Difference between revisions of "Pleopeltis polypodioides"
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| − | + | ===Fire ecology===<!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | |
| − | + | Populations of ''Pleopeltis polypodioides'' have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.<ref>Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref> | |
| − | ===Pollination and | + | <!--===Pollination===--> |
| + | ===Herbivory and toxicology===<!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc--> | ||
''P. polypodioides'' has been found in Fallow Deer rumens in "all seasons, but rarely comprised a significant portion of the diet"<ref name="deer"> Morse, B. W., et al. (2009). "Seasonal Diets of an Introduced Population of Fallow Deer on Little St. Simons Island, Georgia." Southeastern Naturalist 8(4): 571-586. </ref>. | ''P. polypodioides'' has been found in Fallow Deer rumens in "all seasons, but rarely comprised a significant portion of the diet"<ref name="deer"> Morse, B. W., et al. (2009). "Seasonal Diets of an Introduced Population of Fallow Deer on Little St. Simons Island, Georgia." Southeastern Naturalist 8(4): 571-586. </ref>. | ||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
| + | ''P. polypodioides'' should avoid soil disturbance by agriculture to conserve its presence in pine communities.<ref name=ostertag/> | ||
==Cultural use== | ==Cultural use== | ||
Latest revision as of 14:17, 15 July 2022
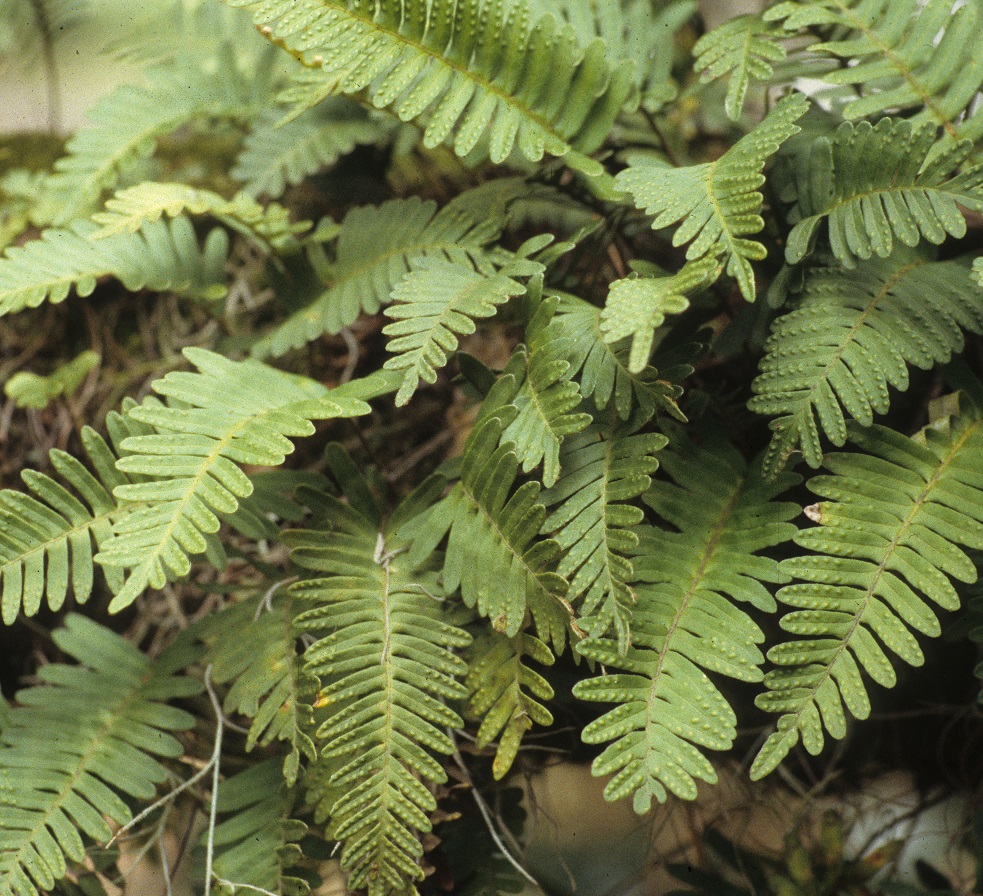
Common names: Resurrection fern
| Pleopeltis polypodioides | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Pteridophyta - Ferns |
| Class: | Filicopsida |
| Order: | Polypodiales |
| Family: | Polypodiaceae |
| Genus: | Pleopeltis |
| Species: | P. polypodioides |
| Binomial name | |
| Pleopeltis polypodioides (L.) Andrews and Windham | |
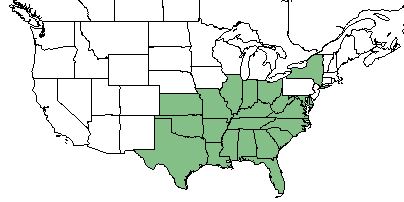
| |
| Natural range of Pleopeltis polypodioides from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Subspecies: P. polypodioides (L.) Andrews & Windham ssp. michauxiana (Weath.) Andrews & Windham, and Pleopeltis polypodioides (L.) Andrews & Windham ssp. polypodioides[1].
