Difference between revisions of "Dichanthelium ovale"
Rwagner914 (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{subst:Template:PlantName}}") |
Adam.Vansant (talk | contribs) |
||
| (50 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | oval-flowered witchgrass; low stiff witchgrass | ||
{{italic title}} | {{italic title}} | ||
<!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| − | | name = | + | | name = Dichanthelium ovale |
| − | | image = | + | | image = Dichanthelium_ovale_PH_2015-10.JPG |
| − | | image_caption = Photo by | + | | image_caption = Photo by Kevin Robertson |
| regnum = Plantae | | regnum = Plantae | ||
| divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | | divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | ||
| − | | classis = Liliopsida - Moncots | + | | classis = Liliopsida - Moncots |
| − | | ordo = | + | | ordo = Poales |
| − | | familia = | + | | familia = Poaceae |
| − | | genus = '' | + | | genus = ''Dichanthelium'' |
| − | | species = ''''' | + | | species = '''''D. ovale''''' |
| − | | binomial = '' | + | | binomial = ''Dichanthelium ovale'' |
| − | | binomial_authority = | + | | binomial_authority = (Elliot) Gould & C.A. |
| − | | range_map = | + | | range_map = DICH_OVAL_DIST.JPG |
| − | | range_map_caption = Natural range of '' | + | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Dichanthelium ovale'' from USDA NRCS [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=DIOVO Plants Database]. |
}} | }} | ||
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
| + | Synonyms: ''Dichanthelium commonsianum'' (Ashe) Freckmann; ''Panicum commonsianum'' Ashe; ''P. ovale'' Elliott var. ''pseudopubescens'' (Nash) Lelong; ''Dichanthelium ovale'' ssp. ''ovale''; ''P. ovale'' Elliott; ''P. ovale'' var. ''ovale'' Lelong<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: ''Dichanthelium ovale'' (Elliott) Gould & Clark var. ''addisonii'' (Nash) Gould & Clark; ''Dichanthelium ovale'' (Elliott) Gould & Clark var. ''ovale''; ''D. wilmingtonense'' (W.W. Ashe) Wipff; ''Panicum addisonii'' Nash; ''P. commonsianum'' W.W. Ashe; ''P. commonsianum'' var. ''addisonii'' (Nash) Fernald; ''P. commonsianum'' var. ''commonsianum''; ''P. mundum'' Fernald; ''P. wilmingtonense'' Ashe<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | Also known as eggleaf rosette grass, ''Dichanthelium ovale'' is a native perennial graminoid that is a member of the Poaceae family. It has a rapid growth rate reaching a mature height of 1.7 meters on average, and a short lifespan. <ref name= "USDA"> USDA Plants Database URL: https://plants.usda.gov/java/charProfile?symbol=DIOV </ref> It is distinguished from ''D. consanguineum'' by the upper blade surface being glabrous with few short basal hairs while ''D. consanguineum'' has strongly pilose upper surfaces on the leaf blade.<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''D. ovale'' does not have specialized underground storage units apart from its fibrous roots.<ref name="Diaz"> Diaz-Toribio, M.H. and F. E. Putz 2021. Underground carbohydrate stores and storage organs in fire-maintained longleaf pine savannas in Florida, USA. American Journal of Botany 108: 432-442.</ref> Diaz-Toribio and Putz (2021) recorded this species to have a water content of 54.1% (ranking 69 out of 100 species studied).<ref name="Diaz"/> | ||
| + | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | ''D. ovale'' grows in the eastern United States, ranging from east Texas up to New York and Michigan, excluding West Virginia, Tennessee, and Missouri.<ref name= "USDA"/> ''D. ovale'' var. ''ovale'' is distributed from New York to Wisconsin as well as south Florida and west to eastern Texas. ''D. ovale'' var. ''addisonii'' can be found from Massachusetts and Minnesota south to Florida and Texas, and is also native to northern Mexico.<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | < | + | ''D. ovale'' var. ''addisonii'' grows in a range of dry to damp soils and in sandy woods and fields, while ''D. ovale'' var. ''ovale'' grows in damp to dry and sandy pinelands.<ref name=weakley/> More specifically, ''D. ovale'' has been observed in a range of habitats including open limestone glades, moist soil, longleaf pineland bogs, moist sandy peat, coarse sand habitats, abandoned fields, sandhills, and other sandy loams. <ref name= "Herbarium"> Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, Cecil R. Slaughter, R. Kral, R. K. Godfrey, R. L. Wilbur, G. W. Pamelee, John W. Thieret, A. E. Radford, Steve Mortellaro, Brenda Herring, Don Herring, D. L. Martin, S. T. Cooper, R. Wunderlin, Bruce Hansen, G. Robinson, Steve L. Orzell, E. L. Bridges, R. Komarek, Andre F. Clewell, George R. Cooley, Richard J. Eaton, Leonard J. Brass, R. D. Houlk, J. B. McFarlin, J. Beckner, C. Chapman, R. R. Smith, A. H. Curtiss, Robert F. Thome, R. A. Davidson, Sidney McDaniel, Nancy Coile, G. Smith, N. MacLeish, M. Garland, D. Coile, Richard Carter, Raymond Athey, D. J. Banks, H. Kurz, and Annie Schmidt. States and counties: Florida: Leon, Liberty, Bay, Gadsden, Madison, Wakulla, Calhoun, Jackson, Clay, Franklin, Okaloosa, Duval, Walton, Escambia, Highlands, Gilchrist, Levy, Citrus, Suwannee, Sumter, Columbia, Lee, and Volusia. Alabama: Washington, Lee, Mobile, and Monroe. North Carolina: Pender, Beaufort, and Brunswick. Georgia: Wheeler, Thomas, Decatur, Baker, Walker, and Emanuel. Michigan: Allegan, and Montcalm. Louisiana: Allen, Ouachita, Union, and Natchitoches. South Carolina: Kershaw. Virginia: Roanoke. South Carolina: Berkeley. Tennessee: Coffee. Kentucky: Crittenden. </ref> It has been seen to be more abundant in disturbed areas. <ref name= "Rodger"> Rodgers, H. L. and L. Provencher (1999). "Analysis of Longleaf Pine Sandhill Vegetation in Northwest Florida." Castanea 64(2): 138-162. </ref> It is listed as a facultative upland species, where it is mostly found in upland non-wetland habitats but can occasionally be found in wetlands as well.<ref name= "USDA"/> It prefers partial shade and low amount of water use.<ref name= "lady bird"/> In Florida, ''D. ovale'' is abundant in the xeric sandhills of the peninsula and the panhandle.<ref name= "Carr"/> |
| − | < | + | |
