Difference between revisions of "Chamaecrista fasciculata"
(→Taxonomic notes) |
(→Pollination) |
||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
Vespidae: ''Stenodynerus histrionalis rufustus'' | Vespidae: ''Stenodynerus histrionalis rufustus'' | ||
| − | Other Hymenoptera observed pollinating ''C. fasciculata'' include ''Dialictus coreopsis'', ''D. miniatulus'', ''D. placidensis'', ''Megachile brevis pseudobrevis'', and ''Xylocopa micans''.<ref name= "Deyrup 2002">Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).</ref> | + | Other Hymenoptera observed pollinating ''C. fasciculata'' include ''Dialictus coreopsis'', ''D. miniatulus'', ''D. placidensis'', ''Megachile brevis pseudobrevis'', and ''Xylocopa micans''.<ref name= "Deyrup 2002">Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).</ref> Fly species in the families Syrphidae and Tachinidae (Diptera) were collected from the plant and are possible pollinators.<ref name= "Tooker">Tooker, J. F., et al. (2006). "Floral host plants of Syrphidae and Tachinidae (Diptera) of central Illinois." Annals of the Entomological Society of America 99(1): 96-112.</ref> |
===Use by animals=== | ===Use by animals=== | ||
Revision as of 20:29, 4 April 2019
| Chamaecrista fasciculata | |
|---|---|
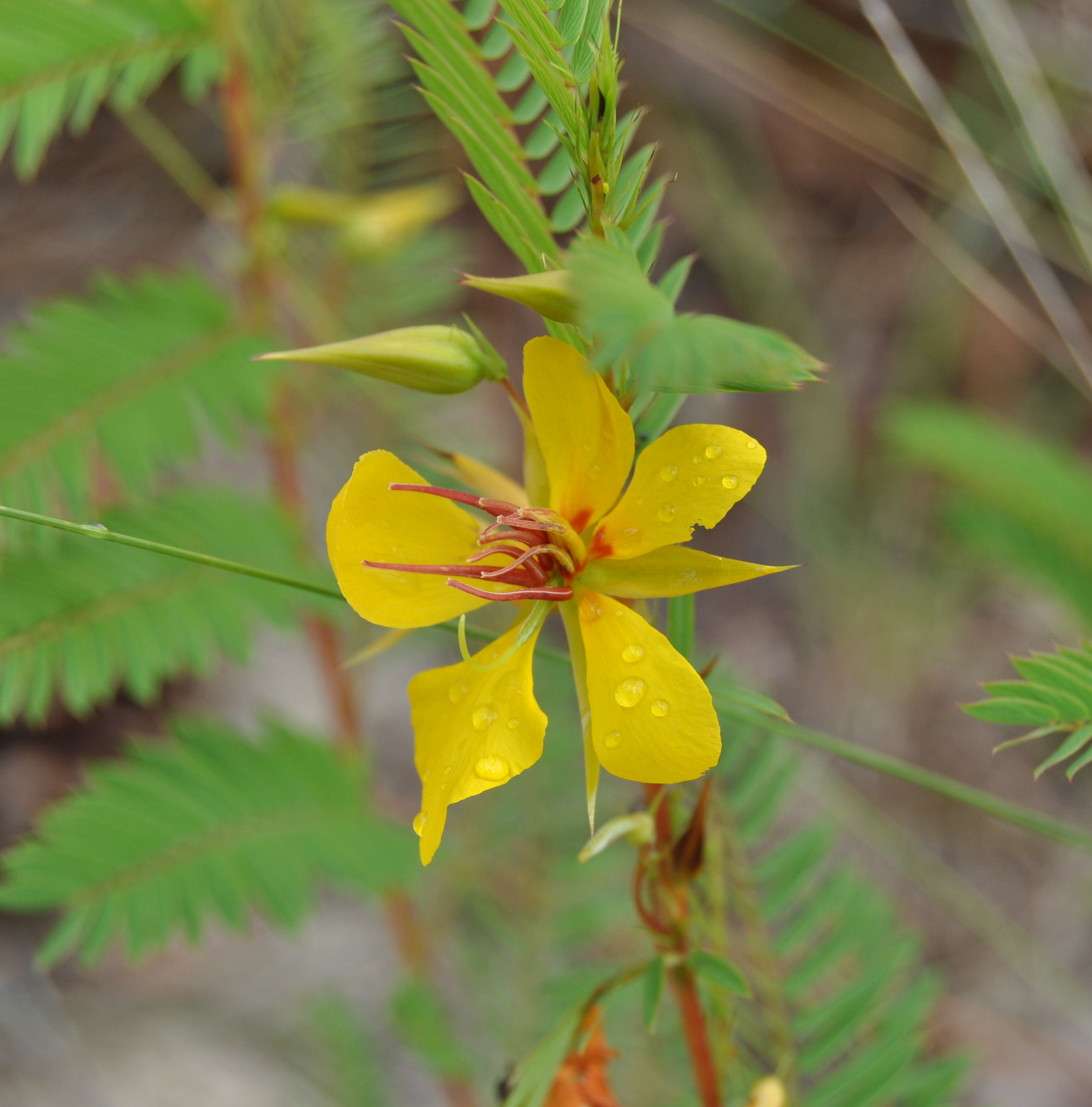

| |
| Photo taken by Michelle M. Smith | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Chamaecrista |
| Species: | C. fasciculata |
| Binomial name | |
| Chamaecrista fasciculata (Michx.) Greene | |
| |
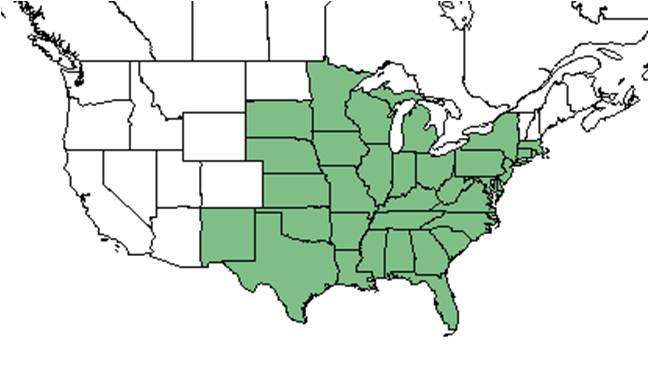
| Natural range of Chamaecrista fasciculata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Partridge Pea
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Chamaecrista littoralis Pollard; Chamaecrista mississipiensis (Pollard) Pollard ex Heller; Cassia fasciculata Michaux var. puberula (Greene) J.F. Macbride; Chamaecrista puberula Greene
Varieties: Chamaecrista fasciculata (Michaux) Greene var. brachiata (Pollard) Isely, Chamaecrista fasciculata (Michaux) Greene var. macrosperma (Fernald) C.F. Reed; Chamaecrista fasciculata (Michaux) Greene var. fasciculata
Description
Generally, in the group Chameacrista it includes trees, shrubs, or herbs. The leaves are evenly 1-pinnate with conspicuous gland(s) on the petiole or rachis. The flowers are either solitary or clustered in axillary racemes or terminal panicles, perfect. The calyx has an inconspicuous tube, 5 lobed, equally imbricate, and often unequal. There are 5 petals and are a little unequal. The stamens 5-10, are often unequal and some are sterile or imperfect. The anthers are basifixed and opening by 2 apical pores. The legume is few-to many-seeded, often septate, and exceedingly variable. Including Chamaecrista Moench, Ditremexa Raf., Emelista Raf. [1]
Specfically, for Chameacrista fasciculata, the species is an annual herb, growing 1.5-6 dm tall from the taproot. The stems and branches are glabrous to more commonly densely puberulent with incurved trichomes and occasionally also with villous trichomes to 2 mm long. The leaves are sensitive with a sessile, depressed, saucer-shaped gland, 0.5-1.5 mm in diam. near the middle of the petiole. Leaflets 12-36, linear-oblong, 1-2.5 cm long, 2-6 mm wide, inequilateral; stipules persistent, striate. Inflorescence are 1-6 flowered axillary fascicle. Pedicels grow up to 1-2 cm long. Sepals are lanceolate in shape, growing 9-12 mm long, and are acute. Petals are bright yellow in color, almost equal, growing 1-2 cm long; stamens 10, unequal, growing 10-13 mm long. The legume are elastically dehiscent, growing 3-7 cm long, and 5-7 mm broad, and are glabrate or appressed-puberulent to villous. [1]
