Difference between revisions of "Lyonia fruticosa"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) (→References and notes) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 11 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| name = Lyonia fruticosa | | name = Lyonia fruticosa | ||
| − | | image = | + | | image = Lyon_frut.jpg |
| − | | image_caption = | + | | image_caption = Photo by Betty Wargo, [http://www.florida.plantatlas.usf.edu/Default.aspx Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants] |
| regnum = Plantae | | regnum = Plantae | ||
| divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | | divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common name: | + | Common name: Coastal plain staggerbush; Poor-grub<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonym: ''Xolisma fruticosa'' (Michaux) Nash.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: none.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The genus ''Lyonia'' is named for John Lyon a 19th century botanist who is best known for his travels in southern Appalachians.<ref name="treasurecoast">[[https://treasurecoastnatives.wordpress.com/2014/01/18/fettered-staggering-and-getting-by/]] Treasure Coast Natives Accessed: February 9, 2016</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
A description of ''Lyonia fruticosa'' is provided in [http://efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=250065691 The Flora of North America]. | A description of ''Lyonia fruticosa'' is provided in [http://efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=250065691 The Flora of North America]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is very similar to ''L. ferruginea'' however, ''L. fruticosa'' has scales on the abaxial side that are all the same size.<ref name="ifas">[[https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/FR/FR37300.pdf]] Accessed: February 9, 2016</ref> | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | ''L. fruticosa'' ranges from southeast South Carolina to southern peninsular Florida, and west to Panhandle Florida.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | + | Habitats of ''L. fruticosa'' include pine flatwoods, pine-oak scrubs, pine/saw palmetto flats, ''Cyrilla'' swamps, cypress-gum swamps, shrub bogs, upland xeric sand pine/sand live oak communities, depression marshes, shore hammock, and mesic hardwood hammocks. It has been observed growing in abandoned dumps and slash pine plantations. Substrates include loamy sand and white sand. | |
| + | |||
| + | ''L. fruticosa'' decreased its cover and stems per acre in response to chopping in south Florida saw palmetto-pineland communities. It has shown resistance to regrowth in reestablished pine habitat that was disturbed by this practice.<ref>Moore, W.H. (1974). Effects of Chopping Saw-Plametto-Pineland Threeawn Range in South Florida. Journal of Range Management 27(2):101-104.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Associated species include ''Lyonia lucida, Ilex glabra, Myrica cerifera, Aronia, Sarracenia minor, Rhododendron, Kalmia, Hypericum, Serenoa repens, Agalinis'' and ''Sphagnum''.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, W.M.B., Edwin L. Bridges, Michael B. Brooks, Andre F. Clewell, Delzie Demaree, Angus Gholson, Robert K. Godfrey, Walter S. Judd, Robert Kral, O. Lakela, K. Lems, S.W. Leonard, Sidney McDaniel, Marc Minno, Richard S. Mitchell, R.A. Norris, C.W. O’Brien, Steve Orzell, Jackie Patman, Elmer C. Prichard, Gwynn W. Ramsey, James D. Ray, Grady Reinert, David Roddenberry, Cecil R. Slaughter, R.F. Thorne, E. Tyson, D.B. Ward, E. West, A.A. Will, Roomie Wilson. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Clay,Collier, Columbia, Duval, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Gilchrist, Indian River, Jefferson, Lafayette, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Martin, Nassau, Okeechobee, Palm Beach, Pasco, Polk, Putnam, Sarasota, Taylor, Volusia, Wakulla. Georgia: Camden. