Difference between revisions of "Hypericum suffruticosum"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
(→Distribution) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common name: pineland St. | + | Common name: pineland St. John's-wort |
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| − | Synonym: ''Ascyrum pumilum'' Michaux | + | Synonym: ''Ascyrum pumilum'' Michaux<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: none<ref name=weakley/> | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| Line 26: | Line 28: | ||
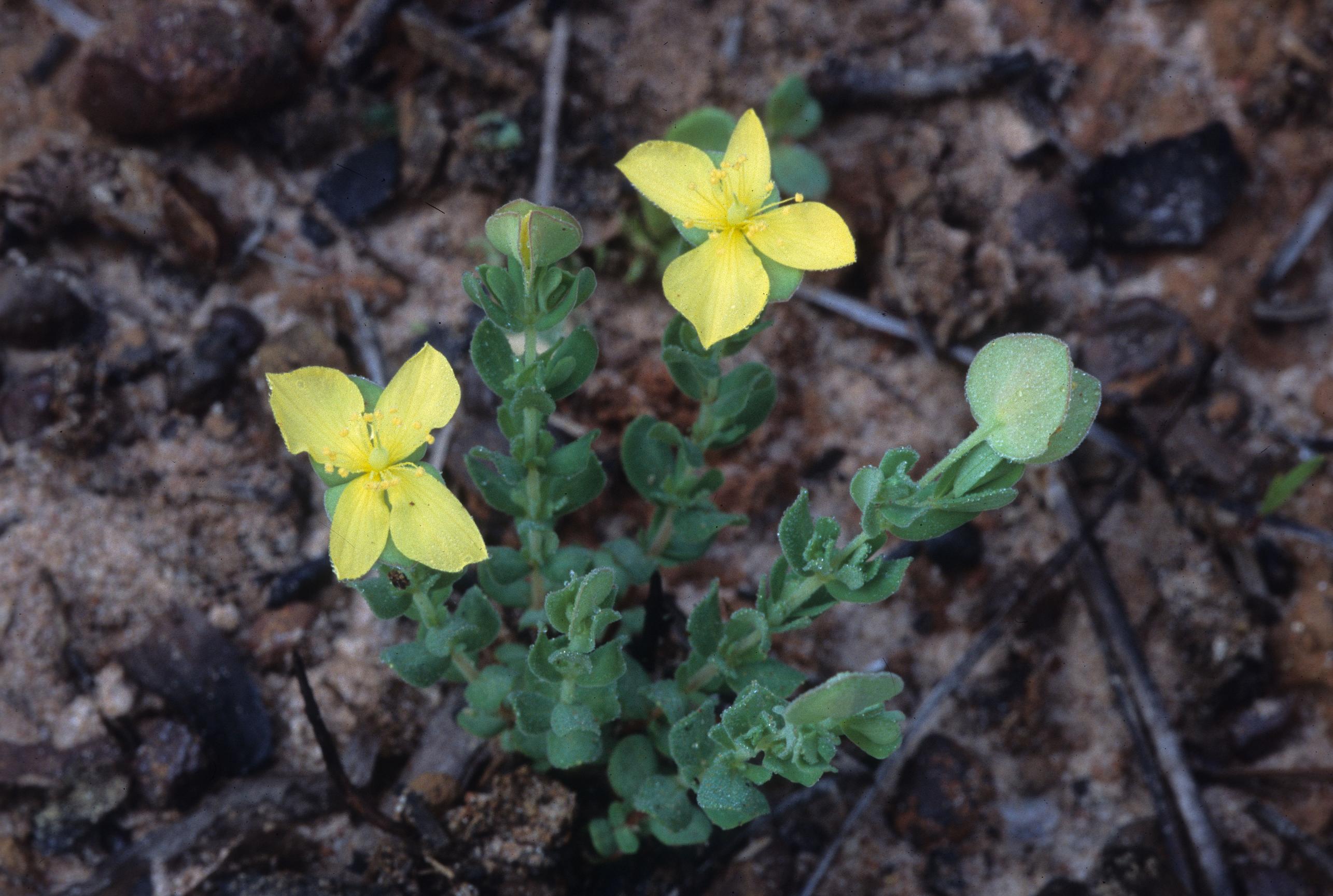
''Hypericum suffruticosum'' is a perennial shrub. | ''Hypericum suffruticosum'' is a perennial shrub. | ||
| − | “Usually glabrous herbs or shrubs. Leaves usually punctate, simple, opposite, entire, usually sessile or subsessile, exstipulate. Inflorescence basically cymose; flowers perfect, regular, bracteates, subsessile or short-pedicellate, sepals 2, 4, or 5, persistent; petals 4 or 5, usually marcescent, yellow or pink; stamens 5-numerous, separate or connate basally forming 3-5 clusters or fascicles, filaments usually persistent; carpels 2-5, stigmas and styles separate or fused, ovary superior, 1-locular or partly or wholly 2-5 locular, placentation axile or parietal. Capsules basically ovoid, longitudinally dehiscent, styles usually persistent; seeds numerous, lustrous, areolate, cylindric or oblong. In general our species form a polymorphic complex with many intergrading taxa.” <ref name="Radford et al 1964">Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 709-710. Print.</ref> | + | “Usually glabrous herbs or shrubs. Leaves usually punctate, simple, opposite, entire, usually sessile or subsessile, exstipulate. Inflorescence basically cymose; flowers perfect, regular, bracteates, subsessile or short-pedicellate, sepals 2, 4, or 5, persistent; petals 4 or 5, usually marcescent, yellow or pink; stamens 5-numerous, separate or connate basally forming 3-5 clusters or fascicles, filaments usually persistent; carpels 2-5, stigmas and styles separate or fused, ovary superior, 1-locular or partly or wholly 2-5 locular, placentation axile or parietal. Capsules basically ovoid, longitudinally dehiscent, styles usually persistent; seeds numerous, lustrous, areolate, cylindric or oblong. In general our species form a polymorphic complex with many intergrading taxa.”<ref name="Radford et al 1964">Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 709-710. Print.</ref> |
