Difference between revisions of "Symphyotrichum dumosum"
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''S. dumosum'' can be found in old fields, disturbed areas, pastures, woodlands, glades.<ref name="Weakley 2015"/> While widely found in the southern extent of its range, it is restricted to shorelines in the northern portion of its range.<ref name="Ladybird"/> | + | ''S. dumosum'' can be found in old fields, disturbed areas, pastures, woodlands, glades.<ref name="Weakley 2015"/> While widely found in the southern extent of its range, it is restricted to shorelines in the northern portion of its range.<ref name="Ladybird"/> In clayhill longleaf woodlands of the Florida panhandle, ''S. dumosum'' occurred in 93% of plots and had a mean coverage of 0.0109 m<sup>-2</sup>. Upper panhandle savannas had the same mean coverage but a higher frequency (100%) of ''S. dumosum'', while panhandle seepage savannas had a 100% frequency but 0.0035 m<sup>-2</sup> mean coverage.<ref name="Carr et al 2010">Carr SC, Robertson KM, Peet RK (2010) A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75(2):153-189.</ref> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 20:35, 12 January 2018
| Symphyotrichum dumosum | |
|---|---|
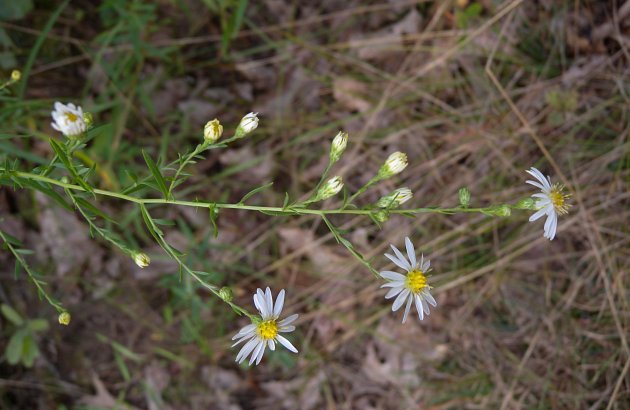

| |
| Photo by John Hilty hosted at IllinoisWildflowers.info | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Genus: | Symphyotrichum |
| Species: | S. dumosum |
| Binomial name | |
| Symphyotrichum dumosum (L.) G.L. Nesom | |
| |
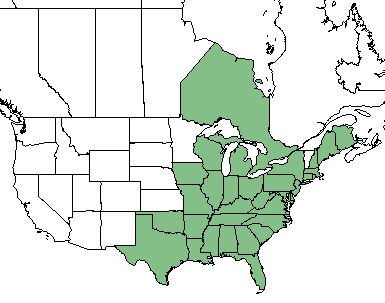
| Natural range of Symphyotrichum dumosum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): long-stalked aster;[1] rice button aster[2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Varieties: S. dumosum var. dumosum; S. dumosum var. gracilipes; S. dumosum var. pergracile; S. dumosum var. strictior; S. dumosum var. subulifolium[1][2]
Description
Symphyotrichum dumosum is a dioecious perennial forb/herb.[2] The plant is stiff with leafy branches possessing numerous flower heads. Flowers consist of white to pale lavender rays with a yellow to brown central disk.[3][4] Rays are 3-5 mm long, 0.9-1.2 mm wide, and numbered between 8-15 per flower. Its roots are creeping, branching, short, stout, and herbaceous.[4]
Distribution
S. dumosum occurs from New Brunswick and Maine, south to Florida, westward to Texas and Oklahoma, and northeast inland to Wisconsin, Michigan and Ontario Canada.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
S. dumosum can be found in old fields, disturbed areas, pastures, woodlands, glades.[1] While widely found in the southern extent of its range, it is restricted to shorelines in the northern portion of its range.[3] In clayhill longleaf woodlands of the Florida panhandle, S. dumosum occurred in 93% of plots and had a mean coverage of 0.0109 m-2. Upper panhandle savannas had the same mean coverage but a higher frequency (100%) of S. dumosum, while panhandle seepage savannas had a 100% frequency but 0.0035 m-2 mean coverage.[5]
Phenology
Flowering occurs in late August through October,[1] although reports of flowering exist for several months throughout the year.[6]
Fire ecology
In a 47 year unburned Florida area (NB66), Symphyotrichum dumosum occurred in 31% of the 1 m2 plots; initially, it did not occur.[7] This may suggest it is not very tolerant of fire.
Pollination
This species is known to attract several species of native bees.[3]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 12 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Plant database: Symphyotrichum dumosum. (12 January 2018) Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. URL: https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=SYDU2
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Chmielewski JG, Semple JC (2001) The biology of Canadian weeds. 113. Symphyotrichum lanceolatum (Willd.) Nesom [Aster lanceolatus Willd.] and S. lateriflorum (L.) Love & Love [Aster lateriflorus (L.) Britt.]. Canadian Journal of Plant Science 81:829-849.
- ↑ Carr SC, Robertson KM, Peet RK (2010) A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75(2):153-189.
- ↑ Nelson G (12 January 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/
- ↑ Clewell AF (2014) Forest development 44 years after fire exclusion in formerly annually burned oldfield pine woodland, Florida. Castanea 79(3):147-167.