Distribution
C. fasciculata is native to the eastern United States, excluding Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine, west to New Mexico, South Dakota, and Minnesota.[2]
Ecology
Like other species in the Fabaceae family, C. fasciculata is a nitrogen-fixing plant that depends on microorganisms to help produce nitrogen compounds necessary for the plant's survival. This is conducted through a symbiosis of microorganisms inhabiting root nodules of the plant to give the plant direct access and the microorganisms a safe habitat.[3]
Habitat
C. fasciculata can be found in sandy savannas of the Gulf Coastal Plain, and bluffs, prairies, river bottoms and banks, and upland woods of the Great Plains region. Soils it generally grows on range from sandy to sandy loam soils.[4] As well, other wide range of soils include slightly acidic to moderately alkaline soils, and it prefers well drained and moderately lime soils.[5] It is a facultative upland species.[2] C. fasciculata is also a common colonizer of disturbed areas.[4] The species can be commonly found to grow on recently abandoned gopher tortoise (Gopherus polyphemus) mounds.[6]
Phenology
C. fasciculata has been observed flowering between April and September with peak inflorescence in June and August.[7]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by consumption by vertebrates. [8]
Seed bank and germination
For propagation, seeds can be cold moist stratified for 56 days to improve germination success. Optimum soil temperature for germination is between 20 and 30 degrees Celsius. With this regiment, about 70% of seeds will germinate between 7 and 25 days.[4]
Fire ecology
Fire helps proliferate this species.[4] Winter burns, rather than spring or summer burns, significantly increase C. fasciculata in frequency as well as overall biomass of the species.[9]
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Chamaecrista fasciculata at Archbold Biological Station:[10]
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens
Halictidae: Augochlora pura, Augochloropsis metallica, A. sumptuosa, Lasioglossum coreopsis, L. placidensis
Megachilidae: Coelioxys sayi, Megachile mendica, M. texana
Vespidae: Stenodynerus histrionalis rufustus
Other Hymenoptera observed pollinating C. fasciculata include Dialictus coreopsis, D. miniatulus, D. placidensis, Megachile brevis pseudobrevis, and Xylocopa micans.[11] Fly species in the families Syrphidae and Tachinidae (Diptera) were collected from the plant and are possible pollinators.[12]
Use by animals
C. fasciculata has raised glands on its petioles that excrete a nectar that attracts predatory ants, with the presumed adaptive benefit of encouraging ants to prey on herbivores.[13] The glands have also been observed to attract bees and wasps, presumably with the same benefit to the plant.[14] As a whole, it is approximately 5-10% of the diet for large mammals, and 10-25% of the diet for terrestrial birds where it is found.[15] It is a major food item for the northern bobwhite quail and other quails due to its persistence through the winter and early spring. Partridge pea is also eaten by ring-necked pheasant, greater and lesser prairie-chicken, grassland birds, mallard, field mice, and deer; it can be poisonous for livestock and is considered potentially dangerous for cattle. Upland game birds and small non-game birds, small mammals, and waterfowl utilize the litter and plant stocks of the species for cover. As well, the common sulfur butterfly (Colias philodice) lays eggs on the leaves so that the larvae use them as their first food source.