Difference between revisions of "Liatris elegans"
(→Taxonomic notes) |
(→Taxonomic notes) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
Common names: pinkscale blazing star; elegant gayfeather; Bridges's elegant blazing-star; cream-yellow blazing star; Carizzo blazing-star; Carizzo elegant blazing-star; common elegant blazing star; Kral's elegant blazing-star<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | Common names: pinkscale blazing star; elegant gayfeather; Bridges's elegant blazing-star; cream-yellow blazing star; Carizzo blazing-star; Carizzo elegant blazing-star; common elegant blazing star; Kral's elegant blazing-star<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: | + | Synonyms: ''Laciniaria elegans'' (Walter) Kuntze; ''Laciniaria flabellata'' Small.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| − | Varieties: | + | Varieties: ''Liatris elegans'' (Walter) Michaux var. ''elegans''; ''Liatris elegans'' (Walter) Nichaux var. ''kralii'' Mayfield.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
Revision as of 15:36, 12 June 2023
| Liatris elegans | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
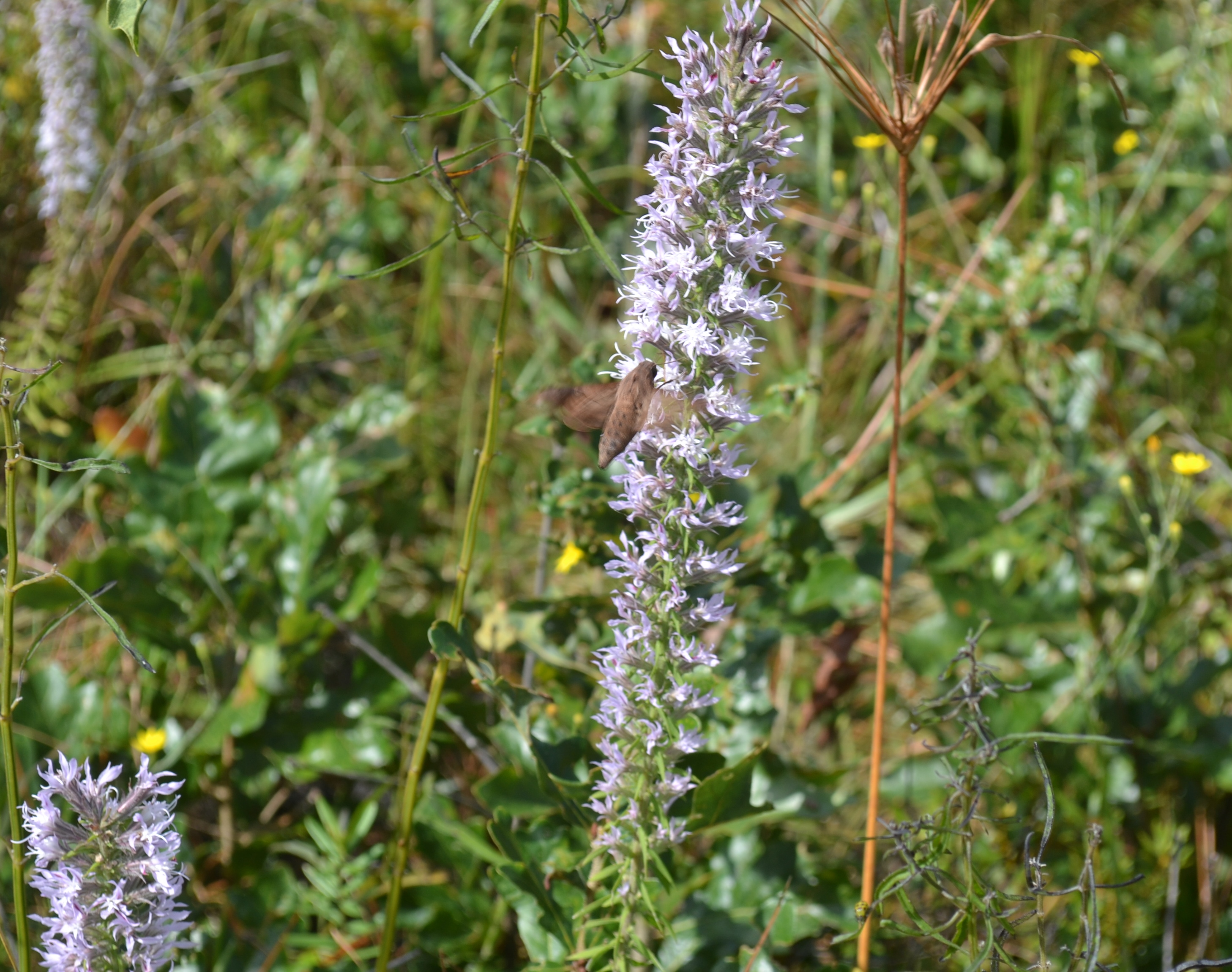
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Liatris |
| Species: | L. elegans |
| Binomial name | |
| Liatris elegans (Walter) Michx. | |
| |
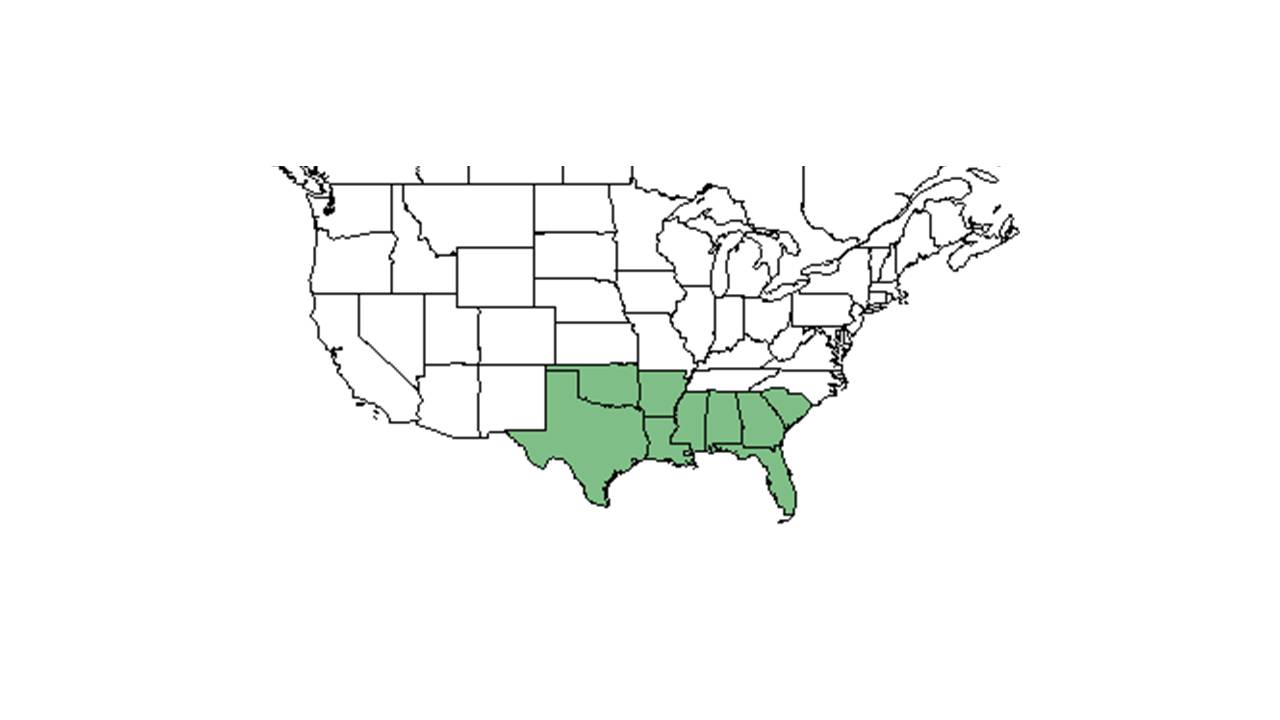
| Natural range of Liatris elegans from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: pinkscale blazing star; elegant gayfeather; Bridges's elegant blazing-star; cream-yellow blazing star; Carizzo blazing-star; Carizzo elegant blazing-star; common elegant blazing star; Kral's elegant blazing-star[1]
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Laciniaria elegans (Walter) Kuntze; Laciniaria flabellata Small.[1]
Varieties: Liatris elegans (Walter) Michaux var. elegans; Liatris elegans (Walter) Nichaux var. kralii Mayfield.[1]
Description
A description of Liatris elegans is provided in The Flora of North America. A rhizomatous perennial that is frequent where it is found.[2]
Distribution
Liatris elegans var. elegans is found from South Carolina through Florida and west to Texas. Liatris elegans var. kralii ranges from southeastern South Carolina through northern Florida Florida and west to southern Mississippi.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
