Difference between revisions of "Oxalis corniculata"
Rwagner914 (talk | contribs) (→Seed bank and germination) |
Rwagner914 (talk | contribs) (→Seed bank and germination) |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| − | Commonly found in seed banks of disturbed areas. <ref> Maliakal, S. K., E. S. Menges, et al. (2000). "Community composition and regeneration of Lake Wales Ridge wiregrass flatwoods in relation to time-since-rire " The Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 127: 125-138 </ref> Forms a persistent soil seed bank. <ref> Navarra, J. J., N. Kohfeldt, et al. (2011). "Seed bank changes with time since fire in Florida rosemary scrub." Fire Ecology 7(2). </ref> Found in the seed bank of a ectone of longleaf pine and scrub communities in the western panhandle | + | Commonly found in seed banks of disturbed areas. <ref> Maliakal, S. K., E. S. Menges, et al. (2000). "Community composition and regeneration of Lake Wales Ridge wiregrass flatwoods in relation to time-since-rire " The Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 127: 125-138 </ref> Forms a persistent soil seed bank. <ref> Navarra, J. J., N. Kohfeldt, et al. (2011). "Seed bank changes with time since fire in Florida rosemary scrub." Fire Ecology 7(2). </ref> Found in the seed bank of a ectone region of longleaf pine and scrub communities in the western panhandle of Florida. <ref>Ruth, A. D., et al. 2008. Seed bank dynamics of sand pine scrub and longleaf pine flatwoods of the Gulf Coastal Plain (Florida). Ecological Restoration 26:19-21. </ref> |
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
Revision as of 14:16, 7 June 2017
| Oxalis corniculata | |
|---|---|
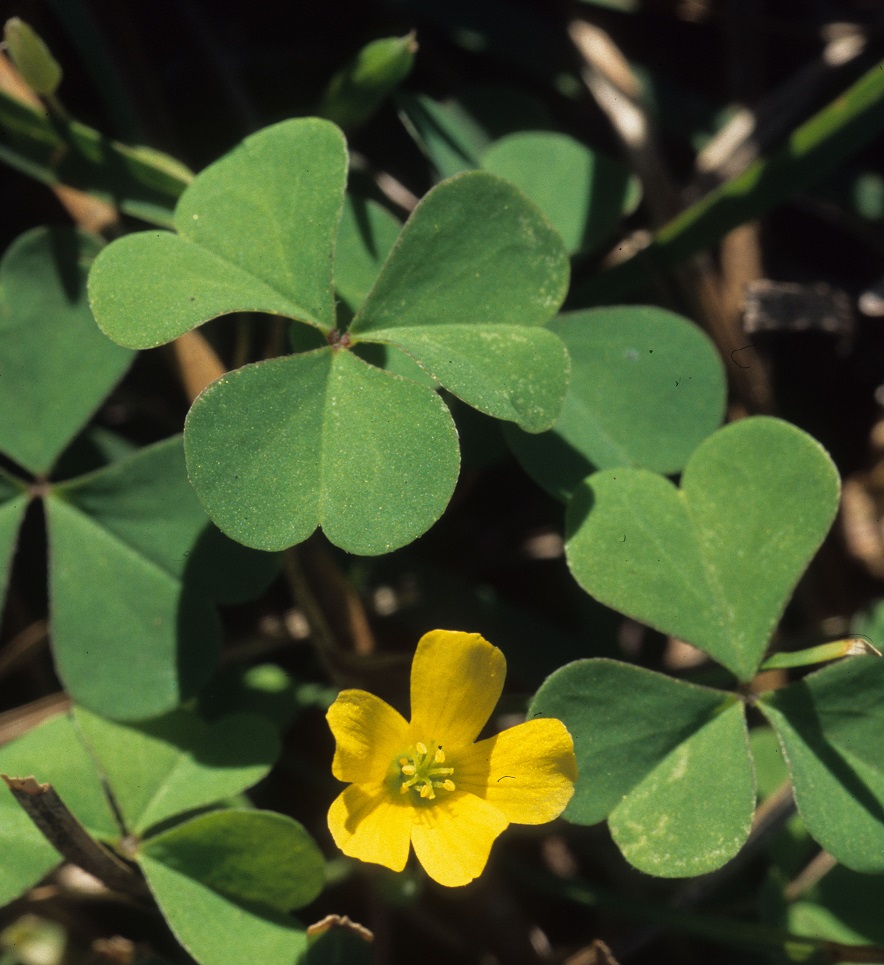

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Geraniales |
| Family: | Oxalidaceae |
| Genus: | Oxalis |
| Species: | O. corniculata |
| Binomial name | |
| Oxalis corniculata L. | |
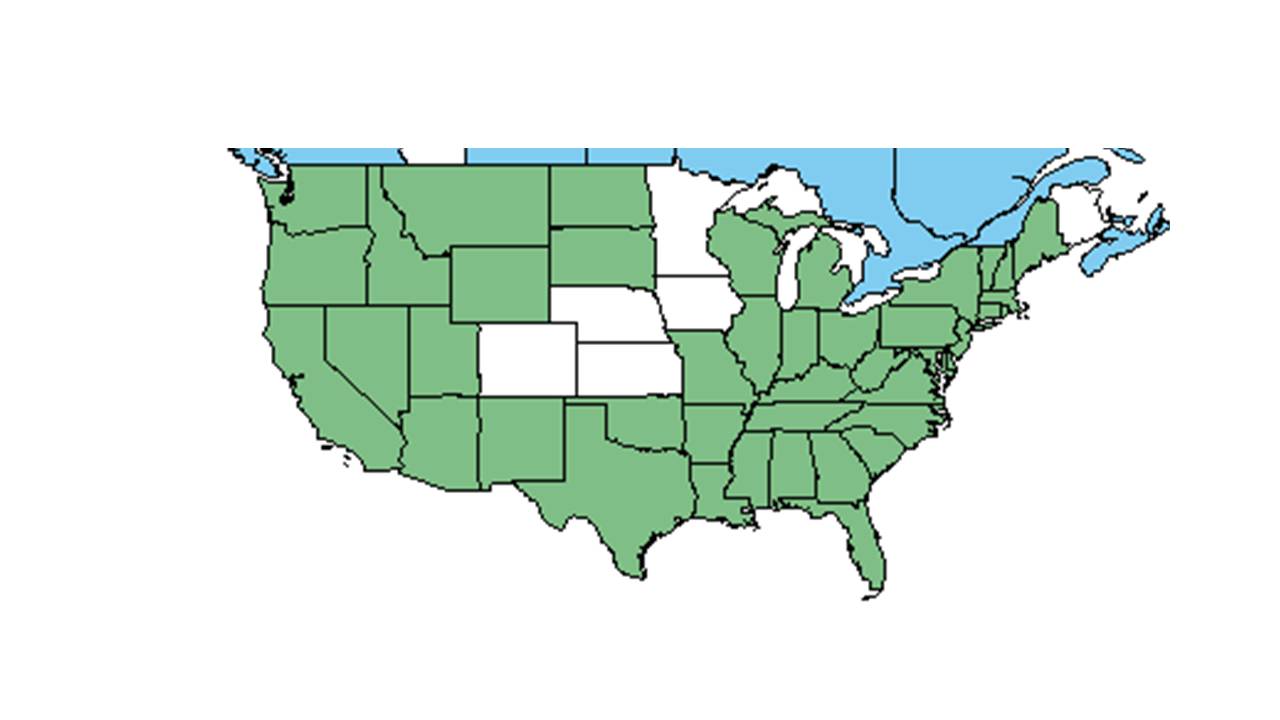
| |
| Natural range of Oxalis corniculata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Creeping woodsorrel; Creeping lady's-sorrel.
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Oxalis repens Thunberg; Xanthoxalis corniculata (Linnaeus) Small; Xanthoxalis langloisii Small; O. corniculata var. corniculata; O. corniculata var. atropurpurea Planchon
Description
