Difference between revisions of "Helianthus angustifolius"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| + | It consists of approximately 5-10% of the diet for various large mammals, small mammals, and terrestrial birds.<ref>Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.</ref> | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
Revision as of 13:36, 21 May 2019
| Helianthus angustifolius | |
|---|---|

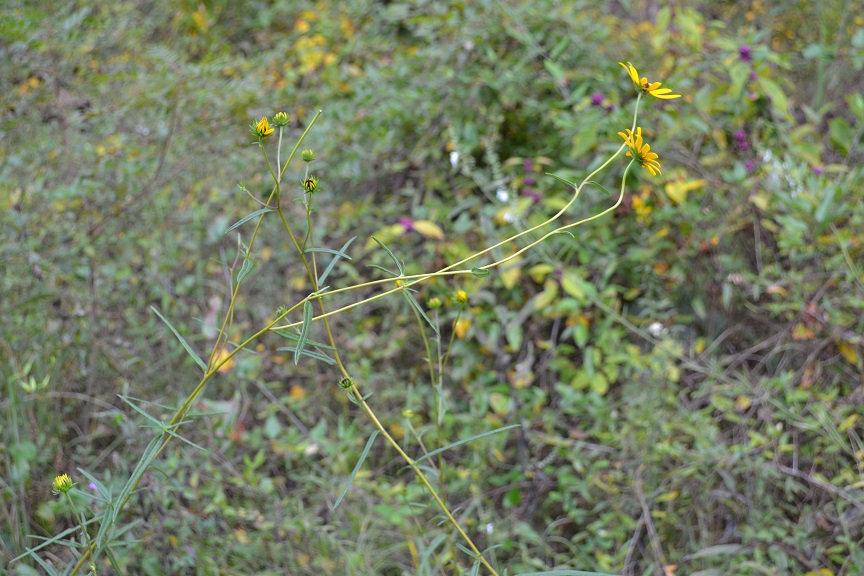
| |
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Tracheophyta- Vascular plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ericaceae |
| Genus: | Helianthus |
| Species: | H. angustifolius |
| Binomial name | |
| Helianthus angustifolius L. | |
| |
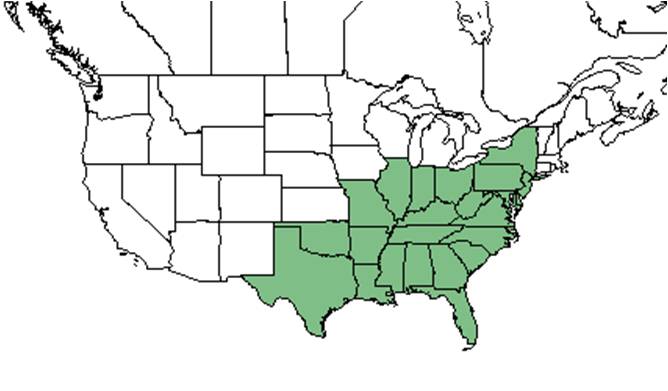
| Natural range of Helianthus angustifolius from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: swamp sunflower; swamp sneezeweed; narrowleaf sunflower
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Helianthus angustifolius L. var. angustifolius; H. angustifolius L. var. planifolius Fernald
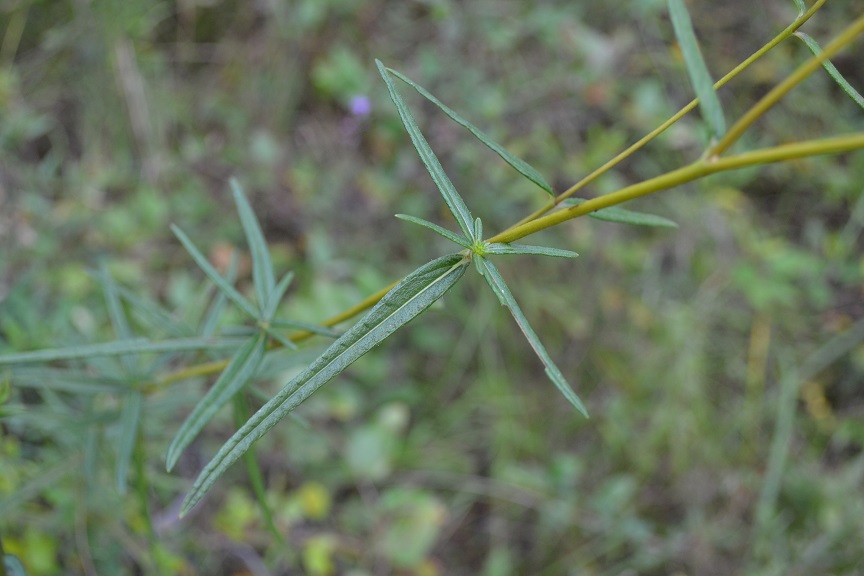
Description
A description of Helianthus angustifolius is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Helianthus angustifolius is mostly found along the southeastern coastal plain, but is distributed from Long Island, New York south to central peninsular Florida and west to Texas, as well as irregularly inland up to Ohio, Missouri, and Indiana.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
Generally, this species is found in savannas, marshes, ditches, and other wet habitats.[1] It is listed by the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service as a facultative wetland species, where it is more often found in wetland habitats, but can also be found in non-wetland habitats.[2]
Phenology
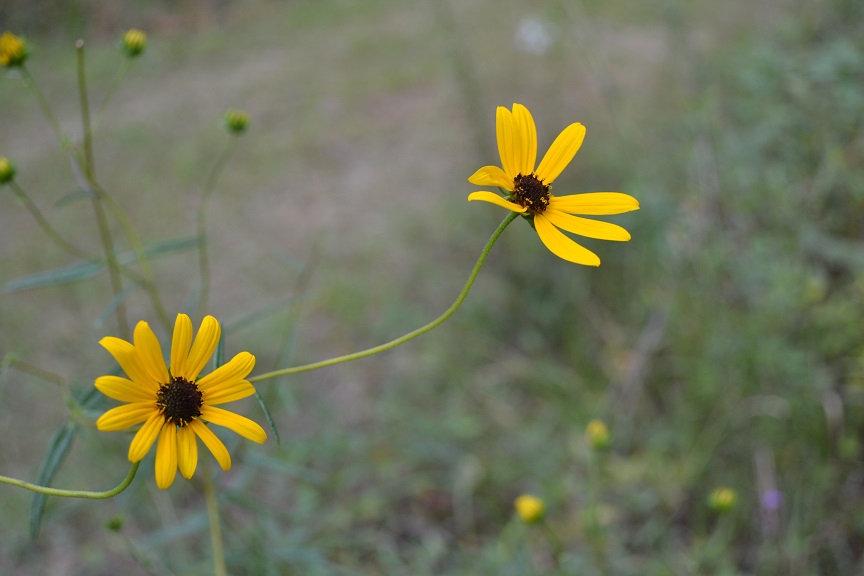
H. angustifolius has been observed flowering in July, and September to November.[3] It is considered very showy along roadsides when it is in flower, especially in October.[1]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by wind. [4]
Use by animals
It consists of approximately 5-10% of the diet for various large mammals, small mammals, and terrestrial birds.[5]
Conservation and management
It is listed as threatened by the Illinois Department of Natural Resources, Endangered Species Protection Board, and by the New York Department of Environmental Conservation, Division of Land and Forests. As well, it is listed as extirpated by the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources.[2]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 21 May 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.

