Difference between revisions of "Ximenia americana"
(→Cultivation and restoration) |
|||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
| − | ''X. americana'' is a medicinal plant known for its antioxidant properties. Traditional medicinal practice for ''X. americana'' was used to treat malaria, fever, leprotic ulcers, and skin infections. In northern Nigeria, ''X. americana'' has been used to treat fever, stiffness, onchocerciasis, sore throat, asthma, and bad headaches. The roots are used to treat abdominal pains, dysentery, inflamed joints, and mouth ulcers. The leaves of ''X. americana'' contain cyanogenic glycosides, flavonoids and tannins, which are also common in many other plants. <ref name=Maikai2009”> Maikai, V.A., Kobo, P.I., and Maikai, B.V.O. (2010). “Antioxidant properties of Ximenia americana.” African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 9(45): 7744-7746.</ref> A study conducted by Kibuge (2015) considered ''X. americana'' as a biofuel and concluded that X. americana ultimately qualifies as a potential biofuel. Also ''X. americana''’s seed oils were mixed with kerosene (a fossil fuel) to see if it reduced the cost of biofuel. Overall, the study found out that kerosene is still the best fuel to burn for energy and for the use inside a home. The study recommends to further research the ''X. americana'' seed oil to determine the burning rate, flame height, and smoke gases for the fuel to be used indoors for lighting and cooking. <ref name="Kibuge2015"> Kibuge, R.M., S.T. Kariuki, and M.R. Njue (2015). “Influence of fuel properties on the burning characterisitcs of sour plum (''Ximenia americana'' L.) seed oil compared with Jatropha curcas L. seed oil.” Renewable Energy 78: 128-131. </ref> Some claim that parts of this plant are edible however, it is advised that you do your own research before consuming any part of this plant. The fruit can be eaten raw or cooked. The leaves can be eaten as well, when well-boiled and eaten, in small amounts. Also, the oil from the seeds can be used for cooking. <ref name="eattheweeds"> [[http://www.eattheweeds.com/ximenia-americana-known-by-many-names-2/]]. Eat the Weeds. Accessed: March 17, 2016. </ref> According to Urso, harvesting ''Ximenia americana'' fruits do not seem to threatened the species (in the near future) since it is widespread in the area. (study area is Namibe) <ref name="Urso2013"/> | + | ''X. americana'' is a medicinal plant known for its antioxidant properties. Traditional medicinal practice for ''X. americana'' was used to treat malaria, fever, leprotic ulcers, and skin infections. In northern Nigeria, ''X. americana'' has been used to treat fever, stiffness, onchocerciasis, sore throat, asthma, and bad headaches. The roots are used to treat abdominal pains, dysentery, inflamed joints, and mouth ulcers. The leaves of ''X. americana'' contain cyanogenic glycosides, flavonoids and tannins, which are also common in many other plants. <ref name=Maikai2009”> Maikai, V.A., Kobo, P.I., and Maikai, B.V.O. (2010). “Antioxidant properties of Ximenia americana.” African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 9(45): 7744-7746.