Difference between revisions of "Sabatia campanulata"
(→Taxonomic Notes) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{italic title}} | {{italic title}} | ||
| + | Common name: slender marsh-pink<ref name= "Weakley 2015"/>, slender rose gentian<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> | ||
<!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| Line 18: | Line 19: | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: | + | Synonyms: ''S. campanulata'' var. ''gracilis'' (Michaux) Fernald |
Varieties: none | Varieties: none | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | ''S. campanulata'' is a perennial forb/herb of the ''Gentianaceae'' family native to North America.<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"> USDA Plant Database [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=SACA26 https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=SACA26] </ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
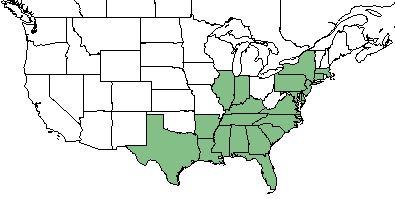
| + | ''S. campanulata'' is found along the southeastern coast of the United States from Texas to Massachusetts.<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| + | ''S. campanulata'' proliferates in pine savannas, bogs, seeps, and fens.<ref name= "Weakley 2015"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref> Specimens have been collected from borders of brackish marshes, moist loam of longleaf pine woodland, mesic pine-oak woods, and cypress pond.<ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R.K. Godfrey, Walter Lewsi, Loran Anderson, R.Kral, Albert Pittman, Kathy Boyle. States and counties: Florida (Calhoun, Jefferson, Gadsden, Liberty, Holmes, Franklin) Georgia (Thomas) South Carolina (Lee)</ref> | ||
<!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | <!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| − | + | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | |
| + | Populations of ''Sabatia campanulata'' have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.<ref>Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref> | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | <!--=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===<!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc--> |
| − | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> |
| + | |||
| + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
| + | ''S. campanulata'' is listed as endangered by the Department of Arkansas Heritage Inventory Research Program, the Kentucky State Nature Preserves Commission, the Maryland Department of Natural Resources Natural Heritage Program, the Massachusetts Division of Fisheries and Wildlife Natural Heritage and Endangered Species Program, and the New York Division of Land and Forests Department of Environmental Conservation, and is listed as extirpated by the Indiana Department of Natural Resources Division of Nature Preserves and the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources.<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
| − | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:45, 15 July 2022
Common name: slender marsh-pink[1], slender rose gentian[2]
| Sabatia campanulata | |
|---|---|
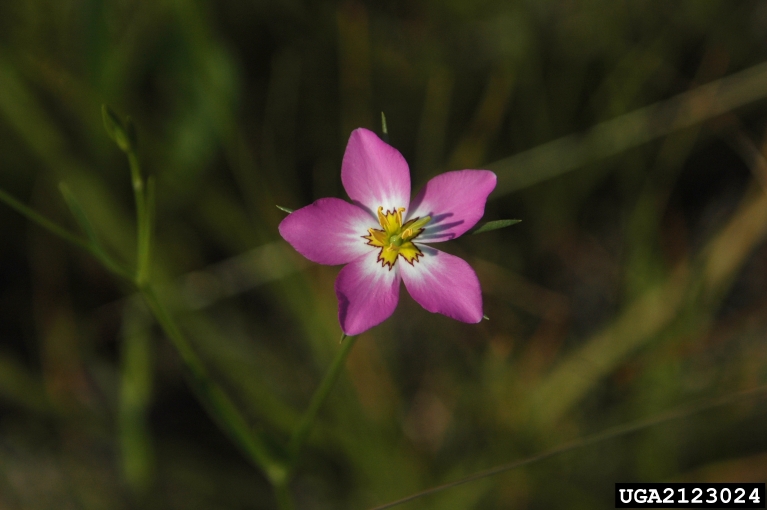

| |
| Photo by Chris Evans, University of Illinois, Bugwood.org, hosted at Forestryimages.org | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Gentianales |
| Family: | Gentianaceae |
| Genus: | Sabatia |
| Species: | S. campanulata |
| Binomial name | |
| Sabatia campanulata L. | |
| |
| Natural range of Sabatia campanulata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: S. campanulata var. gracilis (Michaux) Fernald
Varieties: none
Description
S. campanulata is a perennial forb/herb of the Gentianaceae family native to North America.[2]
Distribution
S. campanulata is found along the southeastern coast of the United States from Texas to Massachusetts.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
S. campanulata proliferates in pine savannas, bogs, seeps, and fens.[1] Specimens have been collected from borders of brackish marshes, moist loam of longleaf pine woodland, mesic pine-oak woods, and cypress pond.[3]
Fire ecology
Populations of Sabatia campanulata have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.[4]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
S. campanulata is listed as endangered by the Department of Arkansas Heritage Inventory Research Program, the Kentucky State Nature Preserves Commission, the Maryland Department of Natural Resources Natural Heritage Program, the Massachusetts Division of Fisheries and Wildlife Natural Heritage and Endangered Species Program, and the New York Division of Land and Forests Department of Environmental Conservation, and is listed as extirpated by the Indiana Department of Natural Resources Division of Nature Preserves and the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources.[2]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=SACA26
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R.K. Godfrey, Walter Lewsi, Loran Anderson, R.Kral, Albert Pittman, Kathy Boyle. States and counties: Florida (Calhoun, Jefferson, Gadsden, Liberty, Holmes, Franklin) Georgia (Thomas) South Carolina (Lee)
- ↑ Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.