Description
P. polypodioides is a perennial forb or vine in the Polypodiaceae family[1]. Leaves of this species "are about 6 in (15 cm) long and 1.5 in (4 cm) wide. The fronds are deeply incised, cut all the way to the rachis"[2]. P. polypodioides is known to curl up and become grey/ brown in times of drought and unfurl and become "reborn" after rain. This is rare for vascular plants[3].
Distribution
This species can be found throughout the southeast United States[1].
Ecology
Habitat
This species is commonly epiphytic, growing on the branches and trunks of trees listed below. It can also be found growing on rock faces, old logs, and the herbaceous layer. It can be found in floodplain forests, hammock, pine savanna, and oak and hickory woods[4]. This species has been described as a "calciphile" due to its affinity for growing on limestone[5].
P. polypodioides became absent or decreased its occurrence in response to soil disturbance by agriculture in southwest Georgia pinelands. It has shown resistance to regrowth in reestablished habitat that was disturbed by agricultural practices.[6]
Associated Species- predominantly epiphytic on Quercus virginiana. Can also be found growing on Quercus nigra, Quercus falcata, Quercus geminata, Magnolia grandiflora, and Quercus stellata and at the base of pines and oaks[4].
Fire ecology
Populations of Pleopeltis polypodioides have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.[7]
Herbivory and toxicology
P. polypodioides has been found in Fallow Deer rumens in "all seasons, but rarely comprised a significant portion of the diet"[8].
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
P. polypodioides should avoid soil disturbance by agriculture to conserve its presence in pine communities.[6]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 USDA Plants Database: https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=PLPO2
- ↑ Floridata link: https://floridata.com/Plants/Polypodiaceae/Polypodium%20polypodioides/573
- ↑ Dubuisson, J.-Y., et al. (2009). "Epiphytism in ferns: diversity and history." Comptes Rendus Biologies 332: 120-128.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2018. Collectors: Cecil R. Slaughter, Robert Kral, Ira L. Wiggins, Dorothy B. Wiggins, Robert K. Godfrey, Loran C. Anderson, J. P. Gillespie, S. W. Leonard, Robert J. Lemaire, Richard S. Mitchell, Kathy Craddock Burks, A. Gholson, Jr., Wilson Baker, Susanne Cooper, Roy Komarek, C. Jackson, Sidney McDaniel, J. B. Nelson, Chris Cooksey, Richard Gaskalla, Patricia Elliot, David Printiss, Gwynn W. Ramsey, B. Auld, B. Moore, C. H. Beck, Tiffani Floyd, R. F. Thorne, P. L. Redfearn, Jr., William Platt, Bert Pittman, and Kathy Boyle. States and Counties: Florida: Brevard, Citrus, Dixie, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Hernando, Indian River, Jackson, Jefferson, Lafayette, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Martin, Okaloosa, Osceola, Pasco, Pinellas, Santa Rosa, Taylor, Wakulla, Washington. Georgia: Grady and Thomas. South Carolina: Lancaster.
- ↑ Huskins, S. D. and J. Shaw (2010). "The Vascular Flora of the North Chickamauga Creek Gorge State Natural Area, Tennessee." Castanea 75(1): 101-125.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Ostertag, T. E. and K. M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference Proceedings 23: 109-120.
- ↑ Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Morse, B. W., et al. (2009). "Seasonal Diets of an Introduced Population of Fallow Deer on Little St. Simons Island, Georgia." Southeastern Naturalist 8(4): 571-586.