Difference between revisions of "Spiranthes praecox"
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
==Description== <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ==Description== <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | ''Spiranthes praecox is a monoecious perennial forb/herb.<ref name="USDA"/> | + | ''Spiranthes praecox'' is a monoecious perennial forb/herb.<ref name="USDA"/> It is also known to naturally hybridize with other orchids, like ''S. gracilis''.<ref name="Ames 1903"/> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
Revision as of 14:42, 16 January 2018
| Spiranthes praecox | |
|---|---|
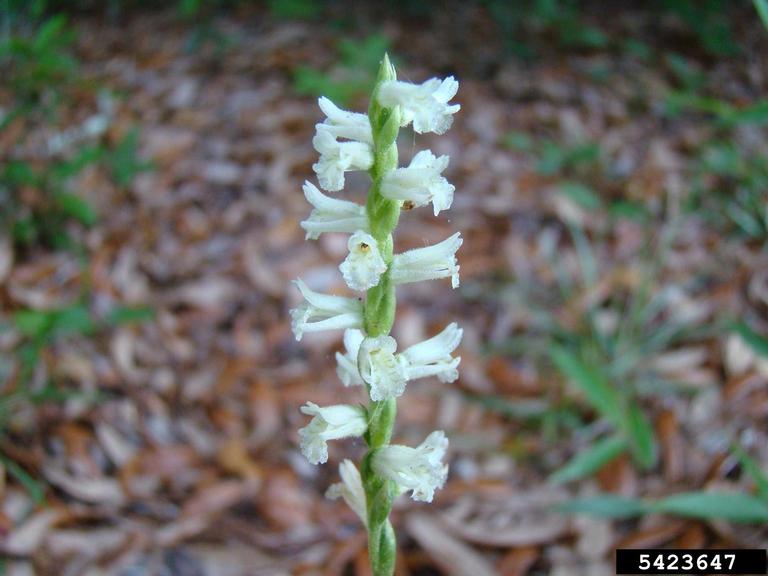

| |
| Photo by Rebekah D. Wallace, University of Georgia, Bugwood.org hosted at Forestryimages.org | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Orchidales |
| Family: | Orchidaceae - Orchids |
| Genus: | Spiranthes |
| Species: | S. praecox |
| Binomial name | |
| Spiranthes praecox (Walter) S. Watson | |
| |
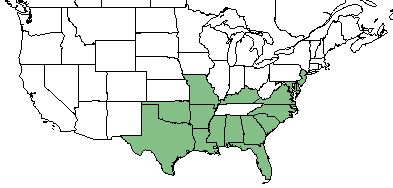
| Natural range of Spiranthes praecox from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): grass-leaved ladies’ –tresses, giant ladies’ –tresses,[1] greenvein lady’s tresses[2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym(s): Ibidium praecox[1][2]
Description
Spiranthes praecox is a monoecious perennial forb/herb.[2] It is also known to naturally hybridize with other orchids, like S. gracilis.[3]
Distribution
This species is endemic to the Southeastern Coastal Plain, being found from New Jersey, south to southern Florida, and westward to Texas.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
S. praecox is found in savannas, swamps, and bogs.[1]
Phenology
It flowers from March through July,[1] peaking in April and May. A report of flowering in December also exists[4] and in New England, it is said to complete its bloom by the end of the second week of September.<ref name="Ames 1903">Ames O (1903) Natural hybrids in Spiranthes and Habenaria. Rhodora 5(59):261-264.<.ref>
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Weakley A. S.(2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 10 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedAmes 1903 - ↑ Nelson G (16 January 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/