Difference between revisions of "Piptochaetium avenaceum"
Lsandstrum (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, ''Piptochaetium avenaceum'' is found in live oak groves, open sandy ridges, mesic coastal hammocks, woodland openings, floodplain edges, along creeks, lake slopes, upland mixed forests, mixed pinewoods, open mixed woodlands, annually burned savannas and pine-oak, open stand of shrubs and trees of ''Ilex vomitoria'', and floodplains. <ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, K. MacClendon, T. MacClendon, Robert K. Godfrey, K. Craddock Burks, Jean W. Wooten, Swallen, George R. Cooley, Joseph Monachino, Gary R. Knight, Brenda Herring, Don Herring, Richard S. Mitchell, H. Kurz, Patricia Elliot, R. Komarek, R. A. Norris, Matt Hils, Annie Schmidt. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Calhoun, Escambia, Gadsden, Hernando, Holmes, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Nassau, Okaloosa, St. Johns, Suwannee, Wakulla. Georgia: Grady, Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> Human disturbed areas include roadsides, recreation areas, nature trails, stands of old field pines cleared of underbrush, and along city roads. It has been observed to grow in dry loamy sand, sandy soils, limestone outcrops, calcareous slopes and moist loamy sands. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, ''Piptochaetium avenaceum'' is found in live oak groves, open sandy ridges, mesic coastal hammocks, woodland openings, floodplain edges, along creeks, lake slopes, upland mixed forests, mixed pinewoods, open mixed woodlands, annually burned savannas and pine-oak, open stand of shrubs and trees of ''Ilex vomitoria'', and floodplains. <ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, K. MacClendon, T. MacClendon, Robert K. Godfrey, K. Craddock Burks, Jean W. Wooten, Swallen, George R. Cooley, Joseph Monachino, Gary R. Knight, Brenda Herring, Don Herring, Richard S. Mitchell, H. Kurz, Patricia Elliot, R. Komarek, R. A. Norris, Matt Hils, Annie Schmidt. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Calhoun, Escambia, Gadsden, Hernando, Holmes, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Nassau, Okaloosa, St. Johns, Suwannee, Wakulla. Georgia: Grady, Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> Human disturbed areas include roadsides, recreation areas, nature trails, stands of old field pines cleared of underbrush, and along city roads. It has been observed to grow in dry loamy sand, sandy soils, limestone outcrops, calcareous slopes and moist loamy sands. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | ||
| + | ''P. avenaceum'' responds negatively to soil disturbance in old field longleaf communities in South Carolina.<ref>Brudvig, L.A. and E.I. Damchen. (2011). Land-use history, historical connectivity, and land management interact to determine longleaf pine woodland understory richness and composition. Ecography 34: 257-266.</ref> | ||
