Difference between revisions of "Agalinis tenuifolia"
(→Description) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
Annual. Parasitic to the roots of grasses and other herbs. Leaves are opposite, linear to filiform, and sometimes will have tufts on the shoots. Flowers are showy, in terminal racemes; the calyx is 5-parted, the lobes are shorter than the tube; the corolla is 5-parted. The flowers are rose-lavender in color and are rarely white. There are usually 2 yellow lines and numerous purple spots in the throat on the tube. The tube is broad, campanulate, and the lobes are shorter than the tube. The throat is usually lanose at the base of the 2 upper corolla lobes. There are 4 stamens, didynamous, that include filaments and anthers that are also lanose. The stigmas are elongated. The capsules are globose or subglobose, loculicidal. (Radford 1964). | Annual. Parasitic to the roots of grasses and other herbs. Leaves are opposite, linear to filiform, and sometimes will have tufts on the shoots. Flowers are showy, in terminal racemes; the calyx is 5-parted, the lobes are shorter than the tube; the corolla is 5-parted. The flowers are rose-lavender in color and are rarely white. There are usually 2 yellow lines and numerous purple spots in the throat on the tube. The tube is broad, campanulate, and the lobes are shorter than the tube. The throat is usually lanose at the base of the 2 upper corolla lobes. There are 4 stamens, didynamous, that include filaments and anthers that are also lanose. The stigmas are elongated. The capsules are globose or subglobose, loculicidal. (Radford 1964). | ||
| − | Is very similar to Agalinis setacea. | + | Is very similar to ''Agalinis setacea''. The difference between ''Agalinis tenuifolia'' and ''Agalinis setacea'' has to do with the upper corolla lobes. On ''A. tenuifolia'', the upper corolla lobes will be arching over the stamens and closing, or nearly closing, the throat. On a dried specimen of ''A. tenuifolia'', the upper lobes are glabrous basally, making it possible for determination. Flower August to October (Radford 1964). |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium | + | Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium Database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, L. Brouillet, J. M. Canne, A. F. Clewell, Angus Gholson, Robert K. Godfrey, R. Karl, S. W. Leonard, and John C. Semple. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Escambia, Gadsden, Jackson, Lafayette, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Walton, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia: Newton. |
Hall, David W. Illustrated Plants of Florida and the Coastal Plain: based on the collections of Leland and Lucy Baltzell. 1993. A Maupin House Book. Gainesville. 343. Print. | Hall, David W. Illustrated Plants of Florida and the Coastal Plain: based on the collections of Leland and Lucy Baltzell. 1993. A Maupin House Book. Gainesville. 343. Print. | ||
Revision as of 17:47, 15 January 2016
| Agalinis tenuifolia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John R. Gwaltney, Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Orobanchaceae |
| Genus: | Agalinis |
| Species: | A. tenuifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Agalinis tenuifolia (Vahl) Raf. | |
| |
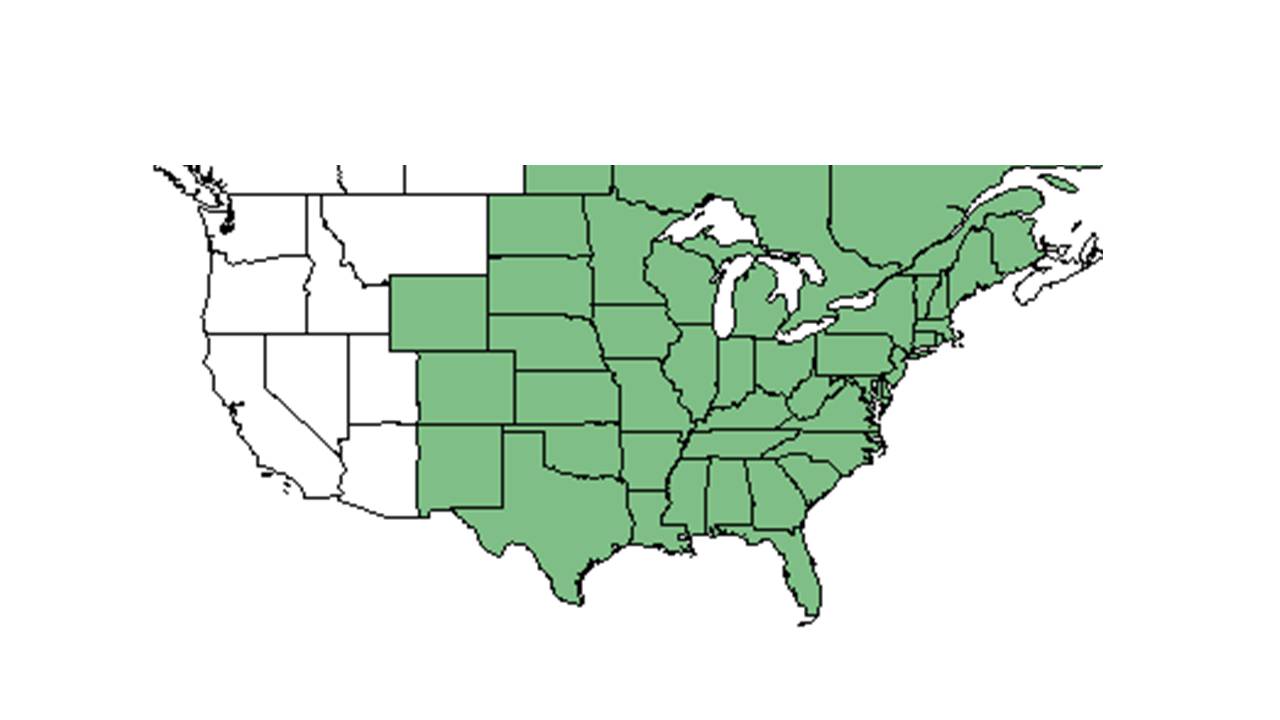
| Natural range of Agalinis tenuifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Slender Garardia; Slenderleaf False Foxglove
Synonyms: Gerardia tenuifolia Vahl; Gerardia tenuifolia subsp. lecuanthera (Raf.) Pennell
Varieties: leucanthera (Raf.) Pennell; macrocarpa (Benth.) S.F. Blake; parviflora (Nutt.) Pennell; polyphylla (Small) Pennell
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