| − | + | ''D. ovale'' was found to be a decreaser in its long-term response following cessation of repeated soil disturbance.<ref name=Dixon>Dixon, C. M., K. M. Robertson, A. M. Reid and M. T. Rother. 2024. Mechanical soil disturbance in a pine savanna has multiyear effects on plant species composition. Ecosphere 15(2):e4759.</ref> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | < | + | Associated species: ''Aristida beyrichiana'', ''Sorghastrum secundum'', and ''Schizachyrium scoparium'' var. ''stoloniferum''.<ref name= "Carr"> Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189. </ref> |
| − | <!--=== | + | |
| + | ''Dichanthelium ovale'' var. ''addisonli'' is frequent and abundant in the Peninsula Xeric Sandhills, Panhandle Xeric Sandhills, North Florida Longleaf Woodlands, North Florida Subxeric Sandhills, and Clayhill Longleaf Woodlands community types as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| + | The species flowers in the springtime beginning in May, and continues to develop fruit throughout October.<ref name=weakley/> Fruit has been seen in the months March through June and August. <ref name= "Herbarium"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| + | This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. <ref> Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| + | A study found seeds of ''D. ovale'' to persist in the seed bank on a restoration project even when herbaceous cover of the species was not found. It was found to germinate at the restoration site with high frequency.<ref>Andreu, M. G., et al. (2009). "Can managers bank on seed banks when restoring Pinus taeda L. plantations in Southwest Georgia?" Restoration Ecology 17: 586-596.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | ''D. ovale'' is mostly found in fire dependent pinelands in sandhill communities,<ref name= "Carr"/> with populations known to persist through repeated annual burns.<ref>Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref><ref>Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref> This was also seen by a fire exclusion study, where this species disappeared when fire regiments were ceased.<ref>Clewell, A. F. (2014). "Forest development 44 years after fire exclusion in formerly annually burned old field pine woodland, Florida." Castanea 79: 147-167.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Pollination=== | ||
| + | Like other grasses, flowers of the ''Dichanthelium'' genus are self-pollinated.<ref name= "lady bird">[[https://www.wildflower.org/plants/search.php?search_field=&newsearch=true]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: May 1, 2019</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--===''Dichanthelium leucothrix'' is an indicator species for the Lower Panhandle Savannas community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> | ||
| + | <!===Herbivory and toxicology===--> | ||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 19:06, 1 August 2024
oval-flowered witchgrass; low stiff witchgrass
| Dichanthelium ovale | |
|---|---|
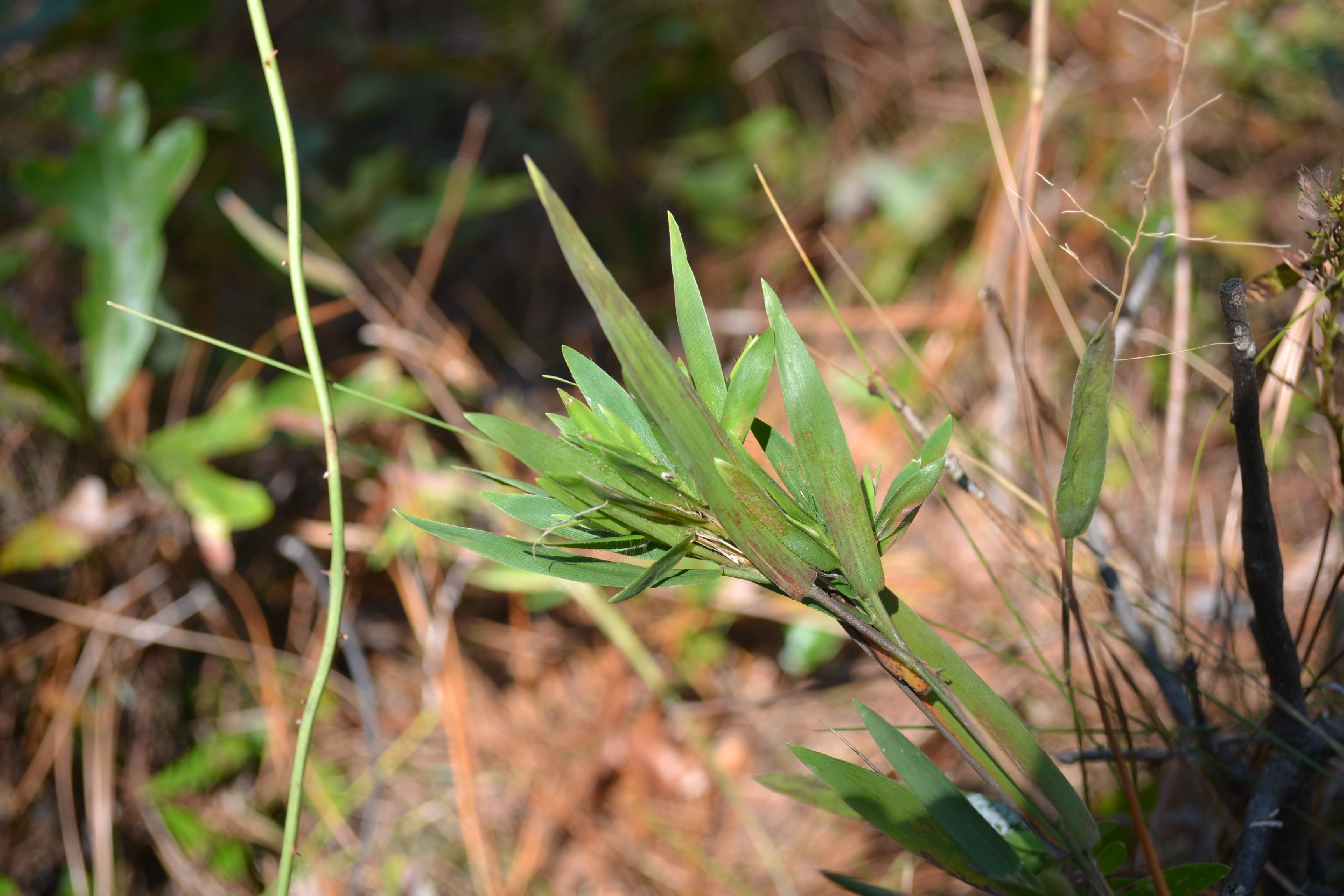

| |
| Photo by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Dichanthelium |
| Species: | D. ovale |
| Binomial name | |
| Dichanthelium ovale (Elliot) Gould & C.A. | |
| |
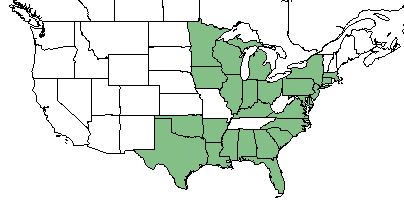