Associated species include ''Melica mutica, Festuca, Erigeron, Verbena, Vitis rotundifolia, Rubus trivialis'' and ''Ilex vomitoria.'' <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | Associated species include ''Melica mutica, Festuca, Erigeron, Verbena, Vitis rotundifolia, Rubus trivialis'' and ''Ilex vomitoria.'' <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | ||
| + | |||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
''P. avenaceum'' has been observed flowering and fruiting March through May with peak inflorescence in April.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016</ref> | ''P. avenaceum'' has been observed flowering and fruiting March through May with peak inflorescence in April.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016</ref> | ||
Revision as of 17:21, 27 June 2019
| Piptochaetium avenaceum | |
|---|---|
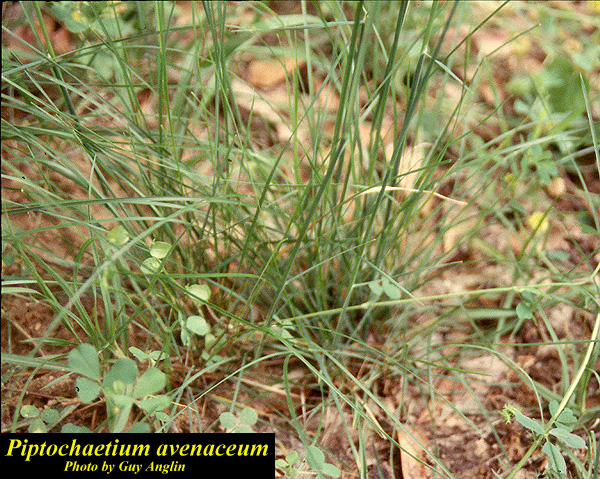

| |
| Photo by Guy Anglin, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae ⁄ Gramineae |
| Genus: | Piptochaetium |
| Species: | P. avenaceum |
| Binomial name | |
| Piptochaetium avenaceum (L.) Parodi | |
| |
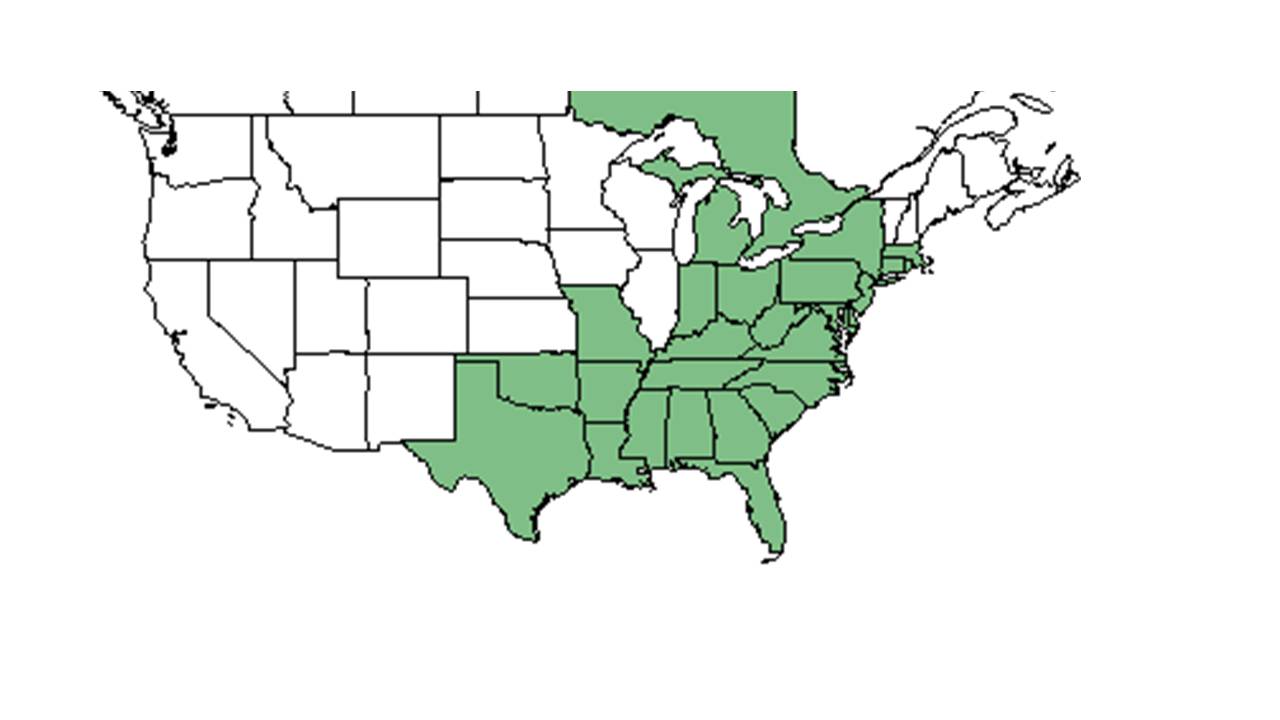
| Natural range of Piptochaetium avenaceum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Blackseed speargrass, Eastern needlegrass,
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Stipa avenacea Linnaeus
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, Piptochaetium avenaceum is found in live oak groves, open sandy ridges, mesic coastal hammocks, woodland openings, floodplain edges, along creeks, lake slopes, upland mixed forests, mixed pinewoods, open mixed woodlands, annually burned savannas and pine-oak, open stand of shrubs and trees of Ilex vomitoria, and floodplains. [1] Human disturbed areas include roadsides, recreation areas, nature trails, stands of old field pines cleared of underbrush, and along city roads. It has been observed to grow in dry loamy sand, sandy soils, limestone outcrops, calcareous slopes and moist loamy sands. [1] P. avenaceum responds negatively to soil disturbance in old field longleaf communities in South Carolina.[2]
Associated species include Melica mutica, Festuca, Erigeron, Verbena, Vitis rotundifolia, Rubus trivialis and Ilex vomitoria. [1]
Phenology
P. avenaceum has been observed flowering and fruiting March through May with peak inflorescence in April.[1][3]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, K. MacClendon, T. MacClendon, Robert K. Godfrey, K. Craddock Burks, Jean W. Wooten, Swallen, George R. Cooley, Joseph Monachino, Gary R. Knight, Brenda Herring, Don Herring, Richard S. Mitchell, H. Kurz, Patricia Elliot, R. Komarek, R. A. Norris, Matt Hils, Annie Schmidt. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Calhoun, Escambia, Gadsden, Hernando, Holmes, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Nassau, Okaloosa, St. Johns, Suwannee, Wakulla. Georgia: Grady, Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Brudvig, L.A. and E.I. Damchen. (2011). Land-use history, historical connectivity, and land management interact to determine longleaf pine woodland understory richness and composition. Ecography 34: 257-266.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016