Difference between revisions of "Stylisma humistrata"
(→Distribution) |
|||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| − | It is found in the Coastal Plains of southwestern Georgia (Baker County) | + | It is found in the Coastal Plains of southwestern Georgia (Baker County). <ref name=kay> Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, R. J. Mitchell and E. B. Moser. 2004. Ground cover recovery patterns and life-history traits: implications for restoration obstacles and opportunities in a species-rich savanna. Journal of Ecology 92:409-421.</ref> |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
Revision as of 16:22, 12 April 2016
| Stylisma humistrata | |
|---|---|
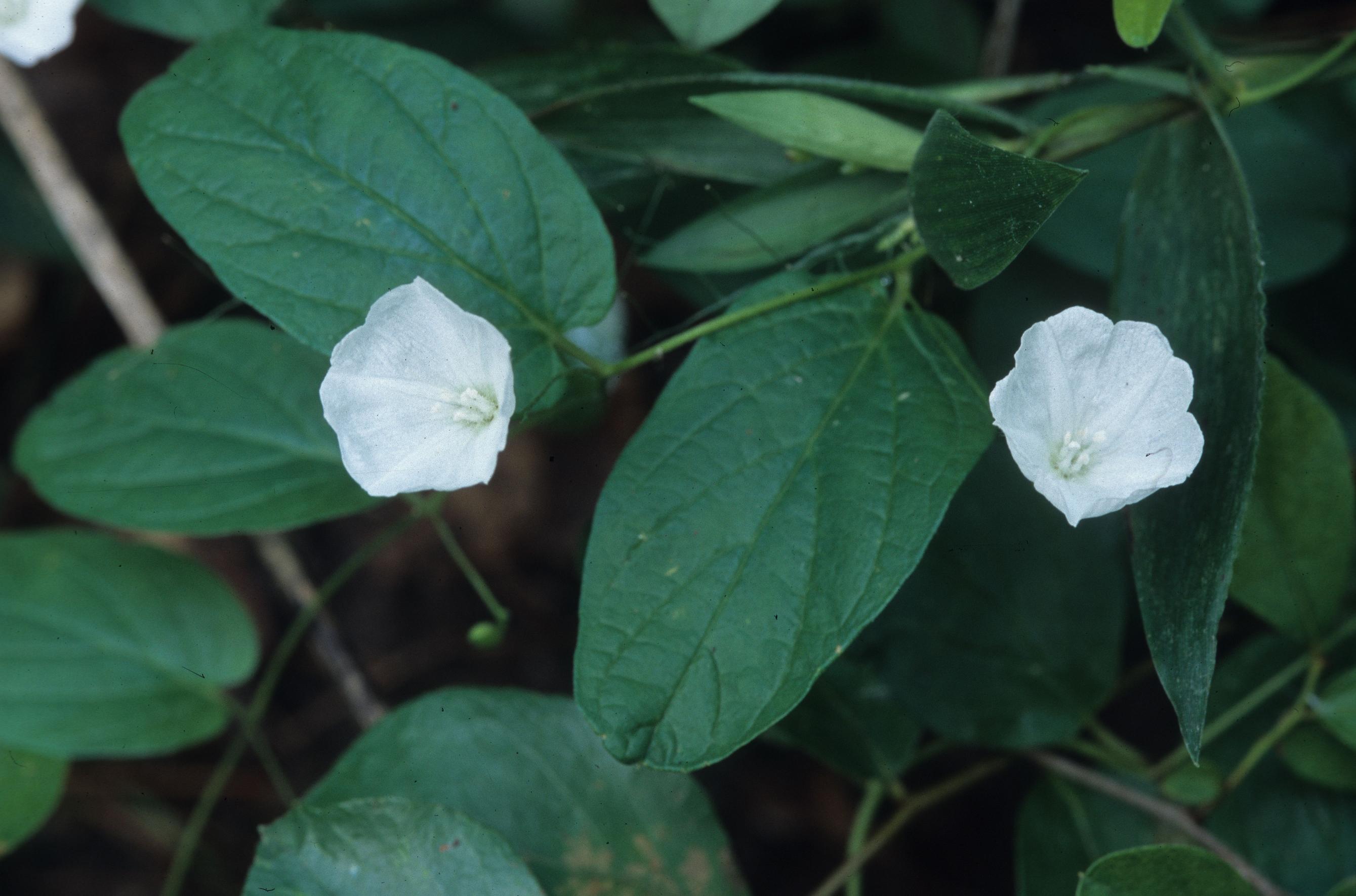

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Solanales |
| Family: | Convolvulaceae |
| Genus: | Stylisma |
| Species: | S. humistrata |
| Binomial name | |
| Stylisma humistrata (Walter) Chapm. | |
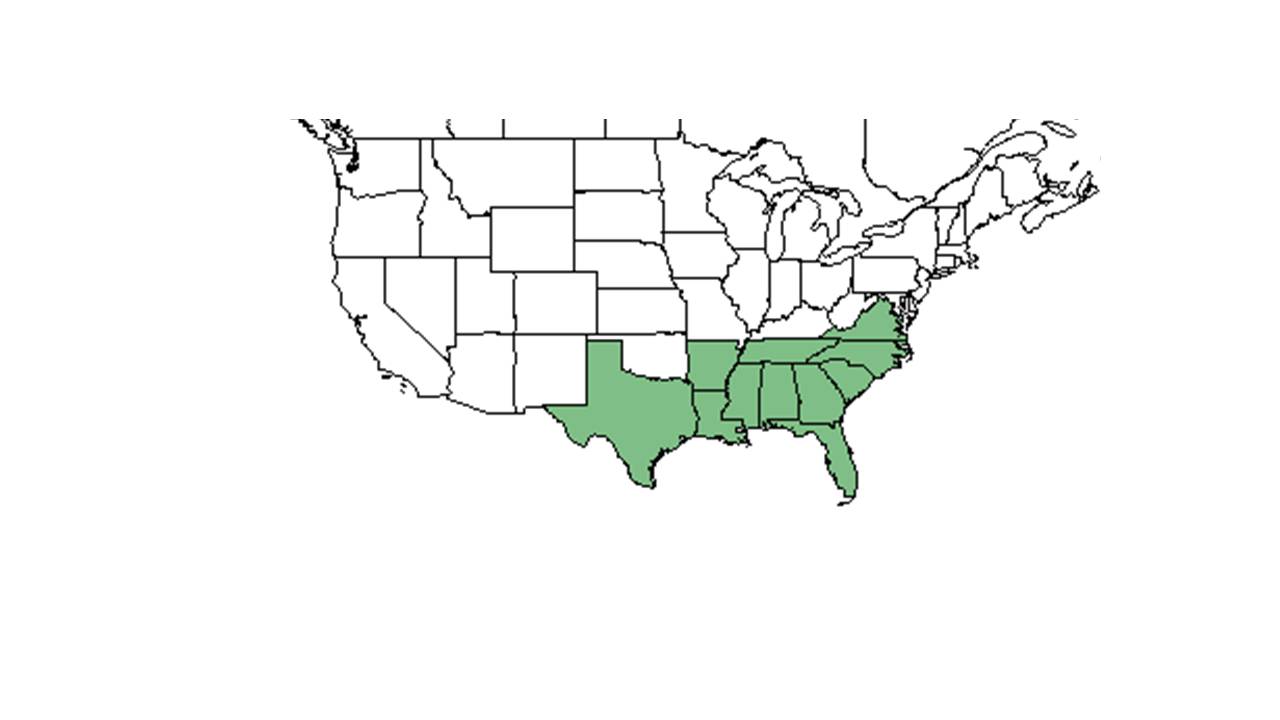
| |
| Natural range of Stylisma humistrata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: southern dawnflower
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
In Radford (1964) this species was recognized as a synonym under Bonamia humistrata which is where this description originated from. "Prostrate or spreading, herbaceous perennial vines, from fascicled or single, slender linear roots. Stems several to many, 0.5-2 m long, the basal portions appearing rhizomatous, older plants often forming large mats or clumps. Leaves entire. Corolla white or pink, campanulate to funnelform, 8-24 mm long; sepals still or leathery, 5-10 mm long, obtuse or acute; stigmas globose or peltate, styles 2, united at base or almost to summit. Capsule chartaceous, 2-locular, 4-seeded, 4-8 mm long, ½ as wide." - Radford et al 1964
