Difference between revisions of "Lespedeza angustifolia"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) (→Seed bank and germination) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) (→Seed bank and germination) |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| − | ''Lespedeza'' | + | Species in the genus ''Lespedeza'' have a hard seed coat characteristic of species that have a persistent seed bank. Seeds of ''L. anguistifolia'' have been shown to remain viable in the soil for at least two years, with most germination occurring only after near freezing temperatures of the first winter following seed dispersal.<ref name=ck> Coffey, K. L. and L. K. Kirkman (2006). "Seed germination strategies of species with restoration potential in a fire-maintained pine savanna." Natural Areas Journal 26: 289-299. </ref> |
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
Revision as of 19:42, 9 June 2020
| Lespedeza angustifolia | |
|---|---|
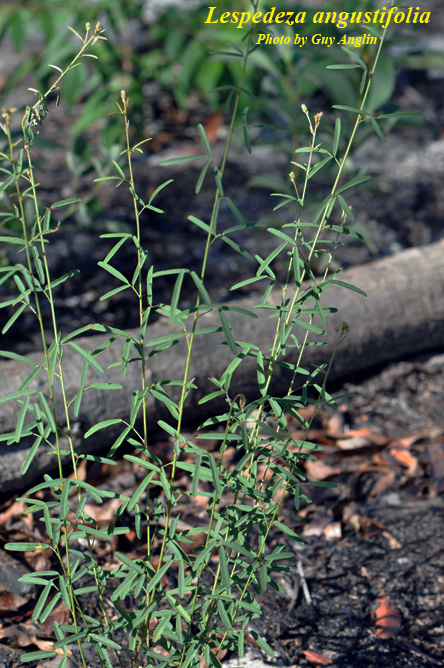

| |
| Photo by Guy Anglin, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Lespedeza |
| Species: | L. angustifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Lespedeza angustifolia (Pursh) Elliott | |
| |
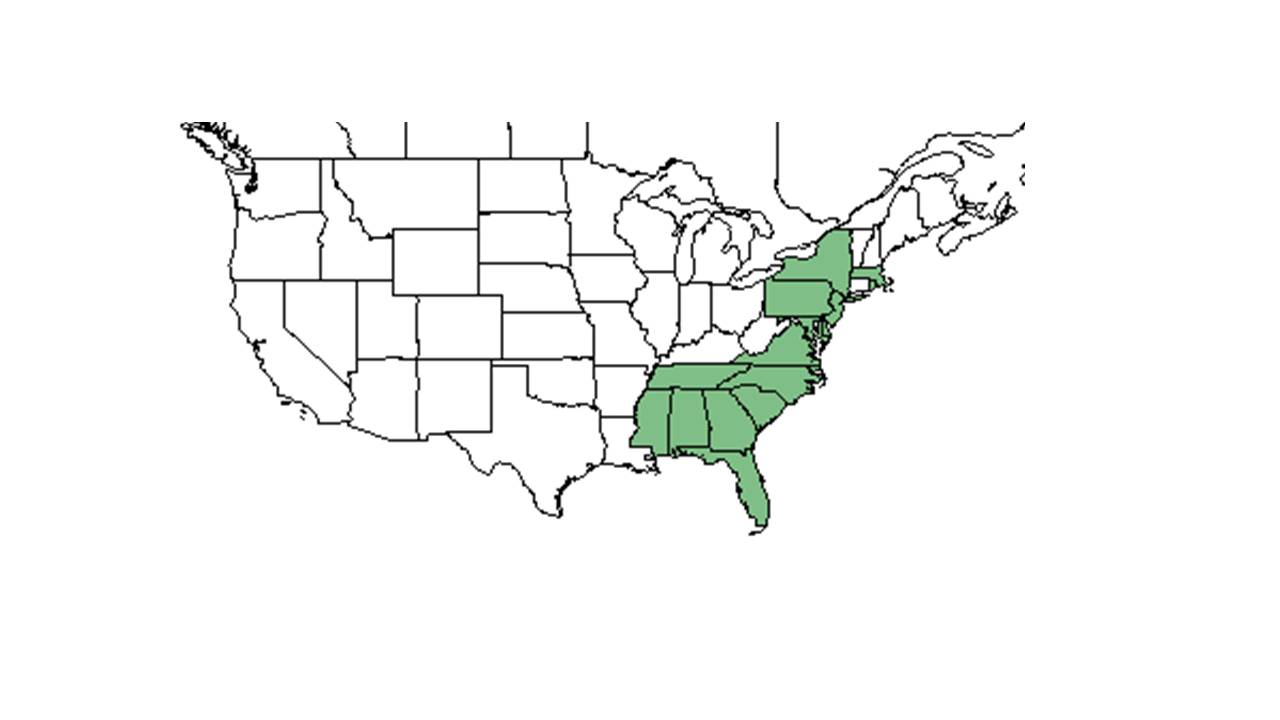
| Natural range of Lespedeza angustifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Narrowleaf lespedeza
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Lespedeza hirta var. intercursa Fernald
Description
“Annual or perennial herbs or shrubs. Leaves pinnately 3-folioate; leaflets entire, estipellate; stipules persistent, setaceous to ovate-lanceolate. Inflorescence usually few-to-many-flowered, loose to compact, sessile to long-pedunculate, axillary or terminal, spictate, racemose, capitate or rarely paniculate cluster; pedicels subtended by a bract and with a pair of inconspicuous bractlets immediately beneath the flower. Both apetalous (cleistogamous) and petaliferous (Chasmogamous) flowers present in most species, but the apetalous flower are more readily detected and more abundant in some species than others. Calyx persistent in fruit, the tube campanulate to cylindric with 5 nearly equal lobes or the upper 2 partly united and shorter; corolla papilionaceous, violet, purplish, roseate, yellow or whitish; stamens diadelphous, 9 and 1. Legume 1-seeded, indehiscent, sessile or stalked, flattened, elliptic, ovate or orbicular.” [1]
“Erect perennial 0.3-1.2 (1.8) m tall, above usually densely strigillose or weakly to strongly spreading, short-pubescent or even short-pilose. Densely strigillose to glabrate below. Leaflets narrowly oblong-elliptic to linear, (1.2) 2-6 cm long, 4-12X as long as wide, glabrous to more commonly densely appressed short-pubescent or strigillose above and densely strigillose beneath; stipules very narrowly linear to linear-subulate. Racemes spicate, or rarely globose, numerous, loose to compact, 0.7-3 cm long; peduncles ca. (0.5) 1-5 cm long, typically equaling or longer than the subtending leaves; peduncles and axes densely spreading short-pubescent; pedicels 1-2 mm long. Calyx densely spreading puberulent, lobes 4-6 mm long and nearly as long on the calyx; petals yellowish, the standard 5-7 mm long bearing a purplish spot. Legume densely spreading short-pubescent, broadly elliptic to oblong-obovate, 4-6 mm long, nearly equaling the calyx in length.” [1]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Lespedeza angustifolia habitats include sandhills, pine flatwoods, and oldfield pinelands, as well as dry pond margins and open flood plains on areas that are mesic to excessively well drained.