Difference between revisions of "Andropogon hirsutior"
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
''A. hirsutior'' is a characteristic wetland species that often frequents the understory vegetation of Upper Panhandle Savannas. <ref name= "Carr">Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189. | ''A. hirsutior'' is a characteristic wetland species that often frequents the understory vegetation of Upper Panhandle Savannas. <ref name= "Carr">Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189. | ||
| − | </ref> It is also found mostly in longleaf pine forests <ref name= "PanFlora"> | + | </ref> It is also found mostly in longleaf pine forests <ref name= "PanFlora"> Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 16 MAY 2018 </ref> , as well as wet savannas, pine flatwoods, adjacent ditches, and other wet disturbed sites. <ref name= "Weakley 2015"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 15:47, 12 September 2018
Common names: bushy bluestem [1], hairy bluestem [2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Andropogon glomeratus (Walter) Britton, Sterns, & Poggenburg var. hirsutior (Hackel) C. Mohr; A. virginicus var. hirsutior (Hackel) A.S. Hitchcock, A. virginicus var. glaucopsis (Elliott) A.S. Hitchcock
Varieties: none
Description
A. hirsutior is a perennial graminoid of the Poaceae family native to North America. [1]
Distribution
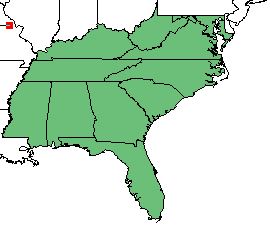
A. hirsutior can be found on the southeastern coast, ranging from Texas and Oklahoma to New Jersey, with the exception of Delaware. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
A. hirsutior is a characteristic wetland species that often frequents the understory vegetation of Upper Panhandle Savannas. [3] It is also found mostly in longleaf pine forests [4] , as well as wet savannas, pine flatwoods, adjacent ditches, and other wet disturbed sites. [2]
Phenology
A. hirsutior has been observed to flower between October and December. [4]
Fire ecology
A. hirsutior thrives when the following burning treatments are applied: periodic winter, periodic summer, annual winter, biennial summer. [5]
Use by animals
A. hirsutior has fair forage value. [6]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=ANGLH
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 16 MAY 2018
- ↑ Lewis, C. E. and T. J. Harshbarger (1976). "Shrub and herbaceous vegetation after 20 years of prescribed burning in the South Carolina coastal plain." Journal of Range Management 29(1): 13-18.
- ↑ Hilmon, J. B. (1964). "Plants of the Caloosa Experimental Range " U.S. Forest Service Research Paper SE-12