"Leaves elliptic to elliptic-lanceolate, 2.5-5 cm long, 1.2-2.8 cm wide, reduced, upward, mucronate, subcordate, sparsely pubescent to pilose, the trichomes stellate or simple. Flowers 1-3 (rarely more) on peduncles normally 1-2X the length of the subtending leaf, bractlets inconspicuous; sepals glabrous; corolla white, usually 15-20 mm long; filaments pubescent to pilose; basal third or less of styles united." - Radford et al 1964
Distribution
It is found in the Coastal Plains of southwestern Georgia (Baker County). [1]
Ecology
Habitat
Stylisma humistrata can be found in longleaf pine-oak woodlands, longleaf pine-wiregrass-scrub oak ridges, annually burned pinelands, mesic woodlands, floodplains, hardwood hammocks (FSU Herbarium), and subxeric and xeric areas in longleaf pine-oak communities.[2] It can also be found along roadsides, edges of cornfields, recently logged oak-pine slopes, and old fields (FSU Herbarium). Soil types include loamy sand, loam, and red sandy clay (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include Spigelia gentianoides and Quercus incana (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Flowers and fruits May through October (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by gravity. [3]
Seed bank and germination
S. humistrata exhibits physical seed dormancy and does not require light for germination (Jayasuriya 2008).
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Carter, R. E., M. D. MacKenzie, D. H. Gjerstad and D. Jones. 2004. Species composition of fire disturbed ecological land units in the Southern Loam Hills of south Alabama. Southeastern Naturalist 3:297-308.