Difference between revisions of "Symphyotrichum cordifolium"
(→Taxonomic notes) |
|||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
<!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | <!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| + | |||
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
| − | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
Revision as of 12:39, 9 June 2021
| Symphyotrichum cordifolium | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John R. Gwaltney, Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Symphyotrichum |
| Species: | S. cordifolium |
| Binomial name | |
| Symphyotrichum cordifolium (L.) G.L. Nesom | |
| |
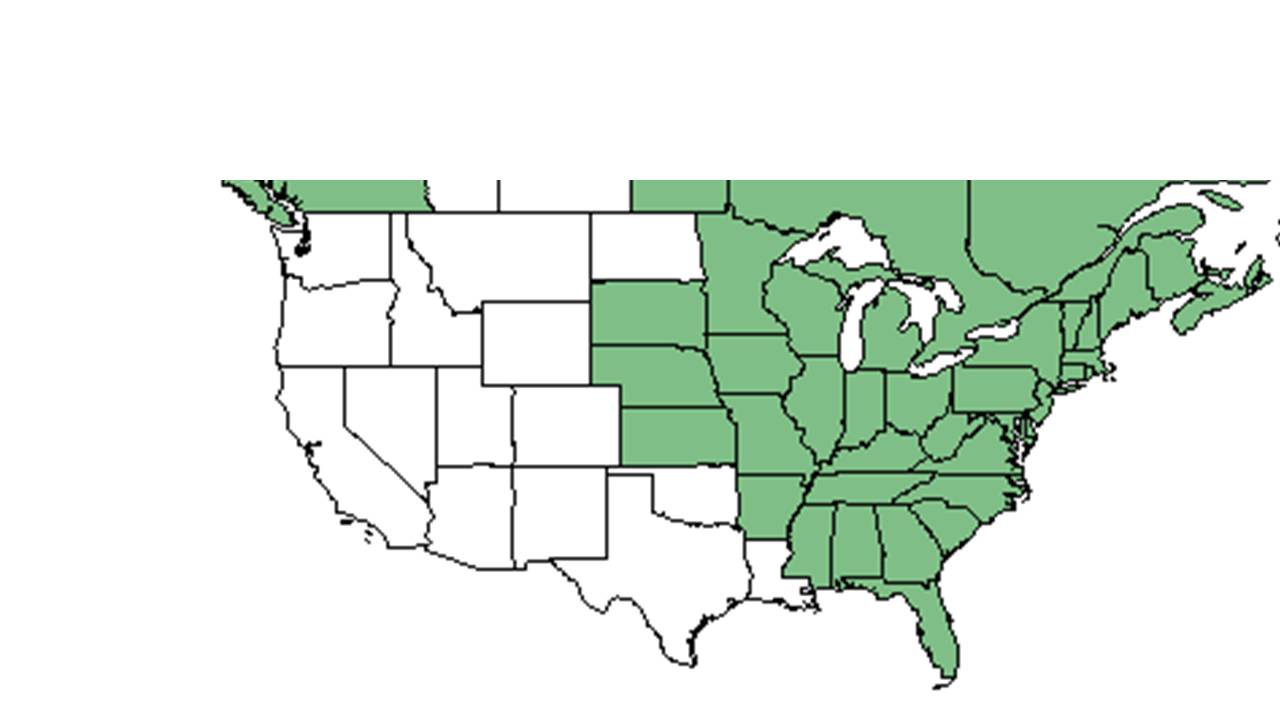
| Natural range of Symphyotrichum cordifolium from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Common blue wood aster, Heart-leaved aster
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Aster cordifolius Linnaeus; A. cordifolius var. polycephalus Porter ; A. cordifolius var. racemiflorus Fernald.[1]
Variations: S. cordifolium (Linnaeus) Nesom var. polycephalum (Porter) Nesom; S. cordifolium (Linnaeus) Nesom var. racemiflorum (Fernald) Nesom.[2]
Description
A description of Symphyotrichum cordifolium is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.