Difference between revisions of "Ilex glabra"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
Vespidae: ''Eumenes fraternus, E. smithii, Leptochilus alcolhuus, L. krombeini, L. republicanus, Mischocyttarus cubensis, Monobia quadridens, Pachodynerus erynnis, Parancistrocerus fulvipes rufovestris, P. salcularis rufulus, Polistes dorsalis hunteri, Stenodynerus fundatiformis, S. lineatifrons, Vespula squamosa, Zethus slossonae, Z. spinipes'' | Vespidae: ''Eumenes fraternus, E. smithii, Leptochilus alcolhuus, L. krombeini, L. republicanus, Mischocyttarus cubensis, Monobia quadridens, Pachodynerus erynnis, Parancistrocerus fulvipes rufovestris, P. salcularis rufulus, Polistes dorsalis hunteri, Stenodynerus fundatiformis, S. lineatifrons, Vespula squamosa, Zethus slossonae, Z. spinipes'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Overall, this species is considered by pollination ecologists to be of special value to honey bees since it attracts such large numbers for pollination.<ref name= "lady bird"/> | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
Revision as of 19:47, 30 May 2019
| Ilex glabra | |
|---|---|
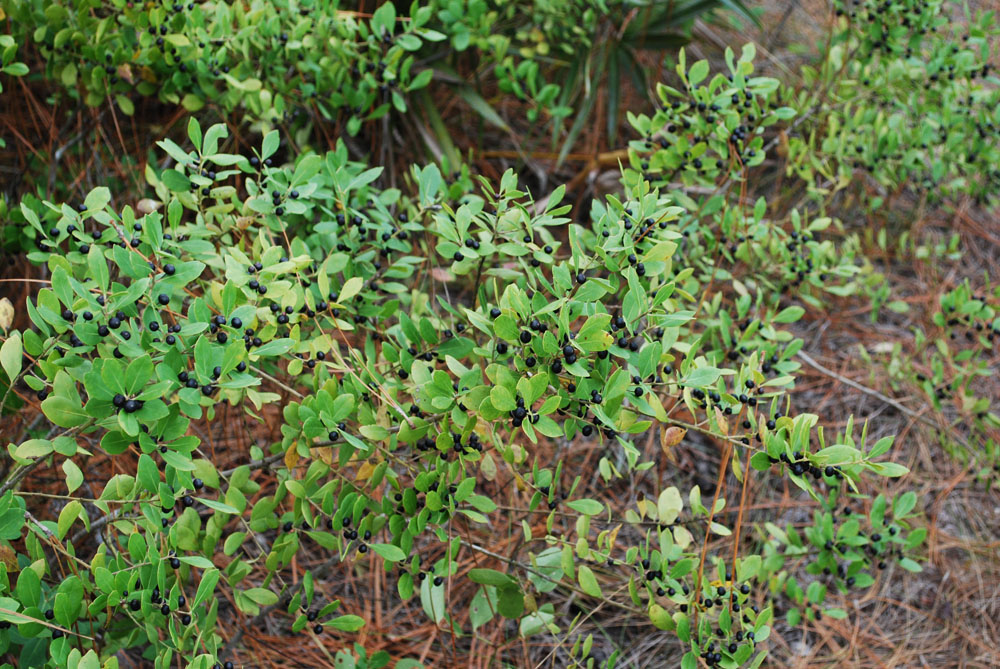

| |
| Photo by Wayne Matchett, SpaceCoastWildflowers.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Celastrales |
| Family: | Aquifoliaceae |
| Genus: | Ilex |
| Species: | I. glabra |
| Binomial name | |
| Ilex glabra (L.) A. Gray | |
| |
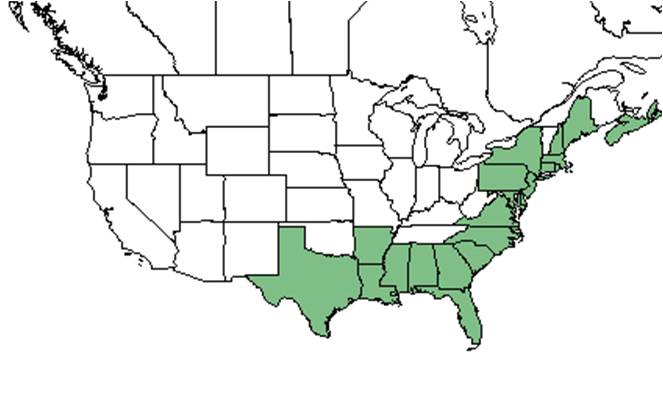
| Natural range of Ilex glabra from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: inkberry; little gallberry
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
“Trees or shrubs, usually with imperfect flowers. Leaves simple, entire, serrate, dentate or crenate; stipules obsolete. Flowers axillary, solitary, fascicled or in cymes, 4-7 merous, 4-8 mm broad; petals united at the base, imbricate in bud; pistillate flowers usually with nonfunctional stamens; anthers opening lengthwise; stigmas 4-7, essentially sessile. Drupe red, black or rarely yellow or white. Seeds with hard, bony endocarp (pyrenes), often grooved or ribbed on the back, 4-7 in a fruit, 1 in each locule.” [1]
"Rhizomatous shrub to 3m tall, usually forming extensive colonies, twigs puberulent. Leaves evergreen, obovate to elliptic, 2.5-6.5 cm long, crenate, but usually only toward the apex, the last pair of teeth usually directly opposite each other, glabrous, lustrous above; petioles 38 mm long, canescent. Pedicels 1-5 mm long, appearing longer when single fruited (careful examination shows that the lower part is peduncle). Staminate flowers in axillary, 3-7 flowered, pedunculate cymes. Pistillate flowers axillary, solitary or in 3-flowered, pedunculate cymes. Flowers 5-7 merous. Drupe black, dull or slightly lustrous, globose, 5-7 in diam.; pyrenes 5-7, smooth, 3-4 mm long." [1]
Distribution
Ilex glabra is distributed from Nova Scotia and Maine south to Florida and west to Texas.[2]
Ecology
Various species in the Ilex genus, including this species, contain a mixture of the alkaloid theobromine that is caffeine-like, actual caffeine, and various glycosides. This gives the opportunity to use this species as a potential caffeine crop that can be used to make beverages.[3]