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref><ref name="Schmalzer and Hinkle 1992">Schmalzer, P. A. and C. R. Hinkle (1992). "Recovery of Oak-Saw Palmetto Scrub after Fire." Castanea 57(3): 158-173.</ref> | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | + | The white urn-shaped flowers and dry, egg shaped fruits appear March through December.<ref name="inaturalist"/><ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> ''L. fruticosa'' has been observed flowering March to December with peak inflorescence in June.<ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016</ref> | |
| + | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
| + | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | ''L. fruticosa'' recovers post-fire from resprouting and clonal growth<ref name="Menges and Maguire 2011">Menges, E. S. and A. J. Maguire (2011). "Post-fire growth strategies of resprouting Florida scrub vegetation." Fire Ecology 7(3).</ref> and shows a significant positive trend in percent frequency with time since last fire in rosemary scrubs.<ref name="Menges and Kohfeldt">Menges, E. S. and N. Kohfeldt (1995). "Life History Strategies of Florida Scrub Plants in Relation to Fire." Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 122(4): 282-297.</ref> Density is the highest 12 months post burn.<ref name="Schmalzer and Hinkle 1992"/> | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | The following | + | The following species were observed visiting flowers of ''Lyonia fruticosa'' at the Archbold Biological Station:<ref name="Deyrup 2015">Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> |
| − | Apidae: ''Bombus impatiens'' | + | Bees from the family Apidae: ''Bombus impatiens'' |
| − | Colletidae: ''Colletes banksi, C. distinctus, C. productus, C.'' sp. ''A'' | + | Plasterer bees from the family Colletidae: ''Colletes banksi, C. distinctus, C. productus, C.'' sp. ''A'' |
| − | Halictidae: ''Augochloropsis sumptuosa'' | + | Sweat bees from the family Halictidae: ''Augochloropsis sumptuosa'' |
| − | Sphecidae: ''Stictia carolina'' | + | Thread-waisted wasps from the family Sphecidae: ''Stictia carolina'' |
| − | Vespidae: ''Monobia quadridens'' | + | Wasps from the family Vespidae: ''Monobia quadridens'' |
| + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> | ||
| + | ===Diseases and parasites=== | ||
| + | The lace bug ''Stephanitis blatchleyi'' has not been observed on ''L. fruticosa'' but has been found on ''L. ferruginea''.<ref name="Wheeler and Stoops 2013">Wheeler, A. G. and C. A. Stoops (2013). "STEPHANITIS BLATCHLEYI (HEMIPTERA: TINGIDAE): FIRST HOST-PLANT ASSOCIATION FOR A RARELY COLLECTED LACE BUG." The Florida Entomologist 96(2): 673-675.</ref> ''Exobasidiaceae'' causes galls on the leaves of ''L. fruticosa.''<ref name="treasurecoast"/> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==Cultural use== | |
| − | == | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
| + | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 19:07, 14 July 2022
| Lyonia fruticosa | |
|---|---|
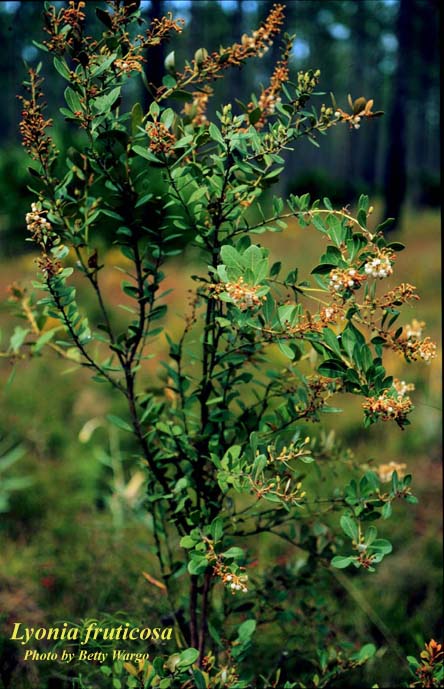

| |
| Photo by Betty Wargo, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ericaceae |
| Genus: | Lyonia |
| Species: | L. fruticosa |
| Binomial name | |
| Lyonia fruticosa (Michx.) G.S. Torr. | |
| |
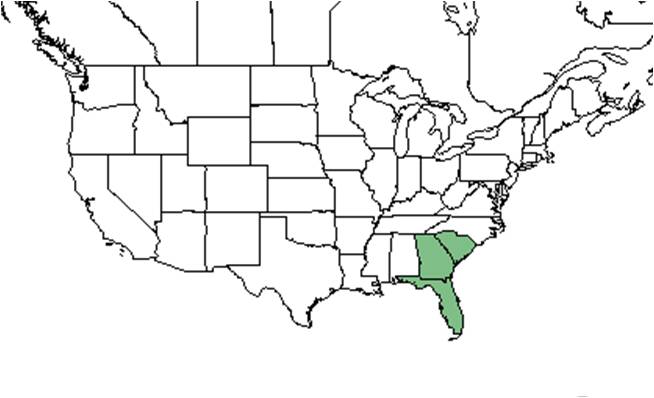
| Natural range of Lyonia fruticosa from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Coastal plain staggerbush; Poor-grub[1]
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Xolisma fruticosa (Michaux) Nash.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
The genus Lyonia is named for John Lyon a 19th century botanist who is best known for his travels in southern Appalachians.[2]
Description
A description of Lyonia fruticosa is provided in The Flora of North America.
