Difference between revisions of "Apocynum cannabinum"
(→Description) |
(→Distribution) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| − | In Florida, reports of ''A. cannabinum'' range from Escambia County, eastward to Clay and Volusia Counties, and southward to Hernando and Brevard Counties.<ref name="Hammer 2018">Observation by Roger Hammer in Falling Waters State Park, Washington County, FL, January 9, 2018, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group August 4, 2017</ref> Otherwise, it can be found throughout the United States in thickets and borders of old fields in pine forests <ref name= "Sievers"/>. | + | In Florida, reports of ''A. cannabinum'' range from Escambia County, eastward to Clay and Volusia Counties, and southward to Hernando and Brevard Counties.<ref name="Hammer 2018">Observation by Roger Hammer in Falling Waters State Park, Washington County, FL, January 9, 2018, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group August 4, 2017</ref> Otherwise, it can be found throughout the United States in thickets and borders of old fields in pine forests <ref name= "Sievers"/>. The species can be seen as a generalist and can grow in numerous types of habitats, but is most common along shores and flood plains <ref name= "DiTommaso"/>. |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
Revision as of 18:19, 16 May 2018
| Apocynum cannabinum | |
|---|---|

| |
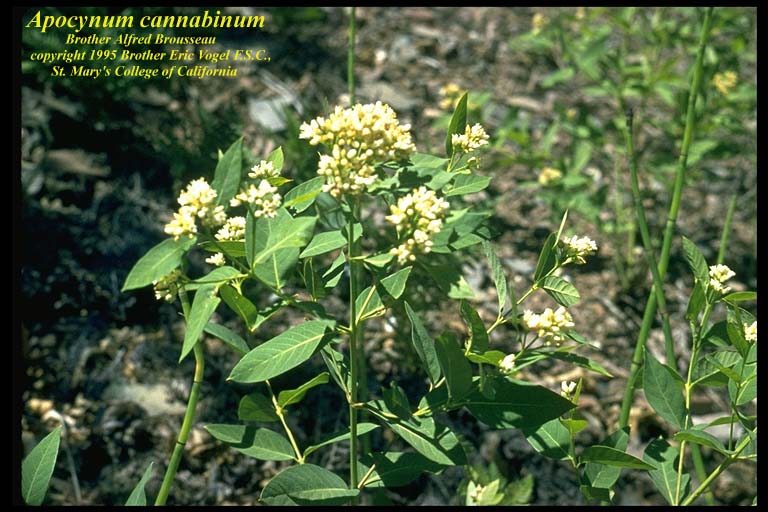
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Gentianales |
| Family: | Apocynaceae |
| Genus: | Apocynum |
| Species: | A. cannabinum |
| Binomial name | |
| Apocynum cannabinum (L) | |
| |
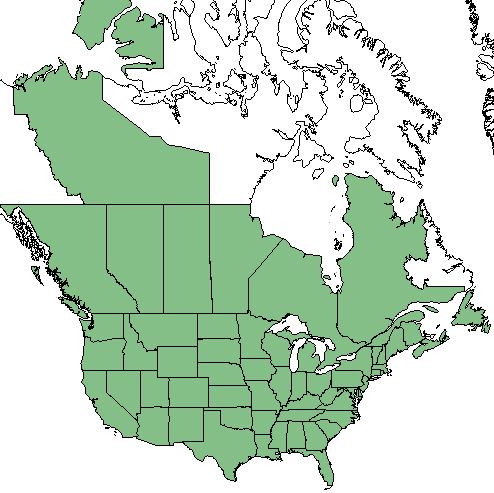
| Natural range of Apocynum cannabinum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Apocynum cannabinum var. cannabinum, Apocynum cannabinum var. pubescens, Apocynum cannabinum var. nemorale, Apocynum cannabinum var. glaberrimum, Apocynum cannabinum var. greeneanum.
Varieties: none
Description
A. cannabinum, also known as Indianhemp, is a native member of the Apocynaceae family, with a perennial forb growth habit [1]. It grows to a height between 2 to 4 feet with erect branches and sharp-pointed leaves. [2]. It also is a tough and fibrous plant which produces a milky latex sap like other Milkweeds. The A. cannabinum root system consists of horizontal roots and short rhizomes [3].
Distribution
In Florida, reports of A. cannabinum range from Escambia County, eastward to Clay and Volusia Counties, and southward to Hernando and Brevard Counties.[4] Otherwise, it can be found throughout the United States in thickets and borders of old fields in pine forests [2]. The species can be seen as a generalist and can grow in numerous types of habitats, but is most common along shores and flood plains [3].
Ecology
Habitat
A. cannabinum can be found in natural communities as well as human disturbed habitats across the United States [2].
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ USDA Plants Database URL: https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=APCA
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Sievers, A. F. (1930). American medicinal plants of commercial importance. Washington, USDA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 DiTommaso, A., et al. (2009). "The Biology of Canadian Weeds. 143. Apocynum cannabinum L." Canadian Journal of Plant Science 89: 977-992.
- ↑ Observation by Roger Hammer in Falling Waters State Park, Washington County, FL, January 9, 2018, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group August 4, 2017