Annual. Parasitic to the roots of grasses and other herbs. Leaves are opposite, linear to filiform, and sometimes will have tufts on the shoots. Flowers are showy, in terminal racemes; the calyx is 5-parted, the lobes are shorter than the tube; the corolla is 5-parted. The flowers are rose-lavender in color and are rarely white. There are usually 2 yellow lines and numerous purple spots in the throat on the tube. The tube is broad, campanulate, and the lobes are shorter than the tube. The throat is usually lanose at the base of the 2 upper corolla lobes. There are 4 stamens, didynamous, that include filaments and anthers that are also lanose. The stigmas are elongated. The capsules are globose or subglobose, loculicidal. (Radford 1964).
Is very similar to Agalinis setacea. The difference between Agalinis tenuifolia and Agalinis setacea has to do with the upper corolla lobes. On A. tenuifolia, the upper corolla lobes will be arching over the stamens and closing, or nearly closing, the throat. On a dried specimen of A. tenuifolia, the upper lobes are glabrous basally, making it possible for determination. Flower August to October (Radford 1964).
Distribution
Agalinis tenuifolia is the most widely distributed throughout eastern North America (Musselman and Mann 1978), although varieties leucanthera and polyphylla are limited to the southeaseastern U.S. (USDA NRCS Plants Database).
Ecology
This species is a vigorous parasite. It forms haustoria on all 19 commercial species included in Appendix III. No clear host preference was shown, although hardwood species supported more parasitic attachments than pine species (Musselman and Mann et al 1978).
Habitat
Agalinis tenuifolia can be found in undisturbed grasslands and areas with low soil nutrients (Hogg and Morton 1983). Other natural habitat includes open upland woodlands, mixed pine-hardwood stands, mesic wooded edges of limestone glades and open grassy limestone glades, scrubby floodplain woods, borders of wooded mesic hammocks, dry sandy slopes, and calcareous clearings (FSU Herbarium). It occurs on xeric limestone prairies of Illinois (Hogg et al 1983), and in moist to dry savannas and bluffs (Wunderlin and Hansen 2003). Prefers semi-shade and sandy soils including sandy loam, sandy clay, and drying or dry loamy sand (FSU Herbarium).
Agalinis tenuifolia also commonly grows in disturbed sites, including clear cut areas and the edges of pine plantations. Large populations may also be found growing at the margins of ditches and in other wet or moist habitats (Musselman and Mann 1978).
Associated species include Aristida, Eupatorium, Juniperus, Schoenus nigricans, Tridens flavus, Agalinis divaricata and others (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
It has been observed flowering September through November, and fruiting in October and November.
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Native vegetation, often including Agalinis tenuifolia, can be completely destroyed and replaced by weeds (Hogg et al 1983) although the soil nutrients increase dramatically when Ring-billed Gulls and other species of gulls nest from April to June (Hogg et al 1983).
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium Database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, L. Brouillet, J. M. Canne, A. F. Clewell, Angus Gholson, Robert K. Godfrey, R. Karl, S. W. Leonard, and John C. Semple. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Escambia, Gadsden, Jackson, Lafayette, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Walton, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia: Newton.
Hall, David W. Illustrated Plants of Florida and the Coastal Plain: based on the collections of Leland and Lucy Baltzell. 1993. A Maupin House Book. Gainesville. 343. Print.
Hogg, E.H. and J.K. Morton. 1983. The effects of nesting gulls on the vegetation and soil of islands in the Great Lakes. Canadian Journal of Botany 61:3240-3254.
Musselman, L.J. and W.F. Mann, Jr. 1978. Root parasites of southern forests. General Technical Report SO-20. New Orleans, LA, USDA Forest Service.
USDA NRCS Plants Database team. URL: USDA NRCS Plants
Wunderlin, Richard P. and Bruce F. Hansen. Guide to the Vascular Plants of Florida. Second edition. 2003. University Press of Florida: Gainesville/Tallahassee/Tampa/Boca Raton/Pensacola/Orlando/Miami/Jacksonville/Ft. Myers. 547. Print.