Difference between revisions of "Rhynchospora corniculata"
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{italic title}} | {{italic title}} | ||
| + | Common name: short-bristled horned beaksedge <ref name= "Weakley 2015"/> | ||
<!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
Synonyms: ''Rynchospora corniculata'', orthographic variant | Synonyms: ''Rynchospora corniculata'', orthographic variant | ||
| − | Varieties: | + | Varieties: ''R. corniculata''' var. ''interior'' Fernald |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | ''R. corniculata'' is a perennial graminoid of the ''Cyperaceae'' family native to North America. <ref name= "USDA Plant Database"> USDA Plant Database [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=RHCO2 https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=RHCO2] </ref> | + | ''R. corniculata'' is a perennial graminoid of the ''Cyperaceae'' family native to North America.<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"> USDA Plant Database [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=RHCO2 https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=RHCO2] </ref> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
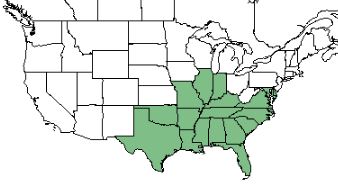
| − | ''R. corniculata'' is found in the southeastern corner of the United States. <ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> | + | ''R. corniculata'' is found in the southeastern corner of the United States.<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''R. corniculata'' proliferates in pondcypress savannas in Carolina bays, swamp forests, and other wetlands. <ref name= "Weakley 2015"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref> | + | ''R. corniculata'' proliferates in pondcypress savannas in Carolina bays, swamp forests, and other wetlands.<ref name= "Weakley 2015"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref> Specimens have been collected from moist loam, shaded mucky soil, floodplain swamp, shaded river bank, bottomland woods, marshy creekbed, edge of water in dense pine canopy, and upper tidal swamp of mixed forest.<ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R.K. Godfrey, R.F. Doren, R.Komarek, R.A. Norris, R. Kral, Richard Mitchell, Madel Kral, Sydney T. Bacchus, Deborah R. Shelley, P.L. Redfearn, Sidney T. Brinson, W. Miley, C.S. Giddeen, A. Redmond, K. Craddock Burks, Cecil Slaughter, Annie Schmidt, Travis MacClendon, Chris Buddenhagen, Becky Lee, M. Darst, H. Light, J. Good, L. Peed. States and counties: Florida (Leon, Wakulla, Jefferson, Marion, Gadsden, Liberty, Holmes, Nassau, Jackson, Citrus, Seminole, Escambia, Okaloosa, Madison, Osceola, Santa Rosa, Dixie) Georgia (Atkinson, Thomas)</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | ''Rhynchospora corniculata'' is an indicator species for the Panhandle Seepage Savannas community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | ''R. corniculata'' | + | ''R. corniculata'' has been observed flowering in July and September.<ref name= "PanFlora"> Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 29 MAY 2018 </ref> |
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | ''R. corniculata'' is not fire resistant, but has a medium fire tolerance. <ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> | + | ''R. corniculata'' is not fire resistant, but has a medium fire tolerance.<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> Populations have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.<ref>Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref> |
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | <!--=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===<!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc--> |
| − | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> |
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| + | ''R. corniculata'' is listed as threatened by the Indiana Department of Natural Resources Division of Nature Preserves, and as a weedy or invasive species by the Southern Weed Science Society.<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:15, 15 July 2022
Common name: short-bristled horned beaksedge [1]
| Rhynchospora corniculata | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John Gwaltney hosted at Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Rhynchospora |
| Species: | R. corniculata |
| Binomial name | |
| Rhynchospora corniculata Lam. | |
| |
| Natural range of Rhynchospora corniculata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Rynchospora corniculata, orthographic variant
Varieties: R. corniculata' var. interior Fernald
Description
R. corniculata is a perennial graminoid of the Cyperaceae family native to North America.[2]
Distribution
R. corniculata is found in the southeastern corner of the United States.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
R. corniculata proliferates in pondcypress savannas in Carolina bays, swamp forests, and other wetlands.[1] Specimens have been collected from moist loam, shaded mucky soil, floodplain swamp, shaded river bank, bottomland woods, marshy creekbed, edge of water in dense pine canopy, and upper tidal swamp of mixed forest.[3]
Rhynchospora corniculata is an indicator species for the Panhandle Seepage Savannas community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[4]
Phenology
R. corniculata has been observed flowering in July and September.[5]
Fire ecology
R. corniculata is not fire resistant, but has a medium fire tolerance.[2] Populations have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.[6]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
R. corniculata is listed as threatened by the Indiana Department of Natural Resources Division of Nature Preserves, and as a weedy or invasive species by the Southern Weed Science Society.[2]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=RHCO2
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R.K. Godfrey, R.F. Doren, R.Komarek, R.A. Norris, R. Kral, Richard Mitchell, Madel Kral, Sydney T. Bacchus, Deborah R. Shelley, P.L. Redfearn, Sidney T. Brinson, W. Miley, C.S. Giddeen, A. Redmond, K. Craddock Burks, Cecil Slaughter, Annie Schmidt, Travis MacClendon, Chris Buddenhagen, Becky Lee, M. Darst, H. Light, J. Good, L. Peed. States and counties: Florida (Leon, Wakulla, Jefferson, Marion, Gadsden, Liberty, Holmes, Nassau, Jackson, Citrus, Seminole, Escambia, Okaloosa, Madison, Osceola, Santa Rosa, Dixie) Georgia (Atkinson, Thomas)
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 29 MAY 2018
- ↑ Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.