Difference between revisions of "Muhlenbergia expansa"
(→Habitat) |
(→Habitat) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
Fine textured soils, and strongly acid sands are part of the ideal habitat for ''M. expansa''<ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> In general, pine savannas, pine flatwoods, and mesic areas in sandhill-pocosin ecotones are the environments where ''M. expansa'' can be found.<ref name= "Weakley"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref> Specimens have been taken from flatwoods with pine savanna sandy loam.<ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: John Nelson, Pat Ferral, Richard Carter, R. Kral States and counties: South Carolina (Berkeley) Georgia (Wane)</ref> | Fine textured soils, and strongly acid sands are part of the ideal habitat for ''M. expansa''<ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> In general, pine savannas, pine flatwoods, and mesic areas in sandhill-pocosin ecotones are the environments where ''M. expansa'' can be found.<ref name= "Weakley"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref> Specimens have been taken from flatwoods with pine savanna sandy loam.<ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: John Nelson, Pat Ferral, Richard Carter, R. Kral States and counties: South Carolina (Berkeley) Georgia (Wane)</ref> | ||
| − | ''M. expansa'' became absent in response to military training in west Georgia longleaf pine forests. It has shown resistance to regrowth in reestablished pine forests that were disturbed this activity.<ref>Dale, V.H., S.C. Beyeler, and B. Jackson. (2002). Understory vegetation indicators of anthropogenic disturbance in longleaf pine forests at Fort Benning, Georgia, USA. Ecological Indicators 1(3):155-170.</ref> | + | ''M. expansa'' became absent in response to military training in west Georgia longleaf pine forests. It has shown resistance to regrowth in reestablished pine forests that were disturbed by this activity.<ref>Dale, V.H., S.C. Beyeler, and B. Jackson. (2002). Understory vegetation indicators of anthropogenic disturbance in longleaf pine forests at Fort Benning, Georgia, USA. Ecological Indicators 1(3):155-170.</ref> |
''M. expansa'' has been determined as an indicator species for the Henslow's Sparrows habitats in southeastern Louisiana, it is one of the preferred seeds of the sparrow.<ref name= "dimiceli">DiMiceli, J. K., et al. (2007). "Seed preferences of wintering Henslow's sparrows." Condor 109: 595-604.</ref> | ''M. expansa'' has been determined as an indicator species for the Henslow's Sparrows habitats in southeastern Louisiana, it is one of the preferred seeds of the sparrow.<ref name= "dimiceli">DiMiceli, J. K., et al. (2007). "Seed preferences of wintering Henslow's sparrows." Condor 109: 595-604.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 12:20, 23 June 2021
Common names: Cutover muhly[1], Savanna hairgrass[2]
| Muhlenbergia expansa | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Photo by Bobby Hattaway at Discoverlife.org | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Muhlenbergia |
| Species: | M. expansa |
| Binomial name | |
| Muhlenbergia expansa Poir. | |
| |
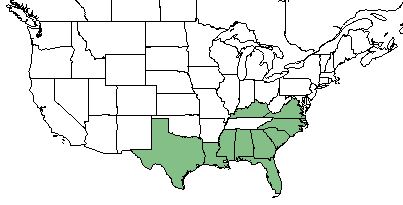
| Natural range of Muhlenbergia expansa from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: M. capillaris var. trichopodes (Elliott) Vasey.[2]
Variety: none.[2]
Description
M. expansa is a perennial graminoid of the Poaceae family that is native to North America.[1]
This species has an open and diffuse panicle which is broader than 4 cm. This panicle is capillary, flexuous, and fragile, tending to break up over the winter. It lacks rhizomes, has old leaf bases that are fibrous and curly, and is tufted with terete and erect culms. The glume bodies are 2.0-3.3 mm long. Its spikelets are borne on slender or capillary pedicels, colored brown or bronze and 2.5-5 mm long. Finally, the lemma is acuminate and its awn is 0-1.5 mm long.[2]
Distribution
M. expansa ranges from southeastern Virginia to Florida and west to eastern Texas - nearly the exact range of Pinus palustris.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
Fine textured soils, and strongly acid sands are part of the ideal habitat for M. expansa[1] In general, pine savannas, pine flatwoods, and mesic areas in sandhill-pocosin ecotones are the environments where M. expansa can be found.[3] Specimens have been taken from flatwoods with pine savanna sandy loam.[4]
M. expansa became absent in response to military training in west Georgia longleaf pine forests. It has shown resistance to regrowth in reestablished pine forests that were disturbed by this activity.[5]
M. expansa has been determined as an indicator species for the Henslow's Sparrows habitats in southeastern Louisiana, it is one of the preferred seeds of the sparrow.[6]
Phenology
April is the common month where much of the growth happens for M. expansa. Seeds are produced during the late summer months that can be dispersed throughout the following year.[1]
Fire ecology
This species is an important component to longleaf pine ecosystems and burning is a successful solution to managing the grass.[1] Flowering is stimulated by fire, so without it, large populations may be in a solely vegetative condition.[2]
Use by animals
Animals use the grass for forage but is not used as a food source for any animal apart from some livestock but even then it is not their entire food source.[1]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 USDA Plant Database Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "USDA" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "USDA" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: John Nelson, Pat Ferral, Richard Carter, R. Kral States and counties: South Carolina (Berkeley) Georgia (Wane)
- ↑ Dale, V.H., S.C. Beyeler, and B. Jackson. (2002). Understory vegetation indicators of anthropogenic disturbance in longleaf pine forests at Fort Benning, Georgia, USA. Ecological Indicators 1(3):155-170.
- ↑ DiMiceli, J. K., et al. (2007). "Seed preferences of wintering Henslow's sparrows." Condor 109: 595-604.