Difference between revisions of "Buchnera floridana"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
| − | It is a host plant of Brevipalpus phoenicis, which vectors viral diseases like citrus leprosis (Childers et al 2003). | + | It is a host plant of ''Brevipalpus phoenicis'', which vectors viral diseases like citrus leprosis (Childers et al 2003). |
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
This species has been observed in Everglades National Park (FSU Herbarium). | This species has been observed in Everglades National Park (FSU Herbarium). | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
===Diseases and parasites=== | ===Diseases and parasites=== | ||
| + | |||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
Revision as of 15:27, 22 September 2015
| Buchnera floridana | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Scrophulariales |
| Family: | Scrophulariaceae |
| Genus: | Buchnera |
| Species: | B. floridana |
| Binomial name | |
| Buchnera floridana L. | |
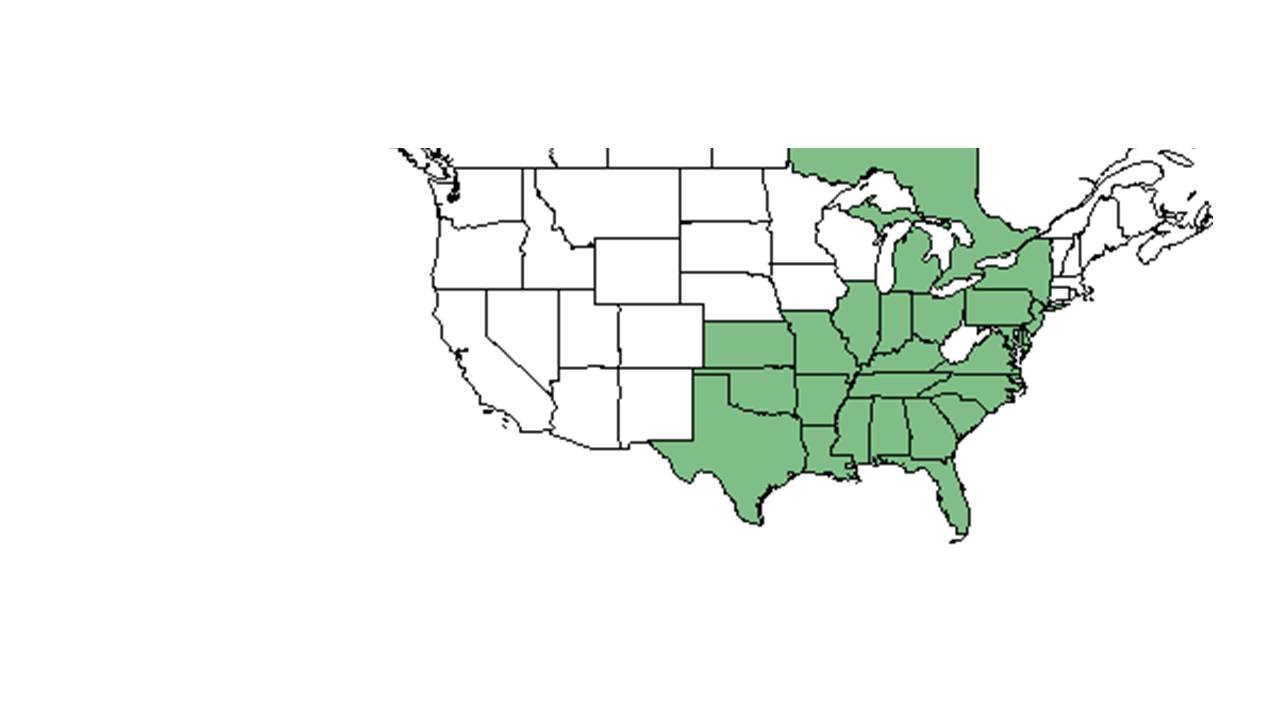
| |
| Natural range of Buchnera floridana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Distribution
Ecology
It is a host plant of Brevipalpus phoenicis, which vectors viral diseases like citrus leprosis (Childers et al 2003).
Habitat
This species has been observed in Everglades National Park (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
B. floridana has been observed flowering and fruiting in December (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Childers, C. C., J. C. V. Rodrigues, et al. (2003). "Host plants of Brevipalpus californicus, B. obovatus, and B. phoenicis (Acari: Tenuipalpidae) and their potential involvement in the spread of viral diseases vectored by these mites." Experimental & Applied Acarology 30: 29-105.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: V. I. Sullivan and J. Wooten. States and Counties: Florida: Monroe.