Difference between revisions of "Hieracium gronovii"
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
| + | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 15:18, 11 June 2015
| Hieracium gronovii | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Hieracium |
| Species: | H. gronovii |
| Binomial name | |
| Hieracium gronovii L. | |
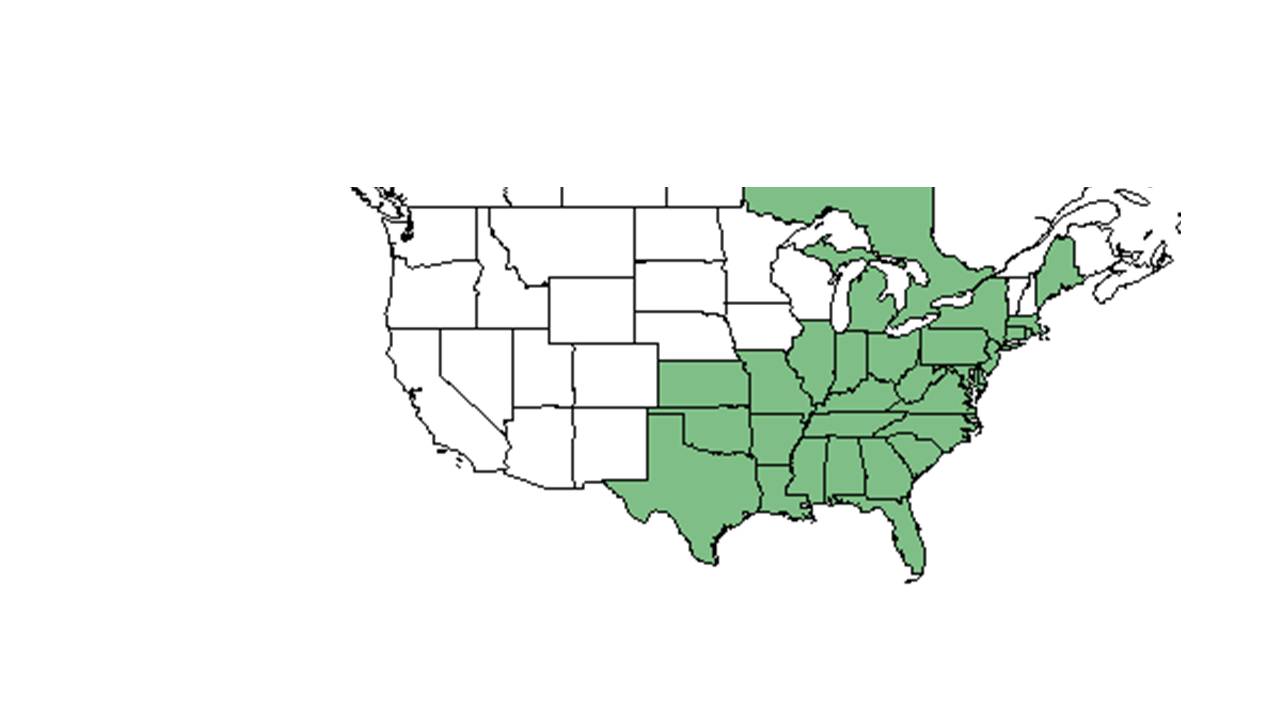
| |
| Natural range of Hieracium gronovii from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Several short-lived perennial forbs also have a seed bank persistent for at least several years.[1]
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Deyrup observed these bees, Augochloropsis sumptuosa, Dialictus coreopsis, Halictus ligatus, Anthidiellum perplexzcm, Anthidium maculifrons, Megachile breuis pseudobrevis, M. georgica, on H. gronovii.[2]
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Platt, W. J., S. M. Carr, et al. (2006). "Pine savanna overstorey influences on ground-cover biodiversity." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 37-50.
- ↑ Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).