Habitat
Ilex glabra can be found in "savannas, pine flatwoods, pocosin margins, swamps, primarily in wetlands, but extending upslope even into sandhills, with a clay lens or spodic horizon below to maintain additional moisture."[2] It is restricted to native groundcover with a statistical affinity in upland pinelands of South Georgia.[4] It is a dominant species in well-drained pocosin and bayland community sites, and is considered a very conspicuous species in longleaf pine communities in Florida. The species is shade tolerant, and can grow in full sun or shady areas, dry or wet areas, and on soils from sandy to heavy peat.[3] It is also tolerant of flooding.[5] In the Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plain, this species is listed by the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service as a facultative wetland species that mostly occurs in wetland habitats, but can also occasionally be found in non-wetland habitats.[6]
Phenology
Generally, I. glabra flowers from May until June and fruits from September until November.[2] It has been observed to flower from April to June with peak inflorescence in May.[7]
Seed dispersal
Due to the use of Ilex glabra by wildlife as well as its ability to colonize a wide variety of habitats, it is thought that the seeds are dispersed by animals.[3]
Seed bank and germination
Seeds of this species can stay dormant in the seed bank for years, where germination could not occur for 2 to 3 years at most.[3]
Fire ecology
It is a common component of "fire-climax communities", and can commonly invade frequently burned sites. Fire disturbance top-kills the plant, which makes it adapted to recurrent fire regimes. While low intensity fires can only kill recent growth, fire disturbance usually kills the aerial portion of the stem. Resprouting from fire occurs through the rhizomes and root crowns of the plant, and is most vigorous during the first year after a fire disturbance. In terms of fire seasonality, summer burn regiments are the most damaging for this species follwed by winter burn regiments.[3]
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Ilex glabra at Archbold Biological Station:[8]
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Bombus griseocollis, B. impatiens, Epeolus erigeronis, E. glabratus, E. pusillus, E. zonatus
Colletidae: Colletes banksi, C. brimleyi, C. distinctus, C. mandibularis, C. nudus, C. sp. A., C. thysanellae, Hylaeus confluens, H. schwarzi
Halictidae: Agapostemon splendens, Augochlora pura, Augochloropsis metallica, Halictus poeyi, Lasioglossum coreopsis, L. miniatulus, L. nymphalis, L. pectoralis, L. placidensis, L. puteulanum, Sphecodes brachycephalus
Leucospididae: Leucospis affinis, L. slossonae
Megachilidae: Anthidiellum notatum rufomaculatum, A. perplexum, Anthidium maculifrons, Coelioxys sayi, Dianthidium floridiense, Megachile brevis pseudobrevis, M. exilis parexilis, M. mendica, M. petulans, M. rugifrons, M. xylocopoides