"Caulescent or acaulescent, herbaceous perennials with rhizomes or bulbs, or annuls with fibrous roots. Leaves alternate, ternately compound, leaflets 3, obcordate; stipules very small or obsolete. Flowers in pedunculate umbels or cymes, or solitary. Sepals 5; petals 5 separate or adnate to each other just above the base; stamens 1-, of 2 lengths. Pistil with 5 carpels. Capsule longitudinally dehiscent. Seeds red, prominently reticulate, pitted or smooth, each completely enclosed by an elastically dehiscent, transparent aril that aids in its distribution. Heterostyly is typical of plants in this genus. " [1]
"Caulescent, stoloniferous herb with fibrous roots. Stolons completely prostrate, usually bearing roots at each node, and usually flowering from the axils of leaves from rooted nodes. Stems, petioles, and peduncles, slightly pilose. Leaflets green, reddish or purplish, ca. 2 cm long or often considerable less. Peduncles mostly shorter than the subtending petioles, mostly 1-or 2-flowered. Sepals not gland-tipped; petals yellow, 5-7 mm long. Capsule prismatic, 0.8-1 cm long, sparsely pubescent. Seeds reticulate." [1]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
O. corniculata occurs in moist to dry sandy or loamy soils. [2] It can be found in lowland woodlands, as well as disturbed sites, including along trails, mowed lawns, and near man-made ponds. [2]
Phenology
Flowering has been observed from December to June, August, and October with peak inflorescecne in March and April.[2][3]
Seed bank and germination
Commonly found in seed banks of disturbed areas. [4] Forms a persistent soil seed bank. [5] Found in the seed bank of a ectone region of longleaf pine and scrub communities in the western panhandle of Florida. [6]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 646-8. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Bian Tan, J. M. Kane, Robert K. Godfrey, and Andre F. Clewell. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Franklin, Leon, and Washington. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Maliakal, S. K., E. S. Menges, et al. (2000). "Community composition and regeneration of Lake Wales Ridge wiregrass flatwoods in relation to time-since-rire " The Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 127: 125-138
- ↑ Navarra, J. J., N. Kohfeldt, et al. (2011). "Seed bank changes with time since fire in Florida rosemary scrub." Fire Ecology 7(2).
- ↑ Ruth, A. D., et al. 2008. Seed bank dynamics of sand pine scrub and longleaf pine flatwoods of the Gulf Coastal Plain (Florida). Ecological Restoration 26:19-21.