Difference between revisions of "Axonopus fissifolius"
Emmazeitler (talk | contribs) (→Taxonomic Notes) |
|||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
''A. fissifolius'' is designated as a weedy or invasive plant by the Hawaiian Ecosystems at Risk Project, Biological Resources Division.<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> For the most production and efficient harvest by livestock, grazing should be rotated each 30 to 40 days with no more than 50% of the current year's growth grazed.<ref name= "Magee"/> | ''A. fissifolius'' is designated as a weedy or invasive plant by the Hawaiian Ecosystems at Risk Project, Biological Resources Division.<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> For the most production and efficient harvest by livestock, grazing should be rotated each 30 to 40 days with no more than 50% of the current year's growth grazed.<ref name= "Magee"/> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Revision as of 19:36, 7 June 2021
Common name: Common Carpetgrass
| Axonopus fissifolius | |
|---|---|
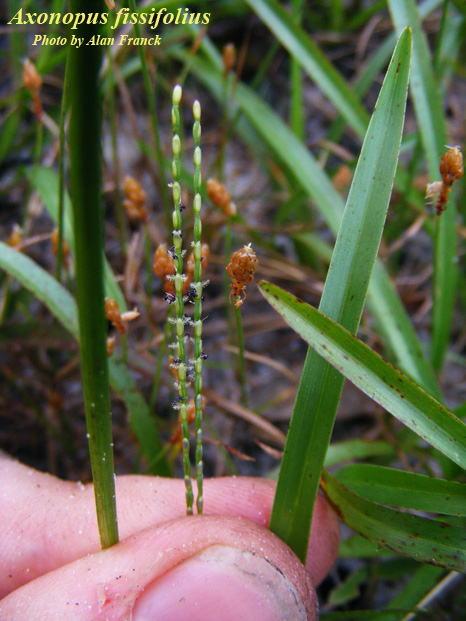

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Axonopus |
| Species: | A. fissifolius |
| Binomial name | |
| Axonopus fissifolius (Raddi) Kuhlmann | |
| |
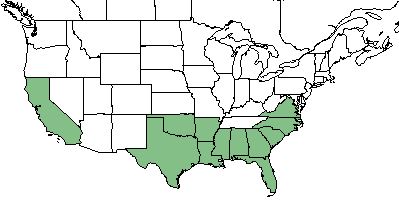
| Natural range of Axonopus fissifolius from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Paspalum fissifolium Raddi; Axonopus affinis Chase. [1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
A. fissifolius is a perennial graminoid of the Poaceae family, is native to North America and Puerto Rico, and has been introduced to Hawaii. [2] Leaf blade can be flat or folded, fine hairs along margin near the base, slightly pointed or rounded, and purplish or reddish when mature. Seedhead has 3 slender racemes, 2 at summit and 1 (rarely 2) below.[3]
Distribution
A. fissifolius can be found in the southeastern United States from Texas to Virginia, California, Hawaii, and Puerto Rico. [2]
Ecology
Habitat
A. fissifolius is found in pine flatwoods, sandy forests, fields, roadsides, and lawns. [4] It has also been found in grassland areas with poor drainage, among other bunchgrasses. [5] Other observances include loamy sand of longleaf pine oak wiregrass sandhills, wet depressions, mixed swamps, hydric hammocks, and wet clayey sand.[6]
A. fissifolius responds positively or not at all to soil disturbance by roller chopping in South Florida.[7] It does not respond to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.[8]
Associated species: Fuirena sp. and Rhynchospora sp.[6]
Phenology
A. fissifolius occurs more in spots where grazing and trampling were particularly heavy. [9]
Use by animals
A. fissifolius is rated as good forage. [10] It is grazed all year by various livestock.[3]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
A. fissifolius is designated as a weedy or invasive plant by the Hawaiian Ecosystems at Risk Project, Biological Resources Division.[2] For the most production and efficient harvest by livestock, grazing should be rotated each 30 to 40 days with no more than 50% of the current year's growth grazed.[3]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=AXFI
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Magee, P. (2005). Plant Fact Sheet: Common Carpetgrass Axonopus fissifolius. N.R.C.S. United States Department of Agriculture. Baton Rouge, LA.
- ↑ . Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Boughton, E., et al. (2013). "Season of fire and nutrient enrichment affect plant community dynamics in subtropical semi-natural grasslands released from agriculture." Biological Conservation 158: 239-247.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: March 2019. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, N. Bristan, Richard R. Clinebell II, E. H. Cooley, S. T. Cooper, A. H. Curtiss, J. A. Duke, R. J. Eaton, R. K. Godfrey, Edwin Keppner, R. Komarek, R. Kral, John M. Kunzer, R. L. Lazor, D. L. Martin, Gil Nelson, R. A. Norris, R. E. Perdue, P. L. Redfearn, G. W. Reinert, Cecil R. Slaughter, and C. Wood. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Charlotte, Clay, Escambia, Flagler, Franklin, Gulf, Hernando, Jackson, Leon, Liberty, Marion, Martin, Okaloosa, Osceola, Polk, Wakulla, Walton, and Washington. Georgia: Clinch, Grady, and Thomas.
- ↑ Lewis, C.E. (1970). Responses to Chopping and Rock Phosphate on South Florida Ranges. Journal of Range Management 23(4):276-282.
- ↑ Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.
- ↑ Lewis, C. E. (1970). "Responses to chopping and rock phosphate on south Florida ranges " Journal of Range Management 23: 276-282.
- ↑ Hilmon, J. B. (1964). "Plants of the Caloosa Experimental Range " U.S. Forest Service Research Paper SE-12