This species has been observed growing in longleaf pine-wiregrass communities, in pine-oak woodlands, bordering sink-ravines, and in live oak hammocks in semi-open to open areas.[2] It also can occur in disturbed areas such as powerline corridors, roadsides, and bulldozed sand scrub.[2] Growing in semi-open and open habitats, L. elegans thrives in dry, coarse, and/or loamy sands as well as red clays.[2] Associated species include longleaf pine, wiregrass, Symphyotrichum dumosum, Solidago, Pityopsis, Liatris pauciflora, Quercus laevis, Heterotheca subaxillaris, Haplopappus divaricatus, Polygonella gracile, Aristidia patula, and Lespedeza hirta.[2]
L. elegans has shown regrowth in reestablished longleaf pine woodlands that were disturbed by agriculture in South Carolina, making it an indicator species for post-agricultural woodlands.[3] However, it became absent in response to soil disturbance by military training in west Georgia. It has shown resistance to regrowth in reestablished longleaf pinelands that were disturbed by these activities.[4]
Phenology
This species has been observed to flower from September to October[5] and fruits from September through November.[2]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by wind.[6]
Fire ecology
Populations of Liatris elegans have been known to persist through repeated annual burns.[7]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "weakley" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "weakley" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "weakley" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, Wilson Baker, Loran C. Anderson, Richard S. Mitchell, E.S. Ford, R.K. Godfrey, Bruce Hansen, JoAnn Hansen, R. Kral, John Morrill, J. P. Gillespie, Sidney McDaniel, R. Komarek, R L Lazor, Gary R. Knight, MacClendons, G. Wilder, Bill Boothe, and Marcia Boothe. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Bay, Calhoun, Clay, Duval, Escambia, Gadsden, Holmes, Leon, Jackson, Jefferson, Madison, Santa Rosa, Taylor, Washington, Wakulla, and Walton. Georgia: Thomas.
- ↑ Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.
- ↑ Dale, V.H., S.C. Beyeler, and B. Jackson. (2002). Understory vegetation indicators of anthropogenic disturbance in longleaf pine forests at Fort Benning, Georgia, USA. Ecological Indicators 1(3):155-170.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.
