Difference between revisions of "Ilex opaca"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| + | Holly cavities provide nesting habitat for the red-cockaded woodpecker<ref name="fed">[[http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/plants/tree/ileopa/all.html]]Accessed: January 6, 2016</ref>. Groves provide shelter to red-eyed towhee, bluebirds, cardinals, white throated sparrow, and robins (Petrides 1942). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The spines on the leafs are used as a defense against herbivory (Ehrlich and Raven 1967). | ||
| + | |||
===Diseases and parasites=== | ===Diseases and parasites=== | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
Revision as of 20:38, 7 January 2016
| Ilex opaca | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Celastrales |
| Family: | Aquifoliaceae |
| Genus: | Ilex |
| Species: | I. opaca |
| Binomial name | |
| Ilex opaca Aiton | |
| |
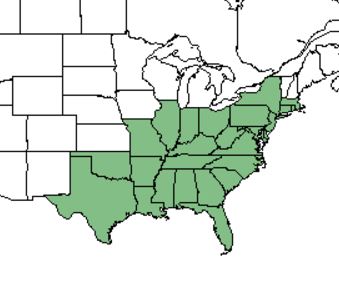
| Natural range of Ilex opaca from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: American holly
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
I. opaca is a upright evergreen tree that is commonly known as the Christmas holly. It is the only native holly in the U.S. to have spiny green, leathery leaves and bright red berries [1]. The fine-textured wood is ideal for inlays in cabinetwork, carvings and vanier [2].
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Ideal habitats are moist, acidic, well-drained soils such as mesic hammocks, sand pine-oak woods, bordering floodplains, deciduous woodland on limestone, and mesic steepheads (FSU Herbarium). Soils include sandy loam, loam, medium loam, and does not favor well in clay[2](FSU Herbarium).
Associated species include Pinus taeda, P. echinata, P. glabra, Quercus hemisphaerica, Q. nigra, Q. incana, Q. virginiana, Cornus florida, Liquidambar styraciflua, Magnolia grandiflora, Sassafras albida, Vaccinium arboretum and V. stamineum (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
This is a dioecious species, with separate male and female plants. The flowers of both sexes retain both male and female reproductive organs, however, only one is reproductively functional. Female flowers synchronously with each flower only lasting a day while males opened their flower buds asynchronously throughout the season, with flowers typically lasting 3 to 4 days. The fecundity of the female flowers is constrained by pollinator service, light, nutrient and water levels. Flowers are borne on the green stems of the new year's growth and can be seen March through July. The fruit is a red drupe containing four pyrenes (Carr 1991).
Seed dispersal
The fruit is a four-seeded drupe that is dispersed by birds and small mammals[3]. Large winter-migrating flocks of small birds such as, cedar waxwing and American goldfinch, are one of the most important seed dispersal mechanisms for this species [3].
Seed bank and germination
Germination is epigeal and very slow, usually requiring 16 months to 3 years. Overwinter storage or cold, moist stratification improves germination rates[3].
Fire ecology
I. opaca is very susceptible to fire and is typically absent from regularly or even occasionally burned forest. The bark is easily injured by fire and large trees may be killed by light fires in the understory[3].
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Ilex opaca var. arenicola at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens
Colletidae: Colletes banksi, C. brimleyi
Halictidae: Augochloropsis metallica, Augochloropsis sumptuosa
Megachilidae: Megachile petulans
Sphecidae: Cerceris rozeni, Gorytes dorothyae ruseolus, Hoplisoides denticulatus denticulatus, H. placidus placidus, Liris argentata, L. muesebecki, Pseudoplisus smithii floridanus, Tachysphex apicalis, T. similis, Tanyoprymnus moneduloides
Vespidae: Pachodynerus erynnis
Use by animals
Holly cavities provide nesting habitat for the red-cockaded woodpecker[4]. Groves provide shelter to red-eyed towhee, bluebirds, cardinals, white throated sparrow, and robins (Petrides 1942).
The spines on the leafs are used as a defense against herbivory (Ehrlich and Raven 1967).
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.