| Natural range of Dichanthelium ovale from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Dichanthelium commonsianum (Ashe) Freckmann; Panicum commonsianum Ashe; P. ovale Elliott var. pseudopubescens (Nash) Lelong; Dichanthelium ovale ssp. ovale; P. ovale Elliott; P. ovale var. ovale Lelong[1]
Varieties: Dichanthelium ovale (Elliott) Gould & Clark var. addisonii (Nash) Gould & Clark; Dichanthelium ovale (Elliott) Gould & Clark var. ovale; D. wilmingtonense (W.W. Ashe) Wipff; Panicum addisonii Nash; P. commonsianum W.W. Ashe; P. commonsianum var. addisonii (Nash) Fernald; P. commonsianum var. commonsianum; P. mundum Fernald; P. wilmingtonense Ashe[1]
Description
Also known as eggleaf rosette grass, Dichanthelium ovale is a native perennial graminoid that is a member of the Poaceae family. It has a rapid growth rate reaching a mature height of 1.7 meters on average, and a short lifespan. [2] It is distinguished from D. consanguineum by the upper blade surface being glabrous with few short basal hairs while D. consanguineum has strongly pilose upper surfaces on the leaf blade.[1]
D. ovale does not have specialized underground storage units apart from its fibrous roots.[3] Diaz-Toribio and Putz (2021) recorded this species to have a water content of 54.1% (ranking 69 out of 100 species studied).[3]
Distribution
D. ovale grows in the eastern United States, ranging from east Texas up to New York and Michigan, excluding West Virginia, Tennessee, and Missouri.[2] D. ovale var. ovale is distributed from New York to Wisconsin as well as south Florida and west to eastern Texas. D. ovale var. addisonii can be found from Massachusetts and Minnesota south to Florida and Texas, and is also native to northern Mexico.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
D. ovale var. addisonii grows in a range of dry to damp soils and in sandy woods and fields, while D. ovale var. ovale grows in damp to dry and sandy pinelands.[1] More specifically, D. ovale has been observed in a range of habitats including open limestone glades, moist soil, longleaf pineland bogs, moist sandy peat, coarse sand habitats, abandoned fields, sandhills, and other sandy loams. [4] It has been seen to be more abundant in disturbed areas. [5] It is listed as a facultative upland species, where it is mostly found in upland non-wetland habitats but can occasionally be found in wetlands as well.[2] It prefers partial shade and low amount of water use.[6] In Florida, D. ovale is abundant in the xeric sandhills of the peninsula and the panhandle.[7]
D. ovale was found to be a decreaser in its long-term response following cessation of repeated soil disturbance.[8]
Associated species: Aristida beyrichiana, Sorghastrum secundum, and Schizachyrium scoparium var. stoloniferum.[7]
Dichanthelium ovale var. addisonli is frequent and abundant in the Peninsula Xeric Sandhills, Panhandle Xeric Sandhills, North Florida Longleaf Woodlands, North Florida Subxeric Sandhills, and Clayhill Longleaf Woodlands community types as described in Carr et al. (2010).[9]
Phenology
The species flowers in the springtime beginning in May, and continues to develop fruit throughout October.[1] Fruit has been seen in the months March through June and August. [4]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. [10]