| − | "Small, usually decumbent shrub, 7-15 cm tall, stems wing-angled. Leaves oblong, elliptic, or slightly obovate, 1-8 mm long, 1-3 mm wide, obtuse, base jointed or notched. Flowers usually solitary, occasionally in cymules; bracts paired, basal; pedicels reflexed, 6-13 mm long. Outer sepals 2, ovate or widely elliptic, 5-9 mm long, 4.5-7 wide, acute, inner sepals usually absent; petals 4, obovate, 5-7 mm long; styles 2, usually separate, ca. 1.5 mm long, ovary 1-locular. Capsules ovoid or ellipsoid, ca. 3 mm long and 2 mm broad; mature seeds not seen." <ref name="Radford et al 1964"/> | + | "Small, usually decumbent shrub, 7-15 cm tall, stems wing-angled. Leaves oblong, elliptic, or slightly obovate, 1-8 mm long, 1-3 mm wide, obtuse, base jointed or notched. Flowers usually solitary, occasionally in cymules; bracts paired, basal; pedicels reflexed, 6-13 mm long. Outer sepals 2, ovate or widely elliptic, 5-9 mm long, 4.5-7 wide, acute, inner sepals usually absent; petals 4, obovate, 5-7 mm long; styles 2, usually separate, ca. 1.5 mm long, ovary 1-locular. Capsules ovoid or ellipsoid, ca. 3 mm long and 2 mm broad; mature seeds not seen."<ref name="Radford et al 1964"/> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | This plant's range extends from North Carolina to central peninsular Florida and west to southeastern Louisiana.<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''H. suffruticosum'' occurs in longleaf pine flatwoods, as well as disturbed areas like roadsides. <ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: R. F. Doren, Leon Neel, Robert K. Godfrey, R. Komarek, and Steve L. Orzell. States and Counties: Florida: Liberty and Nassau. Georgia: Baker and Thomas.</ref> It is found in dry sandy soil most commonly. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> Associated species include ''Pinus palutris''. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | + | ''H. suffruticosum'' occurs in longleaf pine flatwoods, as well as disturbed areas like roadsides.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: R. F. Doren, Leon Neel, Robert K. Godfrey, R. Komarek, and Steve L. Orzell. States and Counties: Florida: Liberty and Nassau. Georgia: Baker and Thomas.</ref> It is found in dry sandy soil most commonly.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> Associated species include ''Pinus palutris''.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | + | ''H. suffruticosum'' has been observed flowering from January to September and also in November with peak inflorescence in April.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016</ref> | |
| + | |||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| − | + | This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity.<ref>Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> | |
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| − | |||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | This species has been found in habitat that is often maintained by frequent fire. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | + | This species has been found in habitat that is often maintained by frequent fire.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | <!--=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> |
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:18, 2 June 2023