It is very similar to L. ferruginea however, L. fruticosa has scales on the abaxial side that are all the same size.[3]
Distribution
L. fruticosa ranges from southeast South Carolina to southern peninsular Florida, and west to Panhandle Florida.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
Habitats of L. fruticosa include pine flatwoods, pine-oak scrubs, pine/saw palmetto flats, Cyrilla swamps, cypress-gum swamps, shrub bogs, upland xeric sand pine/sand live oak communities, depression marshes, shore hammock, and mesic hardwood hammocks. It has been observed growing in abandoned dumps and slash pine plantations. Substrates include loamy sand and white sand.
L. fruticosa decreased its cover and stems per acre in response to chopping in south Florida saw palmetto-pineland communities. It has shown resistance to regrowth in reestablished pine habitat that was disturbed by this practice.[4]
Associated species include Lyonia lucida, Ilex glabra, Myrica cerifera, Aronia, Sarracenia minor, Rhododendron, Kalmia, Hypericum, Serenoa repens, Agalinis and Sphagnum.[5][6]
Phenology
The white urn-shaped flowers and dry, egg shaped fruits appear March through December.[7][5] L. fruticosa has been observed flowering March to December with peak inflorescence in June.[8]
Fire ecology
L. fruticosa recovers post-fire from resprouting and clonal growth[9] and shows a significant positive trend in percent frequency with time since last fire in rosemary scrubs.[10] Density is the highest 12 months post burn.[6]
Pollination
The following species were observed visiting flowers of Lyonia fruticosa at the Archbold Biological Station:[11]
Bees from the family Apidae: Bombus impatiens
Plasterer bees from the family Colletidae: Colletes banksi, C. distinctus, C. productus, C. sp. A
Sweat bees from the family Halictidae: Augochloropsis sumptuosa
Thread-waisted wasps from the family Sphecidae: Stictia carolina
Wasps from the family Vespidae: Monobia quadridens
Diseases and parasites
The lace bug Stephanitis blatchleyi has not been observed on L. fruticosa but has been found on L. ferruginea.[12] Exobasidiaceae causes galls on the leaves of L. fruticosa.[2]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 [[1]] Treasure Coast Natives Accessed: February 9, 2016
- ↑ [[2]] Accessed: February 9, 2016
- ↑ Moore, W.H. (1974). Effects of Chopping Saw-Plametto-Pineland Threeawn Range in South Florida. Journal of Range Management 27(2):101-104.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, W.M.B., Edwin L. Bridges, Michael B. Brooks, Andre F. Clewell, Delzie Demaree, Angus Gholson, Robert K. Godfrey, Walter S. Judd, Robert Kral, O. Lakela, K. Lems, S.W. Leonard, Sidney McDaniel, Marc Minno, Richard S. Mitchell, R.A. Norris, C.W. O’Brien, Steve Orzell, Jackie Patman, Elmer C. Prichard, Gwynn W. Ramsey, James D. Ray, Grady Reinert, David Roddenberry, Cecil R. Slaughter, R.F. Thorne, E. Tyson, D.B. Ward, E. West, A.A. Will, Roomie Wilson. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Clay,Collier, Columbia, Duval, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Gilchrist, Indian River, Jefferson, Lafayette, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Martin, Nassau, Okeechobee, Palm Beach, Pasco, Polk, Putnam, Sarasota, Taylor, Volusia, Wakulla. Georgia: Camden. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Schmalzer, P. A. and C. R. Hinkle (1992). "Recovery of Oak-Saw Palmetto Scrub after Fire." Castanea 57(3): 158-173.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedinaturalist - ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Menges, E. S. and A. J. Maguire (2011). "Post-fire growth strategies of resprouting Florida scrub vegetation." Fire Ecology 7(3).
- ↑ Menges, E. S. and N. Kohfeldt (1995). "Life History Strategies of Florida Scrub Plants in Relation to Fire." Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 122(4): 282-297.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Wheeler, A. G. and C. A. Stoops (2013). "STEPHANITIS BLATCHLEYI (HEMIPTERA: TINGIDAE): FIRST HOST-PLANT ASSOCIATION FOR A RARELY COLLECTED LACE BUG." The Florida Entomologist 96(2): 673-675.