Difference between revisions of "Solidago arguta"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) (→References and notes) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| + | Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: Collectors: States and Counties: Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy. | ||
Revision as of 14:07, 14 October 2015
| Solidago arguta | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Solidago |
| Species: | S. arguta |
| Binomial name | |
| Solidago arguta Aiton | |
| |
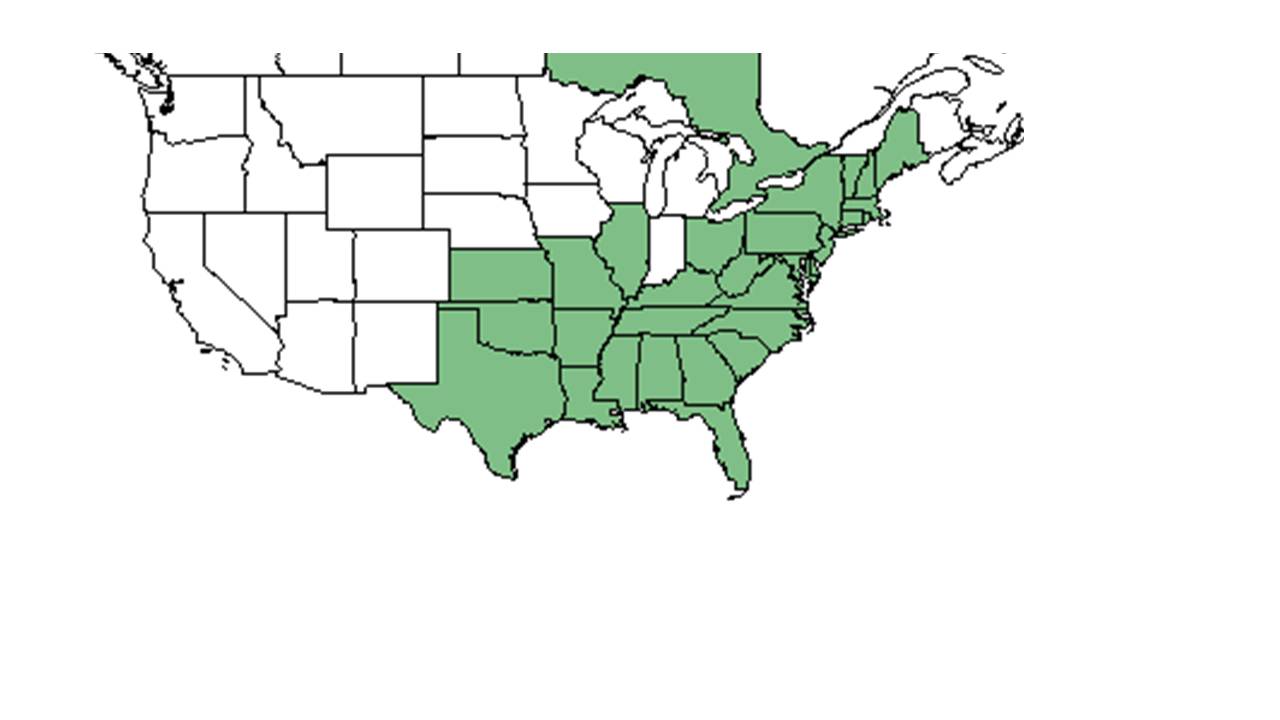
| Natural range of Solidago arguta from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Atlantic goldenrod
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
A description of Solidago arguta is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, S. arguta can be found in remnants of natural Quercus hemisphaerica and Carya glabra woods; pine-oak-hickory woods; pine flatwoods; upland submesic woodlands; open pine woodlands on sandy ridges; along margins of magnolia-beech woodlands; dry loam sand of pinewoods; upland mixed woodlands; lakesides; in shade of mature hardwood forests; mature mesic hardwoods; slopes of sinkholes; annually burned closed canopy of pine-hardwoods; and upland pinewoods (FSU Herbarium). In disturbed habitats it can be found in undergrowth controlled hardwood hammocks; disturbed open pine-oak woodlands; roadside depressions; clay roadside bank near waste dump; pastures; dirt roads; and power line corridors. Substrates include sand, loam, humus, limerock, sandy loam, loamy sand, and clay (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include Quercus hemisphaerica, Carya glabra, Quercus muehlenbergii, Cornus florida, Nyssa sylvatica, Ostrya, Magnolia grandiflora, and Pinus taeda (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
It has been documented flowering February through December and fruiting February through November (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: Collectors: States and Counties: Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.