Pompilidae: Ageniella partita, Anoplius krombeini, Episyron conterminus posterus, Priocnemis cornica, Psorthaspis legata, Sericopompilus apicalis
Sphecidae: Alysson melleus, Bembecinus nanus floridanus, Bembix sayi, Bicyrtes quadrifasciata, Cerceris bicornuta, C. blakei, C. flavofasciata floridensis, C. fumipennis, C. rufopicta, Crabro arcadiensis, Ectemnius rufipes ais, Gorytes dorothyae ruseolus, Isodontia auripes, I. exornata, I. mexicana, Larropsis greeni, Liris muesebecki, Microbembex monodonta, Miscophus americanum, M. slossonae slossonae, Oxybelus laetus fulvipes, Palmodes dimidiatus, Sphex ichneumoneus, Stictiella serrata, Tachysphex apicalis, T. similis, Tanyoprymnus moneduloides, Trypargilum clavatum johannis, T. collinum
Vespidae: Eumenes fraternus, E. smithii, Leptochilus alcolhuus, L. krombeini, L. republicanus, Mischocyttarus cubensis, Monobia quadridens, Pachodynerus erynnis, Parancistrocerus fulvipes rufovestris, P. salcularis rufulus, Polistes dorsalis hunteri, Stenodynerus fundatiformis, S. lineatifrons, Vespula squamosa, Zethus slossonae, Z. spinipes
Overall, this species is considered by pollination ecologists to be of special value to honey bees since it attracts such large numbers for pollination.[5]
Use by animals
It consists of approximately 5-10% of the diet for various large mammals, small mammals, and terrestrial birds.[9] This plant is foraged by white-tailed deer, marsh rabbit, raccoon, opossum, coyote, bobwhite quail, wild turkey, and other species of birds. It provides cover for small rodents, some birds, and white-tailed deer. The nectar from the flowers is also an important source for production of honey.[3]
Conservation and management
This species is listed as threatened by the Connecticut Department of Environmental Protection and by the Maine Department of Conservation, Natural Areas Program. It is also listed as exploitably vulnerable by the New York Department of Environmental Conservation, Division of Land and Forests, and is listed as extirpated by the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources.[6] For management of controlling the species, fire can be used as a tool to reduce the overall population. This can be achieved by successive fires, which can effectively kill the plant, and summer or winter burns can be applied for effective control of the species.[3]
Cultivation and restoration
This species can be used in restoration efforts for erosion control, phosphate mine reclamation, and watershed protection.[3]
Photo Gallery
Flower of Ilex glabra Photo by John R. Gwaltney
Fruit of Ilex glabra Photo by John R. Gwaltney
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 679-84. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 Nesom, G. and G. Guala. (2003). Plant Guide: Inkberry Ilex glabra. N.R.C.S. United States Department of Agriculture. Baton Rouge, LA.
- ↑ Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 [[1]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: May 30, 2019
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 30 May 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.

