Difference between revisions of "Tephrosia virginiana"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | Flowering occurs from April through June.<ref name="Weakley 2015"/><ref name="PanFlora">Nelson G. (12 January 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/</ref> Fruiting occurs from July through October.<ref name="Weakley 2015"/> Germination occurs from March through June when seasonal temperatures are increasing.<ref name="Coffey & Kirkman 2006"/> Flowering is stimulated by fire and occurs within three months of burning.<K. Robertson personal observation at Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, near Thomasville, Georgia.</ref> | + | Flowering occurs from April through June.<ref name="Weakley 2015"/><ref name="PanFlora">Nelson G. (12 January 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/</ref> Fruiting occurs from July through October.<ref name="Weakley 2015"/> Germination occurs from March through June when seasonal temperatures are increasing.<ref name="Coffey & Kirkman 2006"/> Flowering is stimulated by fire and occurs within three months of burning.<ref name="Robertson">K. Robertson personal observation at Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, near Thomasville, Georgia.</ref> |
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
In Georgia, seeds buried in a seed bag for 1 and 2 years yielded 61 and 50% rates of germination, respectively.<ref name="Coffey & Kirkman 2006">Coffey KL, Kirkman LK (2006) Seed germination strategies of species with restoration potential in a fire-maintained pine savanna. Natural Areas Journal 26(3):289-299.</ref> | In Georgia, seeds buried in a seed bag for 1 and 2 years yielded 61 and 50% rates of germination, respectively.<ref name="Coffey & Kirkman 2006">Coffey KL, Kirkman LK (2006) Seed germination strategies of species with restoration potential in a fire-maintained pine savanna. Natural Areas Journal 26(3):289-299.</ref> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Fire ecology=== | ||
| + | ''T. virginiana'' resprouts rapidly following fire and flowers within three months of burning.<ref name="Robertson"/> | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
Revision as of 15:54, 22 January 2018
| Tephrosia virginiana | |
|---|---|

| |
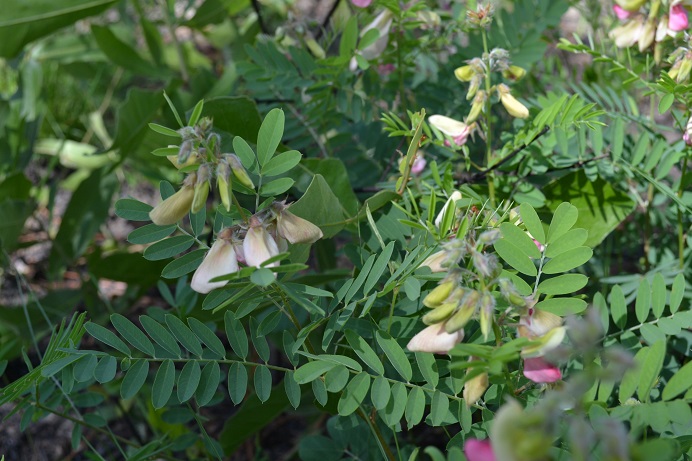
| Photo by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Genus: | Tephrosia |
| Species: | T. virginiana |
| Binomial name | |
| Tephrosia virginiana (L.) Pers. | |
| |
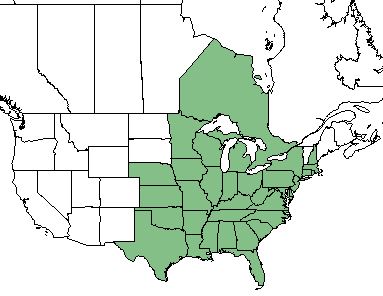
| Natural range of Tephrosia virginiana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): Virginia goat's-rue;[1] Virginia tephrosia;[2][3] goat's rue; devil's shoestring[3]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Varieties: T. virginiana var. glabra; T. virginiana var. virginiana[1]
Synonym(s): Cracca virginiana;[1][2] Cracca latidens; T. latidens[2]
Description
Tephrosia virginiana is covered with soft white hairs, which makes it silvery green in appearance. It grows to 1-3 ft (0.30-0.91 m) and has long stringy roots, from which it gets the name devil's shoestring. Leaves are pinnately compound with 8-15 pairs of leaflets. Flowers are bi-colored with pink and pale yellow and typically cluster at the tip of the stem. In southern portions of its range, flowers can initially be white but will change over time.[3]
Distribution
This species is found from Texas, eastward to Florida, northward to New Hampshire and New York, and inland to Minnesota and Nebraska.[1][2] It is also reported to occur in the Ontario province of Canada.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
T. virginiana is found in sandhills, other pinelands, xeric or rocky woodlands and forests, outcrops, shale barrens, other barrens, and dry roadbanks.[1] In South Carolina forests, it is found in 72% of sites while only 0 and 8% in pastures and cultivated fields.[4] It is considered a characteristic legume species of shortleaf pine-oak-hickory woodlands[5] and longleaf pine/wiregrass communities.[6] This species is one of several species positivily associated with Linum intercursum and Scleria pauciflora. [7]
Phenology
Flowering occurs from April through June.[1][8] Fruiting occurs from July through October.[1] Germination occurs from March through June when seasonal temperatures are increasing.[9] Flowering is stimulated by fire and occurs within three months of burning.[10]
Seed bank and germination
In Georgia, seeds buried in a seed bag for 1 and 2 years yielded 61 and 50% rates of germination, respectively.[9]
Fire ecology
T. virginiana resprouts rapidly following fire and flowers within three months of burning.[10]
Use by animals
T. virginiana comprises 2-5% of the diets of some large mammals and terrestrial birds.[11] In the past, it was used as a goat feed to increase milk production. However, this use stopped after tephrosin, an insecticide and fish poison, was found in it.[3]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Seeds can be collected from August to September. To propagate from seeds, scarification, inoculation, and 10 days of moist stratification should occur.[3]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Weakley A. S.(2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 12 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Plant database: Tephrosia virginiana. (12 January 2018) Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. URL: https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=TEVI
- ↑ Brudvig LA, Damschen EI (2011) Land-use history, historical connectivity, and land management interact to determine longleaf pine woodland understory richness and composition. Ecography 34:257-266.
- ↑ Clewell AF (2013) Prior prevalence of shortleaf pine-oak-hickory woodlands in the Tallahassee red hills. Castanea 78(4):266-276.
- ↑ Andreu MG, Hedman CW, Friedman MH, Andreu AG (2009) Can managers bank on seed banks when restoring Pinus taeda L. plantations in southwest Georgia? Restoration Ecology 17(5):586-596.
- ↑ Clarke GL, Patterson WA III (2007) The distribution of disturbance-dependent rare plants in a coastal Massachusetts sandplain: Implications for conservation and management. Biological Conservation 136:4-16.
- ↑ Nelson G. (12 January 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Coffey KL, Kirkman LK (2006) Seed germination strategies of species with restoration potential in a fire-maintained pine savanna. Natural Areas Journal 26(3):289-299.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 K. Robertson personal observation at Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, near Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Miller JH, Miller KV (1999) Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.