Difference between revisions of "Coleataenia tenera"
(→Taxonomic notes) |
Emmazeitler (talk | contribs) (→Taxonomic notes) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: ''Sorengia tenera'' (Beyrich ex Trinius) Zuloaga & Morrone; ''Panicum tenerum'' Beyrich ex Trinius | + | Synonyms: ''Sorengia tenera'' (Beyrich ex Trinius) Zuloaga & Morrone; ''Panicum tenerum'' Beyrich ex Trinius.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| − | Varieties: none | + | Varieties: none.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
Revision as of 14:18, 15 September 2020
| Coleataenia tenera | |
|---|---|

| |
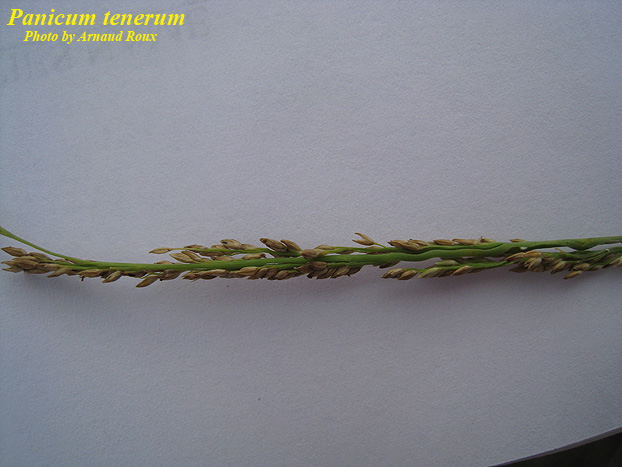
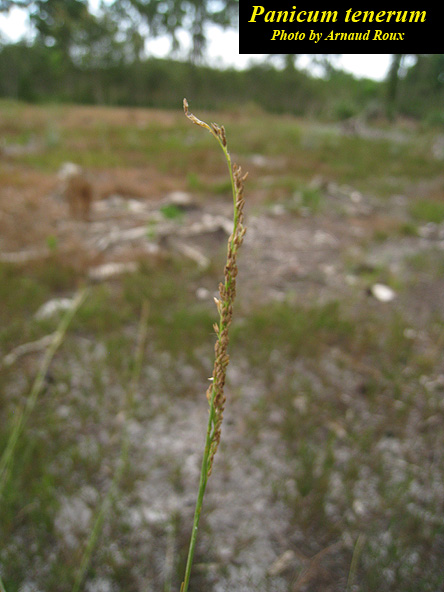
| Panicum tenerum in photo above, a synonym of Coleataenia tenera Photo by Arnaud Roux, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae ⁄ Gramineae |
| Genus: | Coleataenia |
| Species: | C. tenera |
| Binomial name | |
| Coleataenia tenera Bey. ex Trin. | |
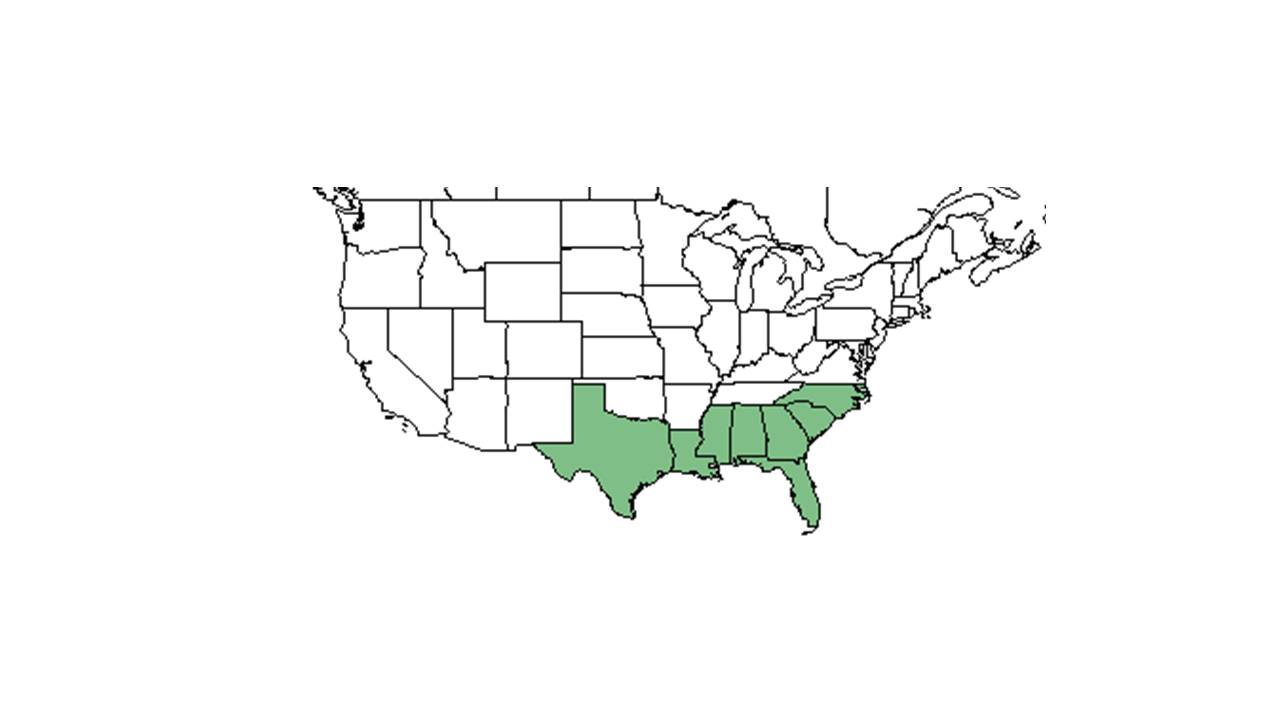
| |
| Natural range of Coleataenia tenera from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Bluejoint panicgrass; Southeastern panic grass
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Sorengia tenera (Beyrich ex Trinius) Zuloaga & Morrone; Panicum tenerum Beyrich ex Trinius.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
This species grows abundantly where it is found.[2]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
This species can be found in shallow depression ponds, pine flatwoods, wet prairies, bogs, swamps, marshes, and savannas. It has been observed in open areas growing in moist to drying sandy peat and loamy sands.[2] C. tenera is a dominant species that has been found in short-hydroperiod prairies occurring in Everglades National Park as well.[3] This species has also been found growing in human disturbed habitats such as pine plantations, clear cut pine flatwoods, along roadsides, disturbed cypress lowlands, and cutover ponds.[2]
Phenology
This species has been observed to flower and fruit from June through November.[2]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
Close up of Seeds on stem of Panicum tenerum synonym of Coleataenia tenera Photo by Arnaud Roux, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R.K. Godfrey, R. Kral, H. Kurz, Cecil R Slaughter, Sidney McDaniel, George R. Cooley, R. J. Eaton, Olga Lakela, Allen G. Shuey, Steve L. Orzell, Edwin L. Bridges, R. A. Norris, and A. F. Clewell. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Brevard, Calhoun, Charlotte, Collier, Franklin, Gulf, Indian River, Manatee, Martin, Okaloosa, Osceola, Palm Beach, Polk, and Wakulla. Countries: Honduras.
- ↑ Slocum, M. G., W. J. Platt, et al. (2003). "Effects of differences in prescribed fire regimes on patchiness and intensity of fires in subtropical savannas of Everglades National Park, Florida." Restoration Ecology 11: 91-102