</ref> A study conducted by Kibuge (2015) considered ''X. americana'' as a biofuel and concluded that X. americana ultimately qualifies as a potential biofuel. Also ''X. americana''’s seed oils were mixed with kerosene (a fossil fuel) to see if it reduced the cost of biofuel. Overall, the study found out that kerosene is still the best fuel to burn for energy and for the use inside a home. The study recommends to further research the ''X. americana'' seed oil to determine the burning rate, flame height, and smoke gases for the fuel to be used indoors for lighting and cooking. <ref name="Kibuge2015"> Kibuge, R.M., S.T. Kariuki, and M.R. Njue (2015). “Influence of fuel properties on the burning characterisitcs of sour plum (''Ximenia americana'' L.) seed oil compared with Jatropha curcas L. seed oil.” Renewable Energy 78: 128-131. </ref> Some claim that parts of this plant are edible however, it is advised that you do your own research before consuming any part of this plant. The fruit can be eaten raw or cooked. The leaves can be eaten as well, when well-boiled and eaten, in small amounts. Also, the oil from the seeds can be used for cooking. <ref name="eattheweeds"> [[http://www.eattheweeds.com/ximenia-americana-known-by-many-names-2/]]. Eat the Weeds. Accessed: March 17, 2016. </ref> According to Urso, harvesting ''Ximenia americana'' fruits do not seem to threatened the species (in the near future) since it is widespread in the area. (study area is Namibe). <ref name="Urso2013"/> |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
Revision as of 17:38, 22 March 2016
| Ximenia americana | |
|---|---|
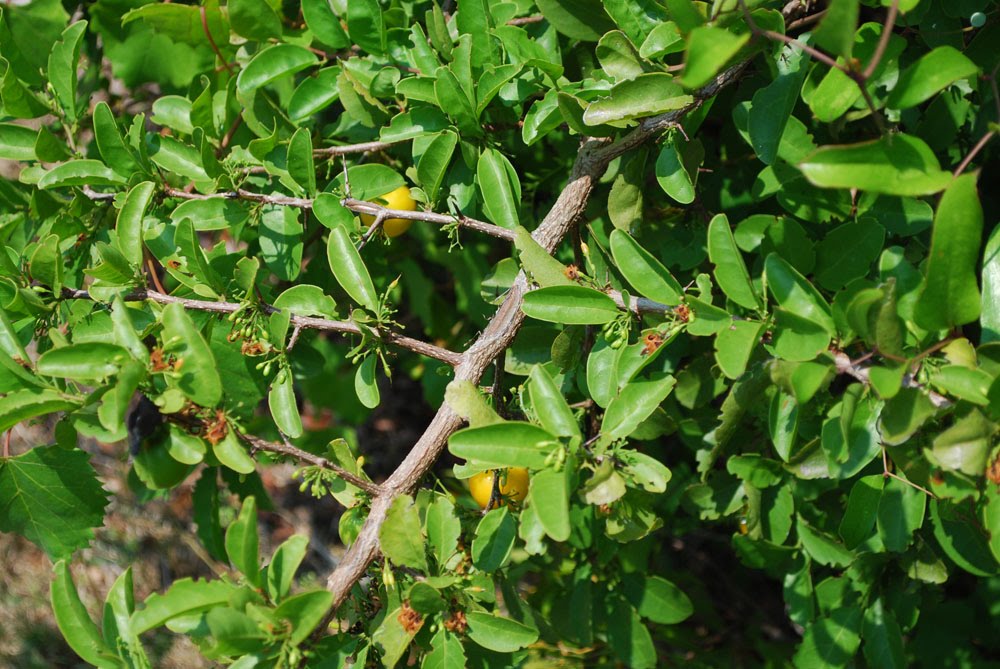

| |
| Photo by Wayne Matchett, SpaceCoastWildflowers.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Santalales |
| Family: | Olacaceae |
| Genus: | Ximenia |
| Species: | X. americana |
| Binomial name | |
| Ximenia americana L. | |
| |
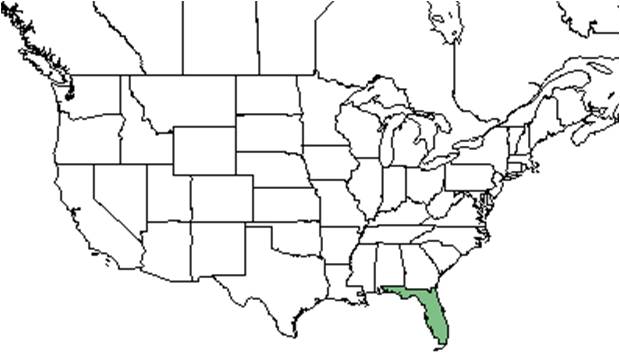
| Natural range of Ximenia americana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: tallow wood, yellow plum
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
Ximenia americana is a perennial, deciduous, shrub growing up to 10-25 feet in height, is salt tolerant, and thrives in a variety of soil types, including sand, loam, and lime rock. [1]
Distribution
In the United States, X. americana occurs in Florida, as well as the U.S. territories, Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands. It is also found throughout the tropical and subtropical countries including Central and South America, Africa, India, and Asia. The entire distribution is mentioned because this plant is used widely for its medicinal and cosmetic uses and has yet to become a threatened species. [2]
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, X. americana has occurred in coastal scrubs, palmetto-oak hammocks, longleaf pine-hickory-oak woods, sand pine scrubs, limestone in palm-cedar hammocks, live oak hammocks, longleaf pine-wiregrass communities, and coastal marine hammocks (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include Liatris laevigata, L. ohlingerae, Tillandsia utriculata, Pinus palustris, Serenoa repens, Quercus geminata, Q. myritfolia, Q. chapmanii, Stillingia, Aristida, Certiola, Carya floridana, and Pinus clausa (FSU Herbarium). In the scrub, xeric hammocks, and swamp habitats, the soil type in which this species thrives incldues sand, loam, lime rock, and organic material. [1]
Phenology
Flowers March through November and fruits January, June through August (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Ximenia americana is one of the most common woody shrub, resprouting species and is included in the top 5 of the fastest growing species post-fire in the Florida scrub habitat in Highlands County, Florida. [3]
