Difference between revisions of "Drosera capillaris"
(→Ecology) |
(→Seed bank and germination) |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| − | Emergence of seedlings typically occurs between early winter and late spring.<ref name="Brewer 1999"/> | + | ''D. capillaris'' seeds are reported to be abundant in the seed banks of disturbed and undisturbed long-leaf pine habitat.<ref>Cohen S., Braham R., and Sanchez F. (2004). Seed bank viability in disturbed long-leaf pine sites. Restoration Ecology 12(4):503-515.</ref> Emergence of seedlings typically occurs between early winter and late spring.<ref name="Brewer 1999"/> |
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
Revision as of 16:28, 6 December 2017
| Drosera capillaris | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John B | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Nephenthales |
| Family: | Droseraceae |
| Genus: | Drosera |
| Species: | D. capillaris |
| Binomial name | |
| Drosera capillaris Poir. | |
| |
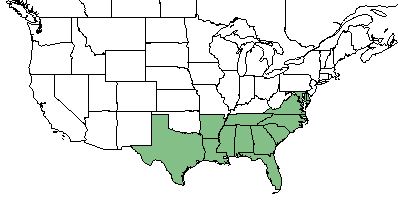
| Natural range of Drosera capillaris from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): pink sundew[1][2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym(s): D. rotundifolia var. capillaris, D. sessilifolia, D. brevifolia var. major, D. minor, D. tenella[3]
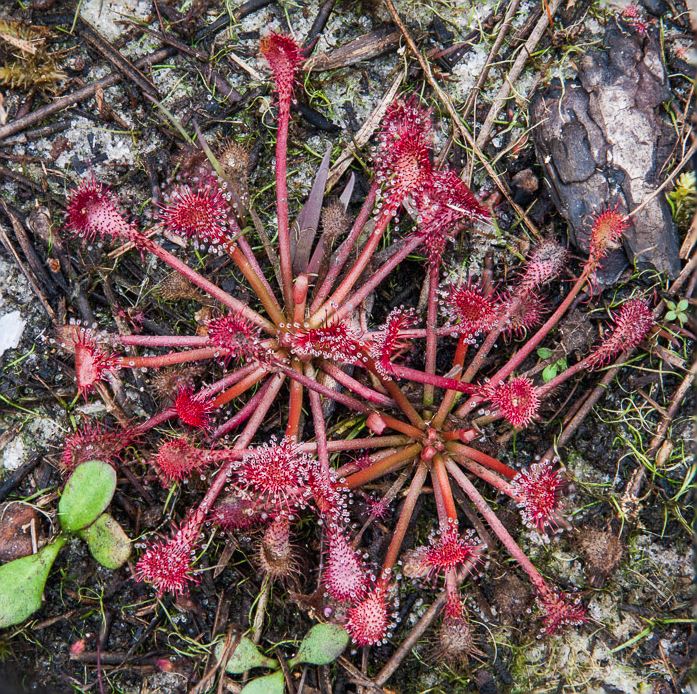
Description
D. capillaris is a dioecious perennial forb/herb.[2]
Distribution
Drosera capillaris is found in the southeastern United States ranging from Virginia, south to Florida, and westward to Texas. It can aslo be found in the West Indies, Mexico, and northern South America.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
It is an obligate wetland species[2] being found in pine savannas and other wet sandy or peaty soils.[1]
Phenology
The peak flowering period occurs in April and May and the probability of a rosette flowering is mostly dependent upon its size.[4]
Seed bank and germination
D. capillaris seeds are reported to be abundant in the seed banks of disturbed and undisturbed long-leaf pine habitat.[5] Emergence of seedlings typically occurs between early winter and late spring.[4]
Fire ecology
Fires facilitate the occurrence of D. capillaris by eliminating or reducing competition.[4] Seedling density also increased following burns, although the growth rates of seedlings remained unaffected.[4] Growth rates are instead dictated by level of competition.[4]
Use by animals
Sundews are generalists, preying upon a range of arthropods including those from Diptera (true flies), Collembola (Springtails), and Formicidae (ants). Diet overlap suggests competition occurs between D. capillaris and predatory insects including wolf spiders (Lycosidae).[6] Although a predator to many insects, the larvae of the plume moth (Trichoptilus parvulus) is known to consume D. capillaris by emerging from hiding at night and eating the stalked glands of the sundew.[7] Larger larvae may also consume parts of the leaf blade in addition to the gland.[7] Indirect effects by other organisms also influence the pink sundew. Crayfish mound excavations bury individuals of D. capillaris as they flatten out causes mortality, especially in smaller individuals.[4]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Weakley A. S.(2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 30 November 2017). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Wunderlin R. P., Hansen B. F., Franck A. R. and Essig. F. B. (2017). Atlas of Florida Plants (http://florida.plantatlas.usf.edu/).[S. M. Landry and K. N. Campbell (application development), USF Water Institute.] Institute for Systematic Botany, University of South Florida, Tampa.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Brewer J. S. (1999). Effects of fire, competition and soil disturbances on regeneration of a carnivorous plant (Drosera capillaris). American Midland Naturalist 141:28-42.
- ↑ Cohen S., Braham R., and Sanchez F. (2004). Seed bank viability in disturbed long-leaf pine sites. Restoration Ecology 12(4):503-515.
- ↑ Jennings D. E., Krupa J. J., Raffel T. R., and Rohr J. R. (2010). Evidence for competition between carnivorous plants and spiders. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, doi:10.1098/rspb.2010.0465
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Eisner T. and Shepherd J. (1965). Caterpillar feeding on a sundew plant. Science 150(3703):1608-1609