Seed bank and germination
A study found seeds of D. ovale to persist in the seed bank on a restoration project even when herbaceous cover of the species was not found. It was found to germinate at the restoration site with high frequency.[11]
Fire ecology
D. ovale is mostly found in fire dependent pinelands in sandhill communities,[7] with populations known to persist through repeated annual burns.[12][13] This was also seen by a fire exclusion study, where this species disappeared when fire regiments were ceased.[14]
Pollination
Like other grasses, flowers of the Dichanthelium genus are self-pollinated.[6]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 USDA Plants Database URL: https://plants.usda.gov/java/charProfile?symbol=DIOV
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Diaz-Toribio, M.H. and F. E. Putz 2021. Underground carbohydrate stores and storage organs in fire-maintained longleaf pine savannas in Florida, USA. American Journal of Botany 108: 432-442.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, Cecil R. Slaughter, R. Kral, R. K. Godfrey, R. L. Wilbur, G. W. Pamelee, John W. Thieret, A. E. Radford, Steve Mortellaro, Brenda Herring, Don Herring, D. L. Martin, S. T. Cooper, R. Wunderlin, Bruce Hansen, G. Robinson, Steve L. Orzell, E. L. Bridges, R. Komarek, Andre F. Clewell, George R. Cooley, Richard J. Eaton, Leonard J. Brass, R. D. Houlk, J. B. McFarlin, J. Beckner, C. Chapman, R. R. Smith, A. H. Curtiss, Robert F. Thome, R. A. Davidson, Sidney McDaniel, Nancy Coile, G. Smith, N. MacLeish, M. Garland, D. Coile, Richard Carter, Raymond Athey, D. J. Banks, H. Kurz, and Annie Schmidt. States and counties: Florida: Leon, Liberty, Bay, Gadsden, Madison, Wakulla, Calhoun, Jackson, Clay, Franklin, Okaloosa, Duval, Walton, Escambia, Highlands, Gilchrist, Levy, Citrus, Suwannee, Sumter, Columbia, Lee, and Volusia. Alabama: Washington, Lee, Mobile, and Monroe. North Carolina: Pender, Beaufort, and Brunswick. Georgia: Wheeler, Thomas, Decatur, Baker, Walker, and Emanuel. Michigan: Allegan, and Montcalm. Louisiana: Allen, Ouachita, Union, and Natchitoches. South Carolina: Kershaw. Virginia: Roanoke. South Carolina: Berkeley. Tennessee: Coffee. Kentucky: Crittenden.
- ↑ Rodgers, H. L. and L. Provencher (1999). "Analysis of Longleaf Pine Sandhill Vegetation in Northwest Florida." Castanea 64(2): 138-162.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 [[1]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: May 1, 2019
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189.
- ↑ Dixon, C. M., K. M. Robertson, A. M. Reid and M. T. Rother. 2024. Mechanical soil disturbance in a pine savanna has multiyear effects on plant species composition. Ecosphere 15(2):e4759.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Andreu, M. G., et al. (2009). "Can managers bank on seed banks when restoring Pinus taeda L. plantations in Southwest Georgia?" Restoration Ecology 17: 586-596.
- ↑ Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Clewell, A. F. (2014). "Forest development 44 years after fire exclusion in formerly annually burned old field pine woodland, Florida." Castanea 79: 147-167.