Difference between revisions of "Pityopsis aspera"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| + | Flowering and fruiting have been recorded August through December (FSU Herbarium). | ||
| + | |||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
Revision as of 15:35, 2 October 2015
| Pityopsis aspera | |
|---|---|
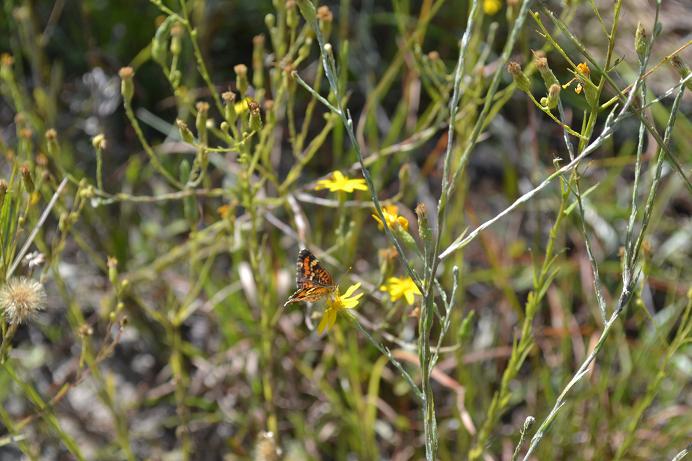

| |
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Pityopsis |
| Species: | P. aspera |
| Binomial name | |
| Physalis arenicola (Shuttlw. ex Small) Small | |
| |
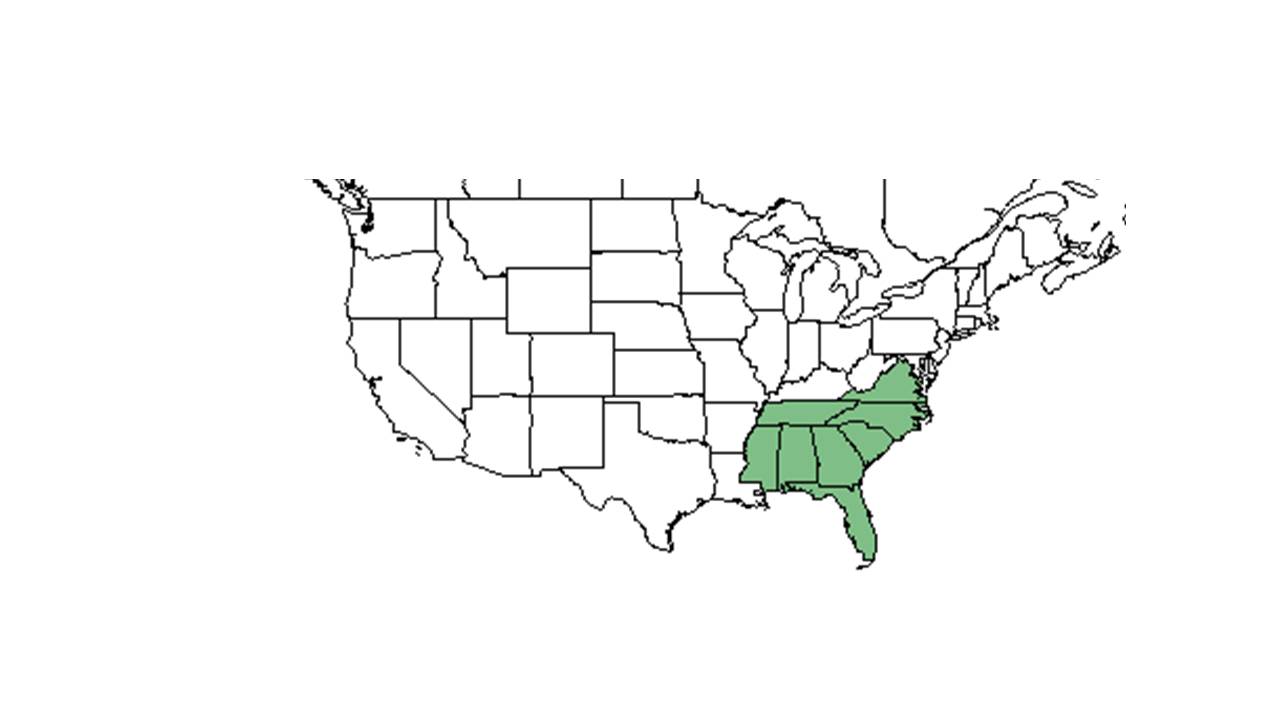
| Natural range of Physalis arenicola from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: pineland silkgrass
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
A description of Pityopsis aspera is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
P. aspera is distributed across southern Georgia and northern Florida (Gowe and Brewer 2005) and is commonly found in Florida sandhill community (Downer-MR_2012_MSThesis.) Habitats documented include longleaf wiregrass sandhills, deep sand banks along hardwood hammocks, open pinewoods, longleaf pine/turkey oaks, scrub oak barrens, longleaf pine savannas, sand pine-evergreen oak scrubs, a high bluff overlooking creek, and chestnut oak woods (FSU Herbarium). In disturbed areas it grows in beds of old railroads, roadsides with bahia grass, a clearing of mixed pine-hardwood stand, harrowed areas, bordering fields, and on golf course edges alongside broomsage (FSU Herbarium). Soil types include sand, dry loamy sand, dry clayey sand, gray sand, wet soil, dry sand-clay bank, loam soil, red clay bank and gravelly-clay (FSU Herbarium).
Associated species include Pityopsis flexuosa, Pinus palustris, Aristida stricta, Chrysopsis latisquamea, Chrysopsis gossypina Quercus, Paronychia, bahia grass, Haplopappus divaricatus, Eupatorium pinnatifidum, Lechea, Diodia teres, Dicanthelium, Lespedeza hirta, Polygonella gracilis, Vaccinium arboreum, sandpine, Microcephala, Liatris, Panicum, Leptoloma cognata, Phoebanthus, Scleria ciliata, Helianthus microcephalus, Helianthus atrorubens, Silphium compositum, Eupatorium, Heterotheca latifolia and chestnut oak (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Flowering and fruiting have been recorded August through December (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
P. aspera occurs in areas with an estimated pre-settlement fire-return interval of 1-3 years (Gowe and Brewer 2005) and flowers within two months of burning in early summer (Robertson).
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Downer, M. R. (2012). Plant species richness and species area relationships in a Florida sandhill community. Integrative Biology. Ann Arbor, MI, University of South Florida. M.S.: 52.
Gowe, A. K. and J. S. Brewer (2005). "The evolution of fire-dependent flowering in goldenasters (Pityopsis spp.)." Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 132: 384-400.
Robertson, Kevin M. 2014. Personal observation.