Difference between revisions of "Toxicodendron vernix"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
It has been observed flowering April through August and fruiting February through October.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021</ref> | It has been observed flowering April through August and fruiting February through October.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021</ref> | ||
| − | |||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 40: | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
<!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | <!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| − | |||
===Diseases and parasites=== | ===Diseases and parasites=== | ||
"A severe contact poison causing extreme inflammation, swelling and itching in susceptible individuals." -Radford et al 1964 | "A severe contact poison causing extreme inflammation, swelling and itching in susceptible individuals." -Radford et al 1964 | ||
| + | |||
==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
Revision as of 18:04, 9 June 2021
| Toxicodendron vernix | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Anacardiaceae |
| Genus: | Toxicodendron |
| Species: | T. vernix |
| Binomial name | |
| Toxicodendron vernix (L.) Kuntze | |
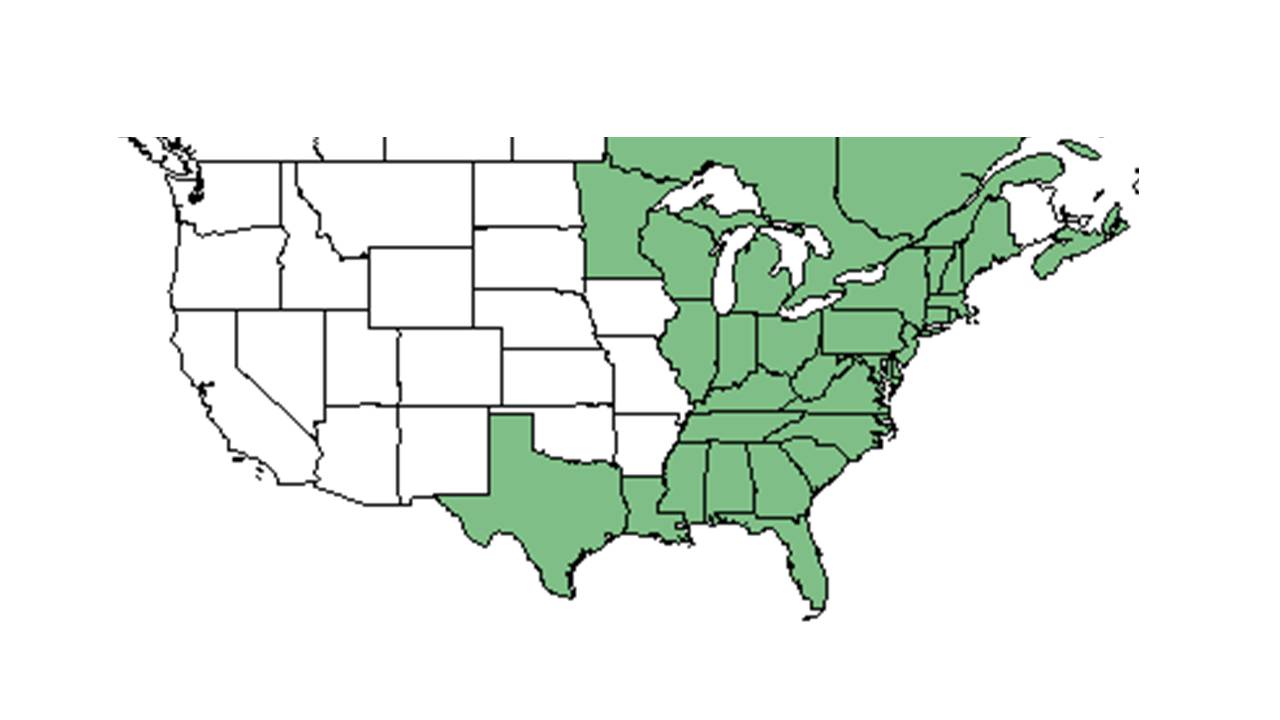
| |
| Natural range of Toxicodendron vernix from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Poison sumac
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Rhus vernix Linnaeus.[1]
Description
In Radford (1964) this species is recognized as a synonym under Rhus vernix which is where this description originated from. "Inflorescence of axillary panicles on new wood. Drupes white or gray, the mesocarp dry, shattering at maturity. Seeds grooved. Flowers proceed simultaneously with the leaves." -Radford et al 1964
"Glabrous shrub or small tree. Leaflets 7-13, elliptic oblong or oblanceolate, 5-12 cm long, 2-5 cm wide, acute to acuminate, entire, bae cuneate; rachis not winged. Panciles 3-5 in the lower leaf axils, drooping or spreading, 1-2 cm long. Drupe glabrous, 5-7 mm broad." -Radford et al 1964
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Toxicodendron vernix has been documented in pine-wiregrass savannas; floodplain woodlands; swamp floodplans; mixed pinewoods; hillside bogs; swamps; bogs; low woods below dam; sphagnum shrub-bog; tamarack bog; wooded swamp; a thicket in loamy sand; and on a berm at the water's edge.[2] It has been found in disturbed habitats such as seepage areas, powerline corridors, wet thickets, cut over swamps, and roadside ditches. It has been observed in loamy sand.[2] Associated species include Decodon, Rhododendron austrinum, Magnolia grandiflora, Myrica, Ilex, Viburnum nudum, Typha, Cornus, Lysimachia thyrsiflora, and titi.[2]
Phenology
It has been observed flowering April through August and fruiting February through October.[2][3]
Diseases and parasites
"A severe contact poison causing extreme inflammation, swelling and itching in susceptible individuals." -Radford et al 1964
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, J. Nelson, Patricia Elliot, Robert K. Godfrey, Robert Kral, P. L. Redfearn, Jr., Elmer C. Prichard, R. D. Houk, T.E. Smith, S. W. Leonard, D. B. Russ, John W. Thieret, William T. Gillis, John B. Nelson, Andre F. Clewell, Roomie Wilson, W. C. Holmes, Sidney McDaniel, Delzie Demaree, N. C. Henderson, J. Richard Moore, Clyde F. Reed, F. H. Sargent, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, Travis MacClendon. States and Counties: Alabama: Baldwin, Mobile. Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Clay, Franklin, Lake, Leon, Liberty, Nassau, Santa Rosa, Wakulla, Walton. Indiana: Wabash. Louisiana: Natchitoches, Rapides, Vernon, Washington. Maryland: Anne Arundel. Michigan: Ingham. Mississippi: Forrest, Harrison, Neshoba. North Carolina: Henderson. Ohio: Portage. South Carolina: Richland. Virginia: Prince William. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021