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R. A. Norris, Robert K. Godfrey, R. Komarek, J. M. Kane, Jean Wooten, R. R. Smith, T. Myint, C. Jackson, Gary R. Knight, Robert Kral, Mabel Kral, S. B. Jones, Carleen Jones, Gwynn W. Ramsey, H. L. Stripling, T.E. Smith, R. D. Whetstone, James G. Teer, John W. Thieret, Sidney McDaniel, C. Ritchie Bell, Roomie Wilson, L. H. Shinners, R. L. Wilbur, Delzie Demaree, Harry E. Ahles, J. A. Duke, Lisa Keppner, Ed Keppner. States and Counties: Alabama: Clarke, Escambia, Geneva, Houston, Sumter. Arkansas: Bradley. Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Gadsden, Jackson, Lafayette, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Okaloosa, Washington. Georgia: Baker, Early, Grady, Lowndes, Thomas. Louisiana: Bienville, Tangipahoa, Union, Washington. Mississippi: Forrest, Jones, Wayne, Winston. North Carolina: Bladen, New Hanover, Narthampton, Pamlico. Texas: Woods. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
Jayasuriya, K.M.G. Gehan, Jerry M. Baskin and Carol C. Baskin (2008). Dormancy, germination requirements and storage behaviour of seeds of Convolvulaceae (Solanales) and evolutionary considerations. Seed Science Research 18: 223-237
Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, R. J. Mitchell and E. B. Moser. 2004. Ground cover recovery patterns and life-history traits: implications for restoration obstacles and opportunities in a species-rich savanna. Journal of Ecology 92:409-421.
Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 863. Print.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, R. J. Mitchell and E. B. Moser. 2004. Ground cover recovery patterns and life-history traits: implications for restoration obstacles and opportunities in a species-rich savanna. Journal of Ecology 92:409-421.
- ↑ Carter, R. E., M. D. MacKenzie, D. H. Gjerstad and D. Jones. 2004. Species composition of fire disturbed ecological land units in the Southern Loam Hills of south Alabama. Southeastern Naturalist 3:297-308.
- ↑ Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015.