Difference between revisions of "Pterocaulon pycnostachyum"
(→Habitat) |
(→Phenology) |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
===Phenology=== | ===Phenology=== | ||
| − | ''P. pycnostachyum'' has been observed flowering in June. <ref name= "Pan Flora"> Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 24 MAY 2018</ref> | + | ''P. pycnostachyum'' has been observed flowering in June.<ref name= "Pan Flora"> Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 24 MAY 2018</ref> |
<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 19:49, 18 March 2021
Common names: dense-spike blackroot [1], wand or coastal blackroot, rabbit tobacco[2]
| Pterocaulon pycnostachyum | |
|---|---|

| |
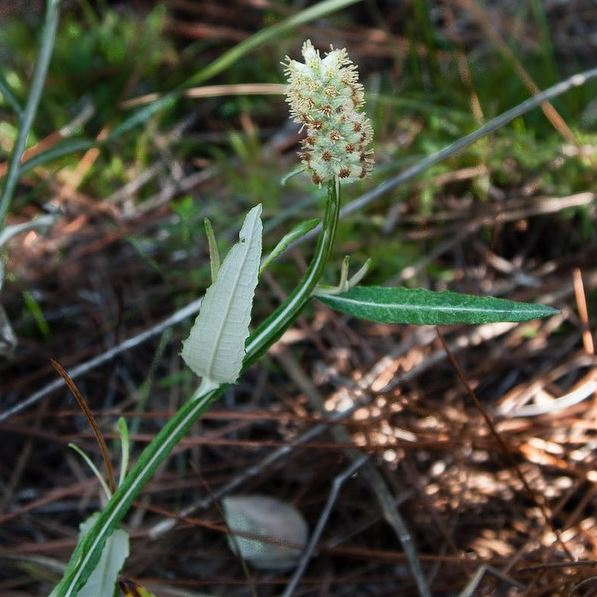
| Photo by John Bradford hosted at Bluemelon.com/poaceae | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Genus: | Pterocaulon |
| Species: | P. pyconstachyum |
| Binomial name | |
| Pterocaulon pycnostachyum (Michx.) Elliot | |
| |
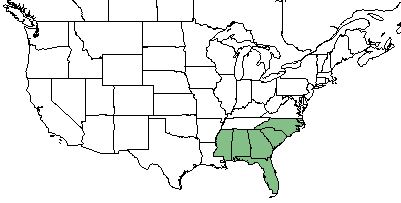
| Natural range of Pterocaulon pycnostachyum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: P. undulatum (Walter) C. Mohr
Variety: none
Description
P. pycnostachyum is a perennial forb/subshrub of the Asteraceae family that is native to North America.[1]
Distribution
P. pycnostachyum is found in Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Alabama, and Mississippi in the eastern United States.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
Natural habitats for the P. pycnostachyum include sandhillas, dry pinelands, dry praire, and pine flatwoods.[3][2] Specimens have been collected from bay forests, pine savannas, bog remnants, loose sand on burned pine flatwoods, longleaf pine regions, dry scrub woods, wiregrass savanna, coastal hammock, cypress flatwoods, moist savannas, slash pine palmetto, cyrillo swamp, and open pine flatwoods.[4] P. pycnostachyum responds positively or not at all to soil disturbance by roller chopping in South Florida.[5] It also responds positively to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.[6]
Pterocaulon pycnostachyum can be found in the same habitats as Deeringothamnus rugelii, Asclepias pedicellata, Aristida beyrichiana, Asimina reticulata, Cuthbertia ornata, Galactia elliotti, Lygodesmia aphylla, and Pinus palustris.[7]
Phenology
P. pycnostachyum has been observed flowering in June.[8]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by wind. [9]
Fire ecology
P. pycnostachyum has been observed blooming in a recently burned pine flatwoods. .[10]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Orzell, S. L. and E. L. Bridges (2006). "Floristic composition of the south-central Florida dry prairie landscape." Florida Ecosystem 1(3): 123-133.
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: A.e. Radford, R.Kral, Sidney McDaniel, Joe Sparling, D.L. Fichtner, R.K.Godfrey, A>F. Harris, K. Draddock Burks, Loran Anderson, B.L. Turner, Elmar Prichard, Mary Margaret WIlliams, Robert Lazor, Delzie Demaree, Lovette E. Williams, A.F. Clewell, R.L. Wilbur, Paul Lemon, Mary Atkinson, LB Trott, Robert Lemaire, J. N. Triplett Jr., Gwynn Ramsey, Richard Mitchell, Roomie Wilson, M. Davsi, CC ALbers, Fred Barkeley, K.M. Meyers, A. Townesmith, Wayne D. Longbottom, David Williams, S. Taylor, Janice Weems. States and counties: South Carolina (Lee) FLroida (Levy, Citrus, Washington, Baker, Leon, Liberty, Escambia, jefferson, Walton, Clay, Volusia, Polk, Wakulla, Franklin, Bay, Hamilton, Broward, Putnam, Okeechobee, ALachua, Taylor, Orange, Seminole, Sarastota) Georgia (Charlton, Ware, Brooks, Berrien, McIntosh, Thomas, Bulloch) Louisiana (Calcasieu) Texas ( Bastrop).
- ↑ Lewis, C.E. (1970). Responses to Chopping and Rock Phosphate on South Florida Ranges. Journal of Range Management 23(4):276-282.
- ↑ Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.
- ↑ [Canfield, S. L. and G. W. Tanner (1997). "Observations of pinywoods dropseed (Sporobolus junceus) phenological development following fire in a sandhill community." Florida Scientist 60(2): 69-72.]
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 24 MAY 2018
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Observation by Alex de la Paz in UCF Arboretum, Orange County, FL, March 2018, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group March 24, 2018.