Difference between revisions of "Lechea sessiliflora"
(→Taxonomic notes) |
(→Seed dispersal) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| − | + | According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by gravity. <ref name="KK"> Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015. </ref> | |
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
Revision as of 19:36, 12 April 2016
| Lechea sessiliflora | |
|---|---|
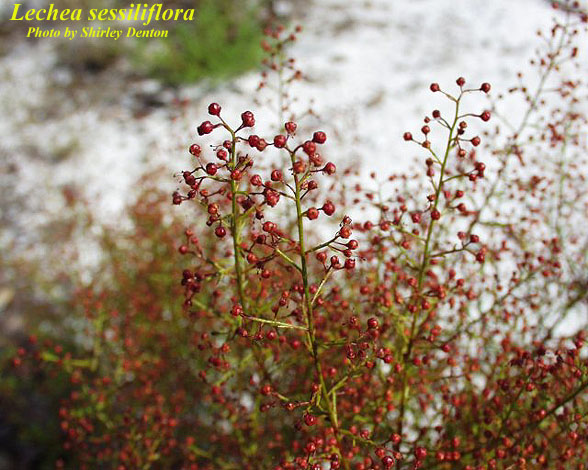

| |
| Photo by Shirley Denton (Copyrighted, use by photographer’s permission only), Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Cistaceae |
| Genus: | Lechea |
| Species: | L. sessiliflora |
| Binomial name | |
| Lechea sessiliflora Raf. | |
| |
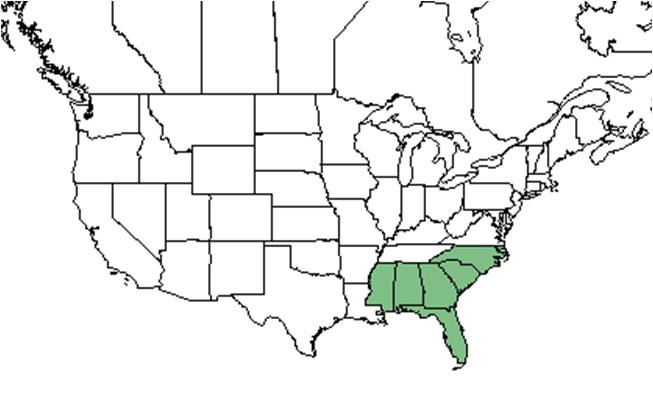
| Natural range of Lechea sessiliflora from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: pineland pinweed
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Lechea patula Leggett; L. exserta Small; L. patula; L. prismatica Small
Lechea species can be hard to distinguish from each other due to microscopic differences, this often leads to problems with correct nomenclature (Barringer 2004).
Description
L. sessiliflora is a herbaceous perennial distinguished from other Lechea species by having a conspicuously exserted, ellipsoid capsule that is capped by a reddish-brown fimbriate stigma [1]. The species in Lechea have a distinctive calyx with the two outer sepals very different in size and shape from the three inner sepals (Barringer 2004). It is often mistaken for L. deckertii because both species have prominently exserted straw-colored capsules with persistent stigmas. The easiest way to distinguish these two species is by the length of the outer slender sepals and the shape of the capsules. L. sessiliflora has ellipsoid capsules and the narrow outer sepals are almost equaling or a little longer than the broad inner sepals[1].
Ecology
Habitat
Habitats include longleaf pine-wiregrass communities, pine-scrub oak barrens, coastal scrubs, and dry pine flatwoods. It has been found in disturbed areas such as cutover pine communities, sandy roadsides, former live oak plantations and along railroad tracks. Associated species include Dalea, Eupatorium, Liatris, Pityopsis, Symphotrichum, and Schizachyrium. Soil types include loamy sand and sand (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
L. sessiliflora has been observed flowering August through October and fruiting in October (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by gravity. [2]
Seed bank and germination
Kirkman et al. (2004) found the vulnerability ratio for soil disturbance to be 3/3(reference sites/recovery sites).
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Lechea sessiliflora at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Halictidae: Lasioglossum placidensis
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Barringer, K. (2004). "New Jersey Pinweeds (Lechea, Cistaceae)." The Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 131(3): 261-276.
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: C. Anderson, M. Davis, Robert K. Godfrey, R. Komarek, H. Roth. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Jackson, Leon, Suwannee, Taylor, Wakulla, Walton. Georgia: Grady. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, et al. (2004). "Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna." Journal of Ecology 92(3): 409-421.