Difference between revisions of "Anchistea virginica ."
(→Ecology) |
(→Conservation and Management) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
| − | ''A. virginica'' is not considered a threatened species; however, it is a rare species in the regions it is present. <ref name= "Huskins"> The Vascular Flora of the North Chickamauga Creek Gorge State Natural Area, Tennessee [Huskins, S. D. and J. Shaw (2010). "The Vascular Flora of the North Chickamauga Creek Gorge State Natural Area, Tennessee." Castanea 75(1): 101-125.]</ref> | + | ''A. virginica'' is not considered a threatened species; however, it is a rare species in the regions it is present. <ref name= "Huskins"> The Vascular Flora of the North Chickamauga Creek Gorge State Natural Area, Tennessee [Huskins, S. D. and J. Shaw (2010). "The Vascular Flora of the North Chickamauga Creek Gorge State Natural Area, Tennessee." Castanea 75(1): 101-125.]</ref> It is listed as exploitably vulnerable in the state of New York, a species of special concern in Tennessee, and listed as threatened in Vermont.<ref name= "USDA"/> |
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
Revision as of 19:26, 5 March 2019
Common names: Virginia Chain Fern[1]
| Anchistea virginica | |
|---|---|
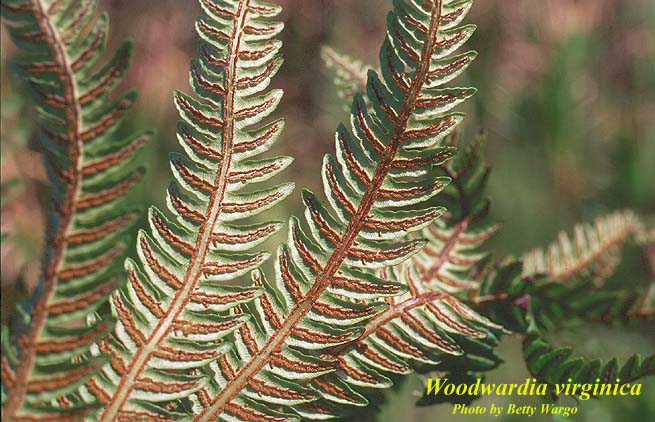

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Pteridophyta - Ferns |
| Class: | Filicopsida |
| Order: | Polypodiales |
| Family: | Blechnaceae |
| Genus: | Anchistea |
| Species: | A. virginica |
| Binomial name | |
| Anchistea virginica (L) C. Presl | |
| |
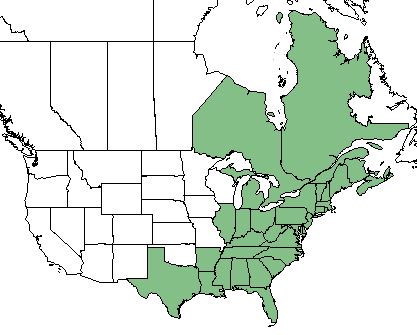
| Natural range of Anchistea virginica from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Woodwardia virginica (Linnaeus) J.E. Smith
Variety: none
Description
Anchistea virginica is a perennial fern of the Blechnaceae family native to North America. [2]
Distribution
Anchistea virginica is found along the east coast of the United States, reaching as far west as Texas, as well as eastern Canada. [2]
Ecology
Habitat
A. virginica is commonly found in wetland habitats that include elm and oak populations. [3]
A. virginica has been spotted in post burned areas of Polk County, Florida in association with Cladium jamaicense, and Pontederia cordata car. lanceolata under a stand of Nyssa biflora. In a deep muck seepage swamp in northern Highlands County, Florida, A. virginica has been seen as part of a Sphagnum mat codominated by magnolia virginiana, gordonia lasianthus, and Osmundastrum cinnamomeum as a base landscape for the rare Peltandra sagittifolia. [4]
Phenology
As a competitive plant in the canopy of the forest, A. virginica has developed a high density leaf structure to compete for light sources; higher density of leaves results in a larger amount of biomass litter on the forest floor. [3]
Conservation and Management
A. virginica is not considered a threatened species; however, it is a rare species in the regions it is present. [5] It is listed as exploitably vulnerable in the state of New York, a species of special concern in Tennessee, and listed as threatened in Vermont.[6]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 USDA Plants Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=WOVI
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 [Bartsch, I. and J. Lawrence (1997). "Leaf Size and Biomass Allocation in Thelypteris dentata, Woodwardia virginica, and Osmunda regalis in Central Florida." American Fern Journal 87(2): 71-76.]
- ↑ Observation by Edwin Bridges in Polk County, FL, April 2018 and Highlands county Fl May 8, 2017 posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group April 26, 2018 and May 8, 2017.
- ↑ The Vascular Flora of the North Chickamauga Creek Gorge State Natural Area, Tennessee [Huskins, S. D. and J. Shaw (2010). "The Vascular Flora of the North Chickamauga Creek Gorge State Natural Area, Tennessee." Castanea 75(1): 101-125.]
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedUSDA