Difference between revisions of "Pseudognaphalium obtusifolium"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | + | ||
An increase in the frequency of ''P. obtusifolium'' was observed five to eight years after thinning of a longleaf pine stand (Harrington et al 2011). | An increase in the frequency of ''P. obtusifolium'' was observed five to eight years after thinning of a longleaf pine stand (Harrington et al 2011). | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''P. obtusifolium'' can be found in mesic hardwoods, turkey oak scrubs, longleaf pine/scrub oak stands, pine flatwoods, bordering cattail marshes, sand ridges, cypress pond margins, annually burned pine savannas, and annually burned mature longleaf pine-wiregrass communities (FSU Herbarium; Nelson 2005). It can also be found in roadside ditches, and open fields. Soil types include loamy sand, peat soils, sandy loam, and clay soil (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include slash pine, loblolly bay, longleaf pine, wiregrass, ''Liatris, Panicum, Leptoloma cognata, Polygonella'', and ''Amphicarpum'' (FSU Herbarium). | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 14:30, 13 October 2015
| Pseudognaphalium obtusifolium | |
|---|---|
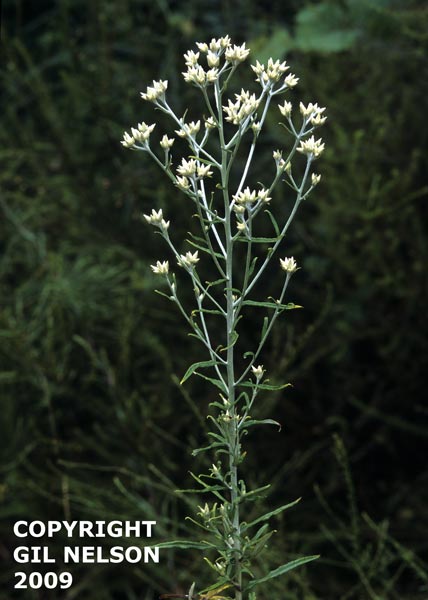

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Pseudognaphalium |
| Species: | P. obtusifolium |
| Binomial name | |
| Pseudognaphalium obtusifolium (L.) Hilliard & B.L. Burtt | |
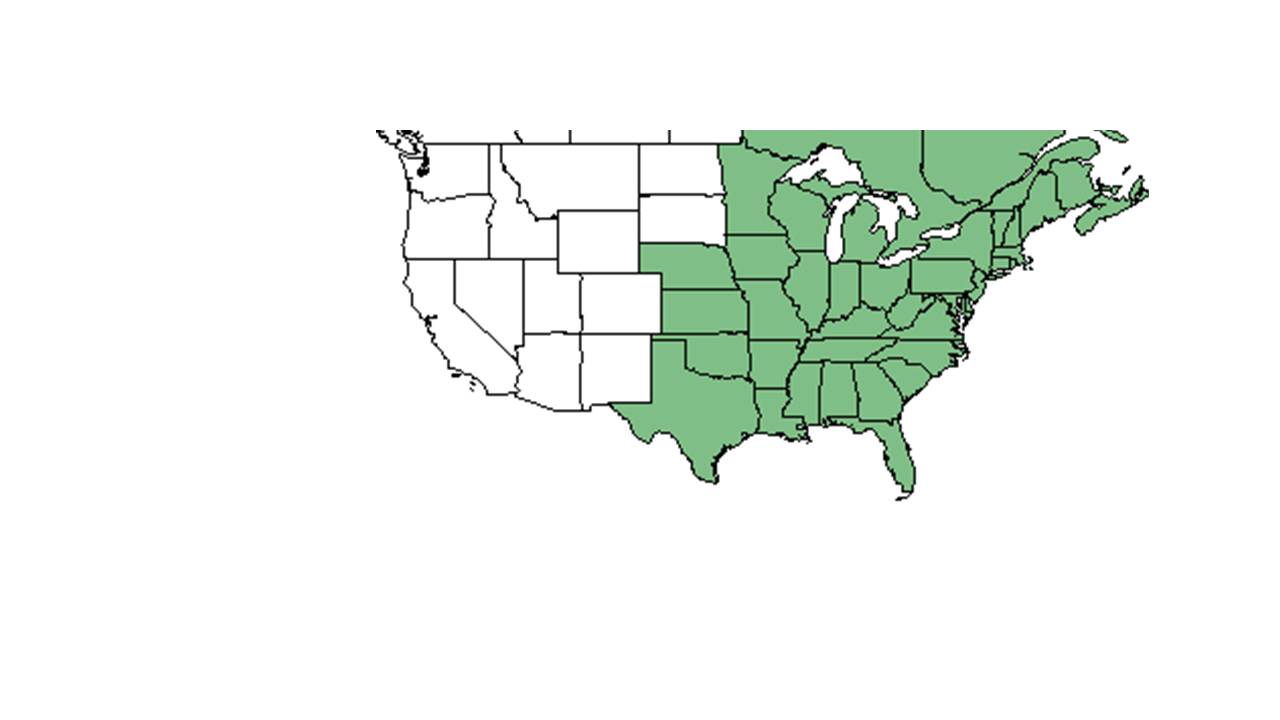
| |
| Natural range of Pseudognaphalium obtusifolium from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Rabbit Tobacco or Sweet Everlasting (Nelson 2005).
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
A description of Pseudognaphalium obtusifolium is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
It is found in medium-sized gaps in a study investigating the interacting effects of overstory removal and ungulate herbivory in a hemlock hardwood forest in Alberta, Michigan (Holmes and Webster 2011).
Ecology
Habitat
An increase in the frequency of P. obtusifolium was observed five to eight years after thinning of a longleaf pine stand (Harrington et al 2011).
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, P. obtusifolium can be found in mesic hardwoods, turkey oak scrubs, longleaf pine/scrub oak stands, pine flatwoods, bordering cattail marshes, sand ridges, cypress pond margins, annually burned pine savannas, and annually burned mature longleaf pine-wiregrass communities (FSU Herbarium; Nelson 2005). It can also be found in roadside ditches, and open fields. Soil types include loamy sand, peat soils, sandy loam, and clay soil (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include slash pine, loblolly bay, longleaf pine, wiregrass, Liatris, Panicum, Leptoloma cognata, Polygonella, and Amphicarpum (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Pseudognaphalium obtusifolium at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Sphecidae: Cerceris blakei
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- Nelson, Gil. East Gulf Coastal Plain Wildflowers. A Field Guide to the Wildflowers of the East Gulf Coastal Plain, including Southwest Georgia, Northwest Florida, Southern Alabama, Southern Mississippi, and Parts of Southeastern Louisiana. Guilford, CT: Falcon, 2005. 115. Print.
- Harrington, T. B. 2011. Overstory and understory relationships in longleaf pine plantations 14 years after thinning and woody control. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 41: 2301-2314.
- Holmes, S. A. and C. R. Webster 2011. Herbivore-induced expansion of generalist species as a driver of homogenization in post-disturbance plant communities. Plant Ecology 212: 753-768.