Difference between revisions of "Erythrina herbacea"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | ''E. herbacea'' generally flowers from May until July.<ref name= "Weakley"/> It has been observed flowering from February to June and fruiting from April to August.<ref name=fsu/> | + | ''E. herbacea'' generally flowers from May until July.<ref name= "Weakley"/> It has been observed flowering from February to June with peak inflorescence in April and May, and fruiting from April to August.<ref name=fsu/><ref>Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 10 MAY 2019</ref> |
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
Revision as of 17:11, 10 May 2019
| Erythrina herbacea | |
|---|---|
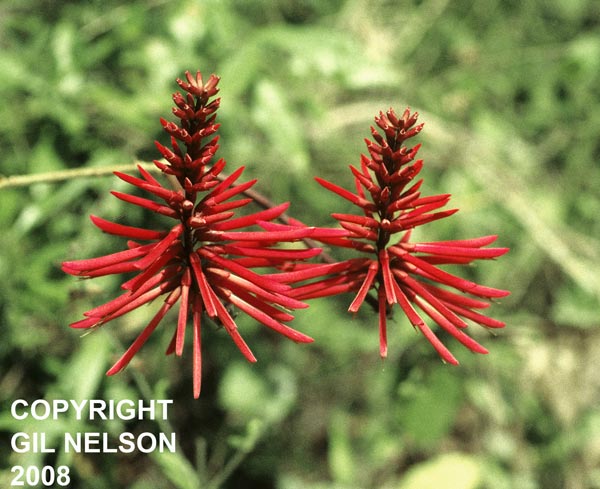

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Erythrina |
| Species: | E. herbacea |
| Binomial name | |
| Erythrina herbacea L. | |
| |
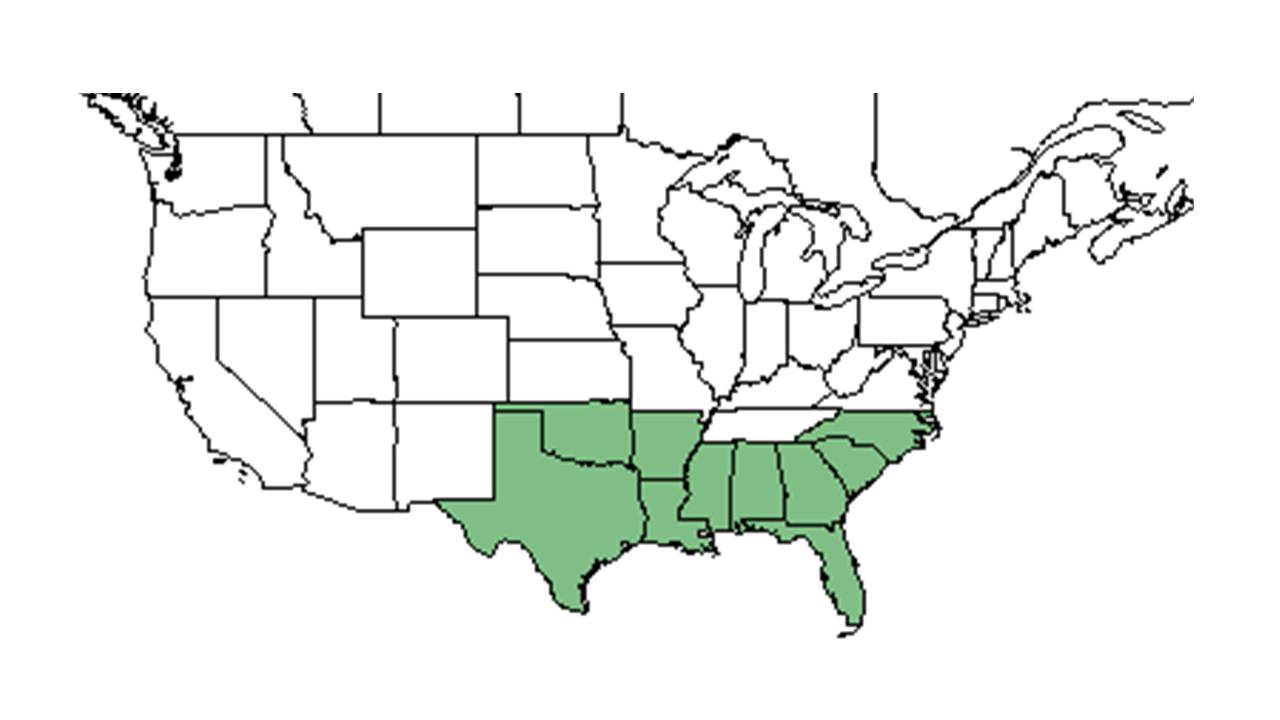
| Natural range of Erythrina herbacea from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Redcardinal, Coral bean, Cherokee bean, Cardinal-spear
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Erythrina arborea (Chapman) Small
Description
"Perennial herb, 0.6-1.2 m tall (or shrub or tree up to 8 m high further south) with usually prickly brachlets. Leaves pinnately 3-foliolate; leatlets thinly chartaceous, glabrous, or nearly so, throughout, occasionally pricky beneath, hastately 3-lobed to widely deltoid, (2) 4-8 (12) cm long, stipellate. Inflorescence terminal, much elongate on usually leafless stems arising from the crown, (1) 3-7 dm long with few to numerous, papilionaceous flowers; pedicels 3-9 mm long, subtended by linear- lanceolate bracts 1-4 mm long and with 2 liner, caduceus bractlets, 1-2 mm long. Calyx glabrous, or nearly so, tubecampanulate, truncate, 5-11 mm long; the standard scarlet, 3-5.3 cm long, wings 5.5-11 mm long, keel 6-13 mm long; stamens diadelphous, 9 and 1; stigma capitate, ovary and stipe pubescent. Legume 7-15 (21) cm long, 1.2-1.6 cm broad, constricted between the several to many, scarlet seeds, stipe 1.5-4.5 cm long." [1]
Distribution
This species is generally distributed from southeast North Carolina south to Florida, west to southeast Texas, and south into eastern Mexico.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
General habitats of E. herbacea includes dry sandy woodlands, maritime forests, and sandhills within the outer Coastal Plain region.[2] It occurs in sand pine woodlands, sandy hills, along edges of sinkholes, live oak-cabbage palm forests, uplands, hammocks, flatwoods, sand pine scrub, pine-palmetto scrub near ocean, longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas, shaded slopes of river bluffs, and in calcareous open prairies. Found in disturbed areas such as along roadsides, in understory of recently clear cut pine woodlands, and edges of woodlands. Can thrive in areas that are shady, semi-shady, or open. Is associated with areas that have sand soil types, sandy loam, loam, thin loamy sand, and calcareous soil types.[3]
