Difference between revisions of "Tragia urens"
(→Conservation and Management) |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
<!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | <!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation and management== |
| + | |||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
Revision as of 18:45, 11 July 2016
| Tragia urens | |
|---|---|

| |
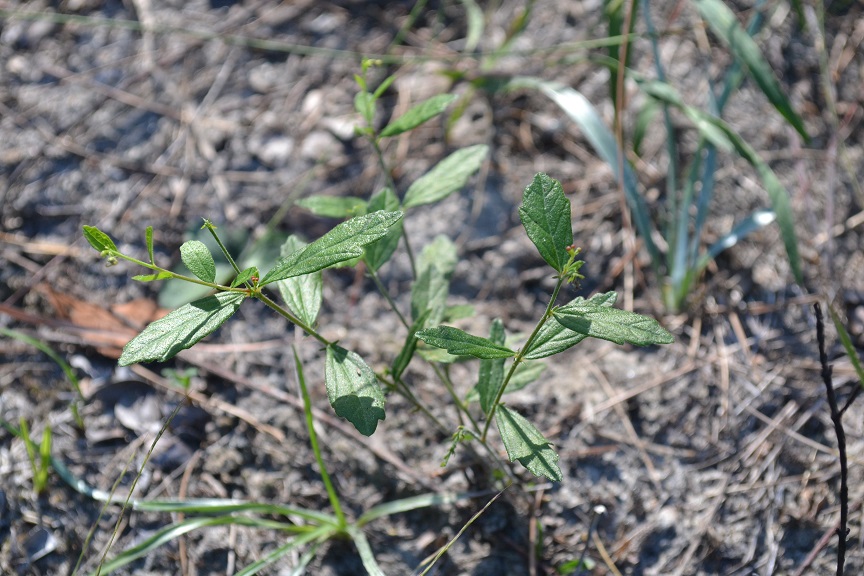
| Photo by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Euphorbiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Tragia |
| Species: | T. urens |
| Binomial name | |
| Tragia urens L. | |
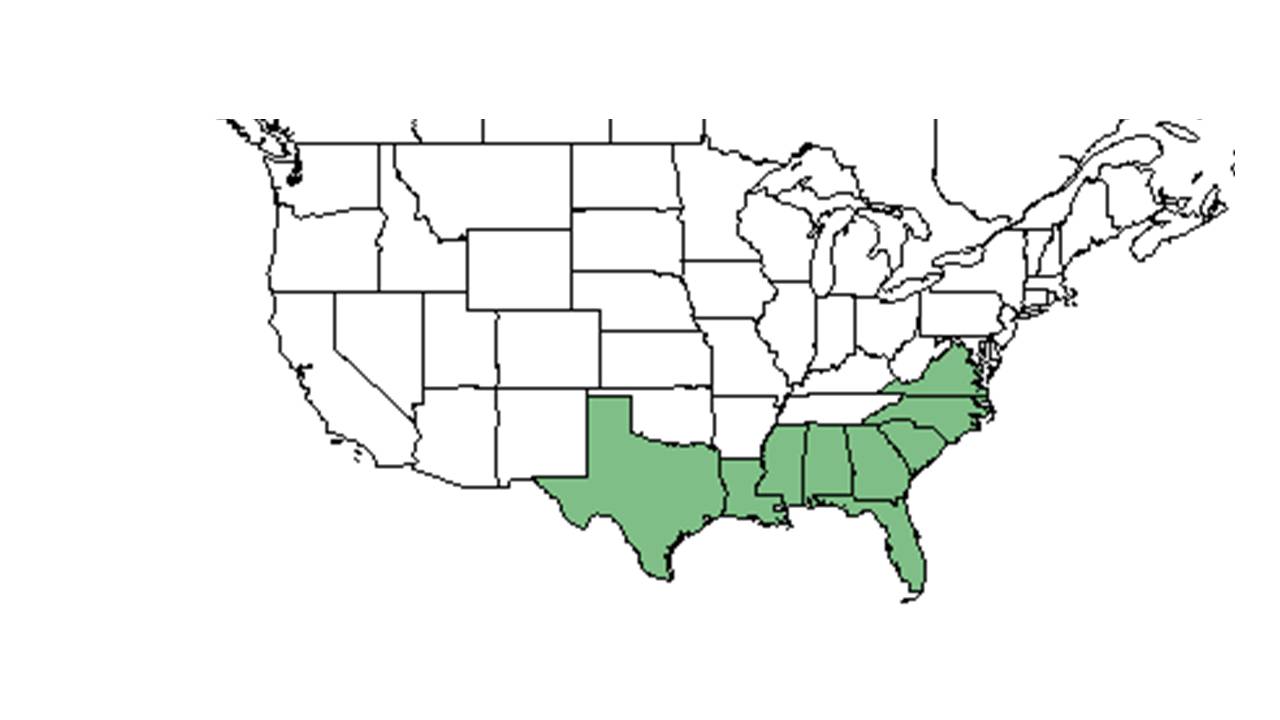
| |
| Natural range of Tragia urens from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Wavyleaf noseburn
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Tragia linearifolia Elliott
Description
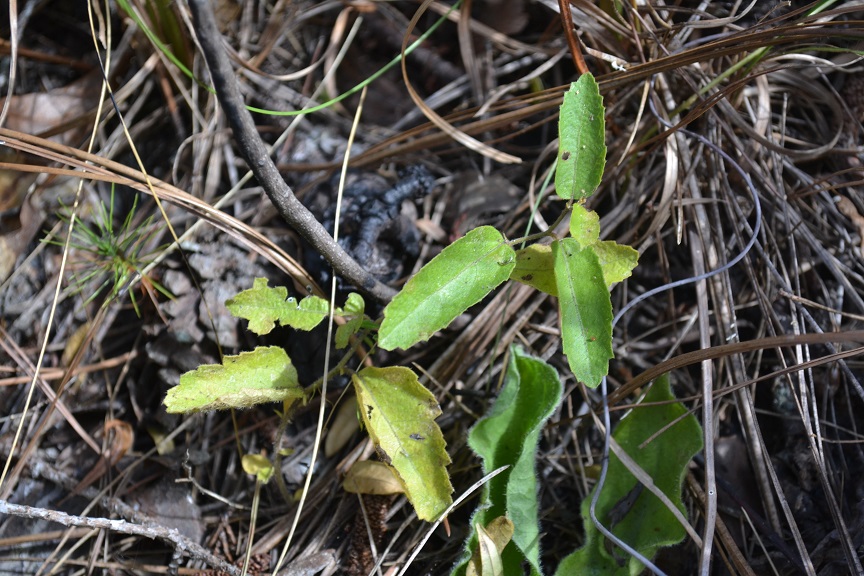
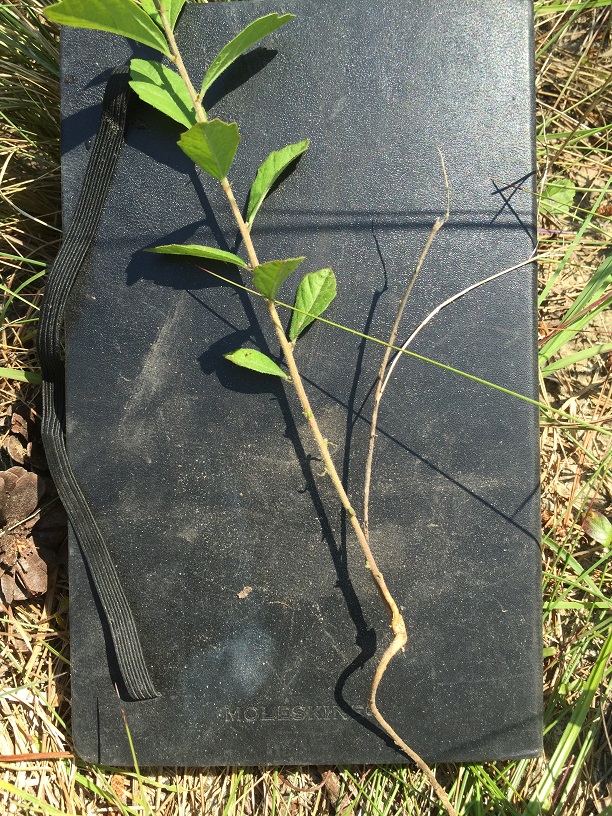
"Monoecious, perennial, rhizomatous herbs, armed with stinging trichomes. Leaves alternate, stipulate. Racemes axillary or terminal, or both, lowest 1 or 2 flowers pistillate, the upper staminate. Flowers greenish or purplish; petals absent; staminate flowers with 3-5 sepals and 2 or 3 stamens; pistillate with 3-8 sepals and 3 stigmas. Capsule 3-locular, 4-5 mm long, 7-8 mm in diam., each locule 1-seeded. Seeds light brown with darker mottling, or entirely dark brown, ovoid, 3-3.5 mm long; caruncle obsolete." [1]
"Plant 2-5 dm tall, freely branched. Leaves narrowly elliptic to oblanceolate or linear, 2-10 cm long, 0.2-2 cm wide, irregularly serrate, undulate or entire, base cuneate to attenuate; petioles 1-3 mm long. Racemes short or elongate, 0.3-12 cm long." [1]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, T. urens has been found in sand of open woodlands, pine uplands, fallow fields, annually burned pineland, sandhills, sand pine scrub, longleaf pine/wiregrass communities, and open pine savannas (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include longleaf pine, sand pine, and wiregrass (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
It has been observed flowering in April and May and fruiting May through September (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by explosion mechanisms or by ants. [2]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R. A. Norris, Robert K. Godfrey, Andre F. Clewell, Chris Cooksey, M. Davis, J. M. Kane, R. Komarek, Lisa Keppner, Cecil R Slaughter, Annie Schmidt. States and Counties: Florida: Duval, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Osceola, Wakulla, Washington. Georgia: Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.