[4] It is also a larval host for other members of Lepidoptera, including the cloudless giant sulpher (Phoebis sennae), the orange sulphur (Colias eurytheme), and the sleepy orange (Abaeis nicippe).[3] Historically, the Cherokee Native American tribe used the species as a medicinal drug to keep ball players from tiring as well as for spells of fainting; the Seminole tribe used C. fasciculata medicinally as a drug for nausea, and used the plant as a bed for ripening persimmons.[4]
Conservation and management
For management, stands that are already established are recommended to be disked lightly in springtime to show mineral soil that the seeds can germinate on. This species can decrease in frequency if there is not regular maintenance, so light disking is necessary to remove old sod, small brush, and other weeds. Fire is also a great management tool to help proliferate this species; for best results, prescribed fire should be conducted in the winter. Mowing can also help control weeds through mowing over the top of C. fasciculata individuals.[4]
Cultivation and restoration
To control erosion, C. fasciculata can be planted along road banks or stream banks for restoration as well as improving soil fertility. This is due to it being able to rapidly establish, fix nitrogen, to reseed, and decrease in frequency as other species start dominating the site. It is commonly included in seed mix with other grasses and forbs that are planted along roadsides to prevent establishment of weeds. Cultivars of C. fasciculata include 'Comanche' from the Knox City Plant Materials Center in Texas and 'Riley' from the Manhattan Plant Materials Center in Kansas.[4]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 577-8. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 4 April 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 [[1]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: April 4, 2019
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 Houck, M. J. and J. M. Row. (2006). Plant Guide: Partridge Pea Chamaecrista fasciculata. N.R.C.S. United States Department of Agriculture. Alexandria, LA.
- ↑ USDA NRCS Plant Materials Program and J. M. Row. (2006). Plant Fact Sheet: Showy Partridge Pea Chamaecrista fasciculata.N.R.C.S. United States Department of Agriculture. Manhattan, KS.
- ↑ Kaczor, S. A. and D. C. Hartnett (1990). "Gopher tortoise (Gopherus polyphemus) effects on soils and vegetation in a Florida sandhill." American Midland Naturalist 123: 100-111.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 7 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Kush, J. S., et al. (2000). Understory plant community response to season of burn in natural longleaf pine forests. Proceedings 21st Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference. Fire and forest ecology: innovative silviculture & vegetation management, Tallahassee, FL, Tall Timbers Research, Inc.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).
- ↑ Tooker, J. F., et al. (2006). "Floral host plants of Syrphidae and Tachinidae (Diptera) of central Illinois." Annals of the Entomological Society of America 99(1): 96-112.
- ↑ Boecklen, W.J. 1984. The role of extrafloral nectaries in the herbivore defence of Cassia fasciculata. Ecological Entomology 9:243-249.
- ↑ David McElveen and Kevin Robertson observation on Tall Timbers Research Station, Tallahassee, Florida, July 17 and 20, 2018.
- ↑ Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.