Difference between revisions of "Rhynchospora grayi"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
[[rcarter]] | [[rcarter]] | ||
| + | Flowers and fruits April through July (FSU Herbarium). | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
Revision as of 20:10, 5 October 2015
| Rhynchospora grayi | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Rhynchospora |
| Species: | R. grayi |
| Binomial name | |
| Rhynchospora grayi Kunth | |
| |
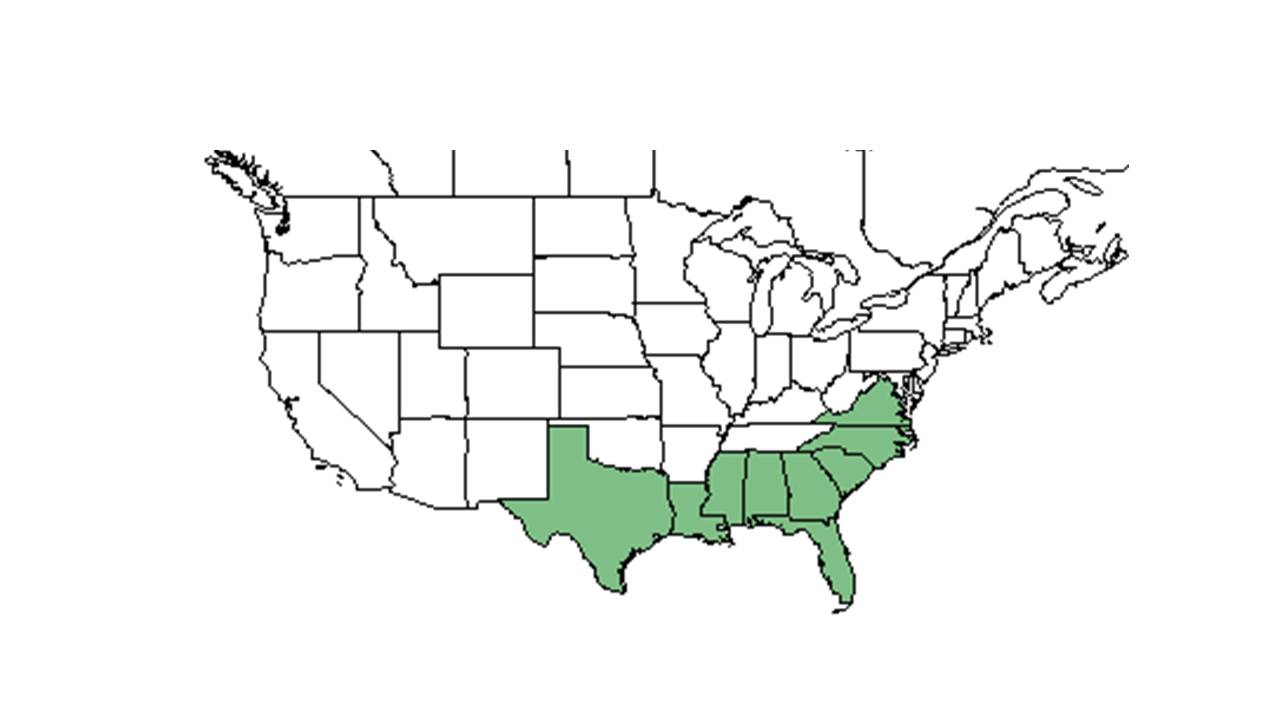
| Natural range of Rhynchospora grayi from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Gray's beaksedge
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
A description of Rhynchospora grayi is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
R. grayi was a species identified as indicating a recovered condition and perhaps high quality groundcover (Archer et al 2007).
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, R. grayi can be found in longleaf pine forests, longleaf pine-wiregrass ridges, pine-oak forests, burned pine flatwoods, dry pine barrens, recently burned wiregrass/pinewoods, peaty depressions in flatwoods, sandy lake shores, turkey oak-slash pine woodlands, and sandy xeric bluffs bordering creeks (Archer et al. 2007, FSU Herbarium). It can also be found in sands of powerline corridors, and sandy fallow fields. Associated species include Pinus palustris, Aristida stricta, Quercus laevis, Q. geminata, Q. margaretta, Q. incana, Licania, Stillingia sylvatica, Tragia smallii, T. urens, Rhynchosia reniformis, Croton argyranthemus and sand pine (FSU Herbarium).
Soil types include dry sand, wet peaty soil, coarse sand, Humaqueptic Psammaquents, and sandy xeric soils (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
rcarter Flowers and fruits April through July (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- Archer, J. K., D. L. Miller, et al. 2007. Changes in understory vegetation and soil characteristics following silvicultural activities in a southeastern mixed pine forest. Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 134: 489-504.