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Ximenia americana at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Mellisodes communis
Halictidae: Agapostemon splendens, Augochloropsis sumptuosa, Lasioglossum placidensis
Megachilidae: Coelioxys germana, Megachile mendica
Sphecidae: Bicyrtes quadrifasciata, Eremnophila aureonotata, Isodontia exornata
Vespidae: Mischocyttarus cubensis, Pachodynerus erynnis, Parancistrocerus perennis anacardivora, Zethus spinipes
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
X. americana is a medicinal plant known for its antioxidant properties. Traditional medicinal practice for X. americana was used to treat malaria, fever, leprotic ulcers, and skin infections. In northern Nigeria, X. americana has been used to treat fever, stiffness, onchocerciasis, sore throat, asthma, and bad headaches. The roots are used to treat abdominal pains, dysentery, inflamed joints, and mouth ulcers. The leaves of X. americana contain cyanogenic glycosides, flavonoids and tannins, which are also common in many other plants. [4] A study conducted by Kibuge (2015) considered X. americana as a biofuel and concluded that X. americana ultimately qualifies as a potential biofuel. Also X. americana’s seed oils were mixed with kerosene (a fossil fuel) to see if it reduced the cost of biofuel. Overall, the study found out that kerosene is still the best fuel to burn for energy and for the use inside a home. The study recommends to further research the X. americana seed oil to determine the burning rate, flame height, and smoke gases for the fuel to be used indoors for lighting and cooking. [5] Some claim that parts of this plant are edible however, it is advised that you do your own research before consuming any part of this plant. The fruit can be eaten raw or cooked. The leaves can be eaten as well, when well-boiled and eaten, in small amounts. Also, the oil from the seeds can be used for cooking. [6] According to Urso, harvesting Ximenia americana fruits do not seem to threatened the species (in the near future) since it is widespread in the area. (study area is Namibe). [2]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Jane Brockmann, Robert K. Godfrey, Robert Kral, O. Lakela, Robert J. Lemiare, S.W. Leonard, Sidney McDaniel, T. Myint, Mary E. Nolan, Jackie Patman, James D. Ray Jr., Cecil R. Slaughter, Earl Smith Jr., R. Smith, D.B. Ward. States and Counties: Florida: Brevard, Collier, Flagler, Highlands, Indian River, Levy, Monroe, Osceola, Palm Beach, Pinellas, Sarasota. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 [[1]]. FNPS. Accessed: March 22, 2016.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Urso, Valeria, Maria Adele Signorini, and Piero Bruschhi (2013). “Survey of the ethnobotanical uses of Ximenia americana L. (mumpeke) among rural communities in South Angola”. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research Vol. 7 (1): 7-18.
- ↑ Maguire, A.J., E.S. Menges (2011). "Post-fire growth strategies of resprouting Florida scrub vegetation". Fire Ecology 7(3):12-25
- ↑ Maikai, V.A., Kobo, P.I., and Maikai, B.V.O. (2010). “Antioxidant properties of Ximenia americana.” African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 9(45): 7744-7746.
- ↑ Kibuge, R.M., S.T. Kariuki, and M.R. Njue (2015). “Influence of fuel properties on the burning characterisitcs of sour plum (Ximenia americana L.) seed oil compared with Jatropha curcas L. seed oil.” Renewable Energy 78: 128-131.
- ↑ [[2]]. Eat the Weeds. Accessed: March 17, 2016.