Difference between revisions of "Morella pumila"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{italic title}} | {{italic title}} | ||
| + | Common names: wax myrtle | ||
<!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
Revision as of 18:58, 15 June 2018
Common names: wax myrtle
| Morella pumila | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Gary Fleming at the Digital Atlas of the Virginia Flora | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Fagales |
| Family: | Myricaceae |
| Genus: | Morella |
| Species: | M. pumila |
| Binomial name | |
| Morella pumila L. | |
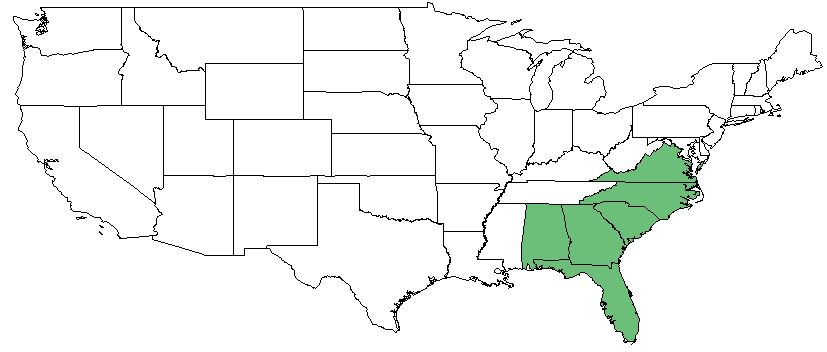
| |
| Natural range of Morella pumila from Weakley [1] | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Myrica pusilla Rafinesque, Morella cerifera (Linnaeus) Small, Myrica cerifera Linnaeus var. pumila Michaux, and Cerothamnus pumilus (Michaux) Small.
Varieties: none
Description
M. pumila, also known as Dwarf Wax-Myrtle, is a native perennial that varies in growth habit from an evergreen shrub and subshrub to a tree growth. It is a member of the Myricaceae family, and can grow up to 6 feet high. The species is dioecious, with aromatic leaves and root nodules that help fix nitrogen in the soil. As well, it has rhizomatous roots which can propagate to form new growth. [2]
Distribution
M. pumila's native distribution ranges along the coast from eastern Texas to New Jersey. It is also native to Puerto Rico, and has been introduced to Hawaii. [2]
Ecology
Habitat
The species can be found in relatively moist to extremely dry sites, including sandhills, savannas, and pine flatwoods. [3] M. pumila has been observed in small clearings beside roads. [4]
Associated species - Vaccinium darrowi, Pityopsis spp. [4]
Phenology
M. pumila flowers in April as well as between the months of August and October. [3]
Seed dispersal
The species is mainly dispersed through animal consumption. [5]
Seed bank and germination
The species requires a period of cold, moist stratification before germinating, where an average germination time is a month to 90 days. However, wax myrtles can also be propagated from semi-hardwood and soft cuttings treated with a rooting hormone. [2]
Use by animals
M. pumila is used by wild birds as a source of food, and the branches are also utilized by wild birds for nesting and perching habitat. It is a minor source of food for large mammals, water birds, and terrestrial birds, and a low source of food for small mammals. [2]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
This Wax-Myrtle is popular for cultivation due to its ornamental value. M. pumila is also a good plant to use for native area restoration in its native communities like sandy coastal and woodland communities. It is a good plant for dune stabilization and further restoration. [2]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, Alan S. 2015. Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States: Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. 1320 pp.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 USDA Plants Database URL: https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=MOCE2
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson and Ron Miller. States and counties: Florida: Santa Rosa.
- ↑ Kirkman, L.K. and K.L. Coffey, unpublished database of dispersal modes of plants found at the Jones Ecological Research Center, Ichauway, Georgia.