| Hypericum suffruticosum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Theales |
| Family: | Clusiaceae ⁄ Guttiferae |
| Genus: | Hypericum |
| Species: | H. suffruticosum |
| Binomial name | |
| Hypericum suffruticosum P. Adams & N. Robson | |
| |
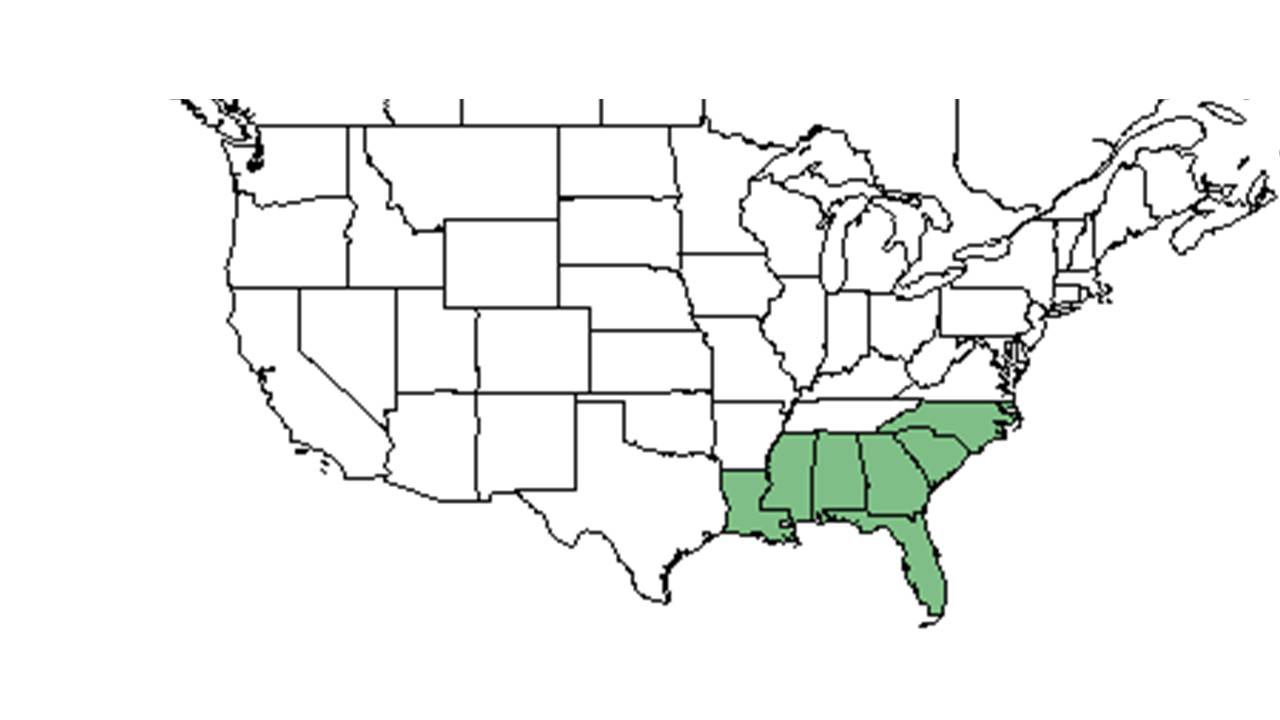
| Natural range of Hypericum suffruticosum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: pineland St. John's-wort
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Ascyrum pumilum Michaux[1]
Varieties: none[1]
Description
Hypericum suffruticosum is a perennial shrub.
“Usually glabrous herbs or shrubs. Leaves usually punctate, simple, opposite, entire, usually sessile or subsessile, exstipulate. Inflorescence basically cymose; flowers perfect, regular, bracteates, subsessile or short-pedicellate, sepals 2, 4, or 5, persistent; petals 4 or 5, usually marcescent, yellow or pink; stamens 5-numerous, separate or connate basally forming 3-5 clusters or fascicles, filaments usually persistent; carpels 2-5, stigmas and styles separate or fused, ovary superior, 1-locular or partly or wholly 2-5 locular, placentation axile or parietal. Capsules basically ovoid, longitudinally dehiscent, styles usually persistent; seeds numerous, lustrous, areolate, cylindric or oblong. In general our species form a polymorphic complex with many intergrading taxa.”[2]
"Small, usually decumbent shrub, 7-15 cm tall, stems wing-angled. Leaves oblong, elliptic, or slightly obovate, 1-8 mm long, 1-3 mm wide, obtuse, base jointed or notched. Flowers usually solitary, occasionally in cymules; bracts paired, basal; pedicels reflexed, 6-13 mm long. Outer sepals 2, ovate or widely elliptic, 5-9 mm long, 4.5-7 wide, acute, inner sepals usually absent; petals 4, obovate, 5-7 mm long; styles 2, usually separate, ca. 1.5 mm long, ovary 1-locular. Capsules ovoid or ellipsoid, ca. 3 mm long and 2 mm broad; mature seeds not seen."[2]
Distribution
This plant's range extends from North Carolina to central peninsular Florida and west to southeastern Louisiana.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
H. suffruticosum occurs in longleaf pine flatwoods, as well as disturbed areas like roadsides.[3] It is found in dry sandy soil most commonly.[3] Associated species include Pinus palutris.[3]
Phenology
H. suffruticosum has been observed flowering from January to September and also in November with peak inflorescence in April.[3][4]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity.[5]
Fire ecology
This species has been found in habitat that is often maintained by frequent fire.[3]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 709-710. Print.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: R. F. Doren, Leon Neel, Robert K. Godfrey, R. Komarek, and Steve L. Orzell. States and Counties: Florida: Liberty and Nassau. Georgia: Baker and Thomas.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.