Associated species include Quercus geminata, Q. chapmanii, Q. incana, Osmanthus megacarpus, Ilex ambigua, Vitis rotundifolia, Serenoa repens, Persea, Myrica, Carya glabra var. megacarpa, Pinus palutris, Baccharis halimifolia, Rhus copalina, Callicarpa americana, Diospyros virginiana, Morus.[3]
Phenology
E. herbacea generally flowers from May until July.[2] It has been observed flowering from February to June with peak inflorescence in April and May, and fruiting from April to August.[3][4]
Seed bank and germination
Seeds germinate easily when scarified.[5]
Fire ecology
Is associated with annually burned pinelands.[3]
Pollination
Hummingbirds drink the nectar and pollinate E. herbacea.[5]
Use by animals
It is a nectar food source for hummingbirds. This species has toxic seeds for humans, which are used in Mexico for poisoning rats and various fish; the seeds are also made into novelties and necklaces which should be kept away from children.[5]
Conservation and management
For general management, dead stem tips should be trimmed once new growth emerges in the spring when frost damage is visible.[5]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 634. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: D. B. Ward, G. Crosby, R. Kral, George R. Cooley, Carroll E. Wood, Jr., Kenneth A. Wilson, R.K. Godfrey, Grady W. Reinert, James D. Ray, Jr., C. E. Smith, Olga Lakela, Jackie Patman, Richard J. Eaton, Richard S. Mitchell, Tom Barnes, C. Jackson, A. F. Clewell, Loran C. Anderson, Gary R. Knight, K. Craddock Burks, S. W. Leonard, Elbert L. Little, Jr., Robert J Lemaire, Jack P. Davis, Rodie White, Wilson Baker, R. Komarek, Lisa Keppner, Annie Schmidt, Travis MacClendon, Karen MacClendon, Tim Clemons, R. L. Wilbur, C. Ritchie Bell, Samuel B. Jones, Nancy Coile, et al., Roomie Wilson, Clarke Hudson, Sidney McDaniel, and A Traverse. States and Counties: Florida: Brevard, Calhoun, Citrus, Collier, Dade, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Hardee, Indian River, Jackson, Leon, Liberty, Marion, Okaloosa, Pasco, Pinellas, St Lucie, Suwannee, Wakulla, Walton, and Washington. Georgia: Grady and McIntosh. Louisiana: Hammond. Mississippi: Adams, Jasper, and Kemper. South Carolina: Berkeley and Horry. Texas: Harris.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 10 MAY 2019
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 [[1]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: May 10, 2019