Difference between revisions of "Baptisia lecontei"
(→Description) |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | Common Name: pineland wild indigo | ||
| + | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
Revision as of 15:48, 2 July 2015
| Baptisia lecontei | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Baptisia |
| Species: | B. lecontei |
| Binomial name | |
| Baptisia lecontei Torr. & A. Gray | |
| |
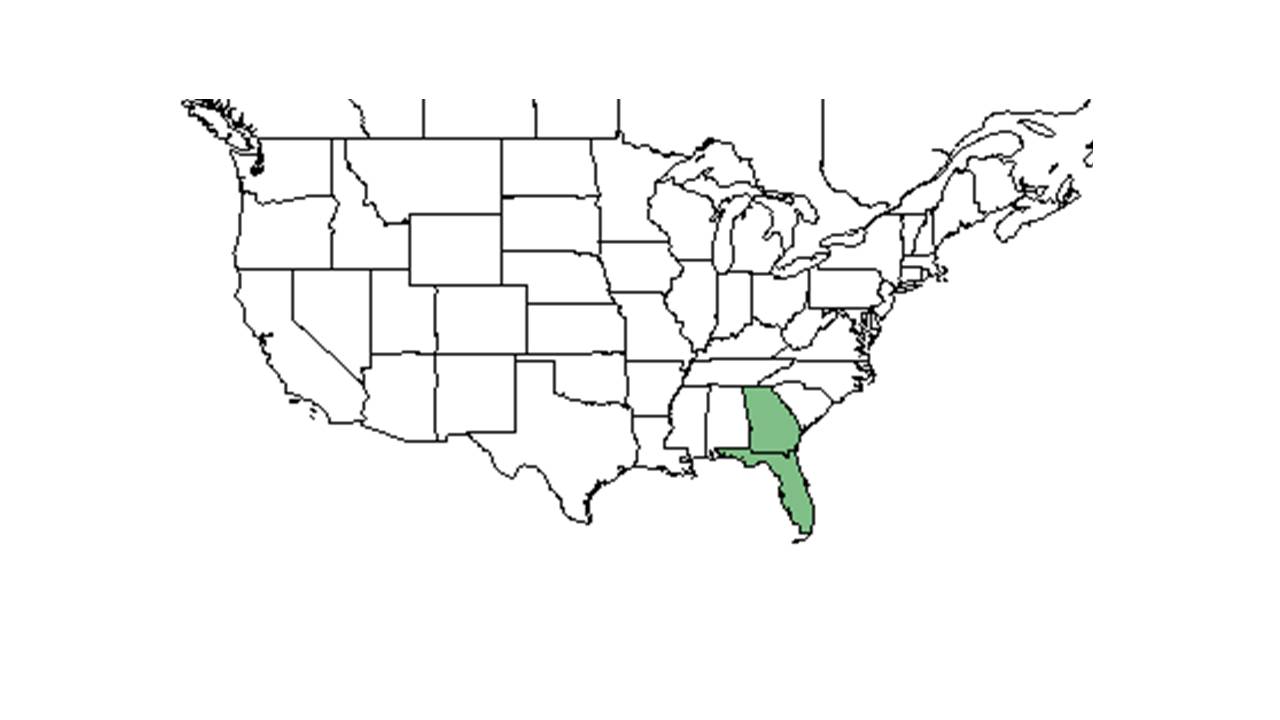
| Natural range of Baptisia lecontei from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Common Name: pineland wild indigo
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
B. lecontei requires open areas and strong, consistent winds for seed dispersal.It is found in sandhill communities.[1]
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Baptisia lecontei uses tumbleweed dispersal, a type of long-distance dispersal mechanism by which means the whole or a part of the plant serves to disperse seeds by being blown into the wind.[2] Mehlman observe that B. lecontei could be found over 50 meters away from where it originated, evidently by wind dispersal [1]