[2] It has been strongly associated with hydric habitats[3] because of a higher tolerance for periodically inundated soil conditions.[4] It has been documented to occur in dried up bottoms of sinkhole ponds.[2] Soils include sand and sandy loams, including Ultisols, Entisols, and dry Spodosols.[5] Other soil types includes red sandy clay hills and sandy peat.[2] L. angustifolia is prevalent along eroded roadsides and railroads and in disturbed high pine habitats.[2] Plants associated include Aristida, Ctenium, Andropogon, Sporobolus and Panicum hemitomon.[2]
Phenology
L. angustifolia has been observed to flower from September to November with peak inflorescence in September.[2][6] Frequent where present by populations tend to be separated from one another.[5]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by consumption by vertebrates. [7]
Seed bank and germination
Species in the genus Lespedeza have a hard seed coat characteristic of species that have a persistent seed bank. Seeds of L. anguistifolia have been shown to remain viable in the soil for at least two years, with most germination occurring only after near freezing temperatures of the first winter following seed dispersal.[8]
Fire ecology
Frequent dormant season burning increased legume populations in southern pine forests, although fires during the growing season at the same frequency tended to reduce legume abundance. [4] Presence of Imperata cylindrica (cogan grass), an invasive plant found in the southeastern United States, did not deter the occurrence of L. angustifolia in plots that had been burned every 1 to 2 years in southeastern Mississippi.[9] In its natural habitat it requires frequent fire for persistence. It is primarily located in undisturbed sites and sometimes colonizes frequently burned old-field pinelands.[5]
Pollination
Bee and Lepidopteran pollinated in chasmogamous flowers.[5]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 613-8. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, A. F. Clewell, James R. Coleman, Delzie Demaree, William B. Fox, J. P. Gillespie, Robert K. Godfrey, Gary R. Knight, R. Komarek, R. Kral, T. MacClendon, John Morrill, A. E. Radford, John K. Small. States and Counties: Alabama: Baldwin. Florida: Franklin, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Nassau, Wakulla, Washington. Georgia: Appling, Baker, Camden, Clinch, Grady, Lowndes, Miller, Seminole, Thomas, Walton, Wilcox. North Carolina: Cumberland, Harnett, Pitt. South Carolina: Sumter. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Hainds, M. J., R. J. Mitchell, et al. (1999). "Distribution of native legumes (Leguminoseae) in frequently burned longleaf pine (Pinaceae)-wiregrass (Poaceae) ecosystems." American Journal of Botany 86: 1606-1614.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Hainds, M. J., R. J. Mitchell, et al. (1997). "Legume population dynamics in frequently burned longleaf pine-wiregrass fire ecosystem." Proceedings Longleaf Alliance Conference: Longleaf Alliance Report 1: 82-86.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Clewell, Andre. 2014. Personal observations.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Coffey, K. L. and L. K. Kirkman (2006). "Seed germination strategies of species with restoration potential in a fire-maintained pine savanna." Natural Areas Journal 26: 289-299.
- ↑ Brewer, J. S. and S. P. Cralle (2003). "Phosphorus addition reduces invasion of a longleaf pine savanna (southeastern USA) by a non-indigenous grass (Imperata cylindrica)." Plant Ecology 167: 237-245.