Family: | Scrophulariaceae |
| Genus: | Buchnera |
| Species: | B. floridana |
| Binomial name | |
| Buchnera floridana L. | |
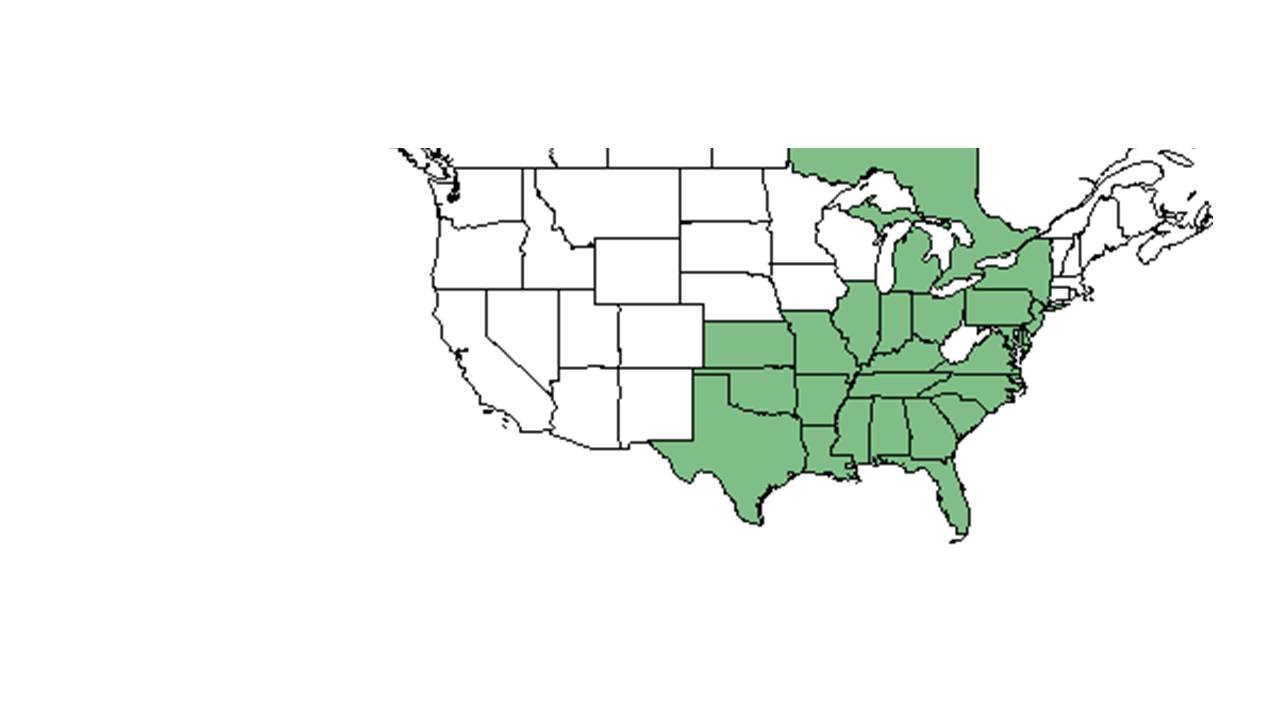
| |
| Natural range of Buchnera floridana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Florida Bluehearts; Savanna Bluehearts
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Buchnera americana Linnaeus; B. longifolia Swartz (by misattribution); B. breviflora Pennell (by misattribution); B. elongata Swartz.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
The genus Buchnera are hairy perennials with erect, simple stems growing between 40 - 80 cm tall. The entire plant turns black when dried. The leaves are oppositely arranged, elliptic to ovate-lanceolate in shape, entire or irregularly serrate, and grow up to 3 - 7 cm long and 5 - 15 mm wide, and is reduced above. The inflorescence is an open spike with the flowers in the axils of opposite bracts and supported by 2 bractlets. The 3.5 - 5 mm long calyx tube is cylindrical with lobes 5, lanceolate in shape, slightly unequal, up to 1 mm or less long. The bilaterally symmetrical flowers are purple or white in color and form a tube with 5 petals bent abruptly at right angles. Up to 4 fertile stamens are present with anthers with only a single sac. The 5 - 6 mm capsule seed is ovoid or pyriform.[2]
Specifically, for Buchnera floridana, the leaves are not 3-veined or not as conspicuous are B. americana. The leaves are lanceolate to elliptic in shape. The flower tube grows up to 8 - 10 mm long and the petals grow up to 4 - 5 mm long.[2]
Distribution
Mostly restricted to the coastal plain.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
General habitats are pine savannas, seepage bogs, flatwoods, and sandy roadsides.[4] Other habitats include low lying swamp and sandy acidic pine and palm barrens.[5] This species has been observed in Everglades National Park.[6]
Phenology
B. floridana flowers and fruits all year.[6] Flowers are blue-violet or white and bisexual with a superior ovary.
Fire ecology
Thrives in fire-maintained pine graminoid ecosystems in strongly acidic soils.[3]
Pollination and use by animals
B. floridana is noted to have poor forage value.[7] It is a host plant of Brevipalpus phoenicis, which vectors viral diseases like citrus leprosis.[8]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
Flowers of Buchnera floridana Photo by John R. Gwaltney, Southeastern Flora.com
Plant of Buchnera floridana Photo by John R. Gwaltney, Southeastern Flora.com
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 954-5. Print.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 [[1]]Accessed: April 4, 2016
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ [[2]]
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: V. I. Sullivan and J. Wooten. States and Counties: Florida: Monroe. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "fsu" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Hilmon, J. B. (1964). "Plants of the Caloosa Experimental Range " U.S. Forest Service Research Paper SE-12
- ↑ Childers, C. C., J. C. V. Rodrigues, et al. (2003). "Host plants of Brevipalpus californicus, B. obovatus, and B. phoenicis (Acari: Tenuipalpidae) and their potential involvement in the spread of viral diseases vectored by these mites." Experimental & Applied Acarology 30: 29-105.

