Difference between revisions of "Lithospermum caroliniense"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) (→References and notes) |
(→Distribution) |
||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 11 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common name: Carolina puccoon | + | Common name: Carolina puccoon, coastal plain puccoon |
| − | |||
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| − | ==Description== | + | Synonyms: ''Batschia caroliniensis'' Walter ex J.F. Gmelin; ''Lithospermum carolinense'' ssp. ''carolinense''; ''L. carolinense'' var. ''carolinense''<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: none<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | "Annual or perennial, pubescent or hispid herbs. Leaves usually alternate. Cymes leafy-bracteate, some flowers heterostylic; fruiting pedicels mostly erect or ascending. Calyx cleft into narrow lobes; corolla yellow, yellow-orange, or white (to blue), tubular to funnelform or salverform, throat pubescent, crested or open, lobes spreading and imbricate; anthers included; gynobase flat or depressed. Mericaps 4 or fewer, smooth or wrinkled, with a broad basal attachment scar, the scar often surrounded by a sharp rim."<ref name="Radford et al 1964">Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 882. Print.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | "Plant 3-10 dm tall, arising from a strong-staining taproot; stems simple or branched, very leafy, hirsute. Cymes dense, leafy-bracteate, elongate at maturity and loosely flowered; flowers heterostylic, all subtended by a bract. Calyx 6-8 mm long at anthesis, 8-10 mm long at maturity; corolla orange-yellow, funnelform, 13-25 mm long; anthers in short-styled flowers at the top of the corolla tube and just below the appendages at the throat, style extending only to the middle of tube; anther in long-styled flowers near the middle of the corolla tube, the long style reaching to and beyond the top of the tube, the appendages weakly developed at the throat; corolla nectary 1-0lobed, villous at the base of tube; stigma terminal, minutely villosulous, bilobed. Mericaps white, smooth, often pitted, 3-3.5 mm long."<ref name="Radford et al 1964"/> | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | This plant is a southeastern coastal plain endemic. It's found from southeastern South Carolina to Panhandle Florida, and west to Texas.<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, ''L. caroliniense'' has been found in pinewoods and sand dunes. | + | In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, ''L. caroliniense'' has been found in pinewoods and sand dunes. In human-disturbed areas it has occurred in cut over secondary sandhill forest and along highways.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Bill Anderson, Loran C. Anderson, Pam Anderson, R. Komarek, T. MacClendon, K. MacClendon, Sidney McDaniel, R. A. Norris. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Jackson, Liberty Georgia: Decatur, Dougherty. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> Associated species include ''Berlandiera pumila, Chrysopsis, Licania michauxii, Cnidoscolus stimulosus, Phlox pilosa, Rubus cuneifolius'', and ''Solidago door''.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> Soils include sand and loamy sand.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | + | ''L. caroliniense'' flowers from April through June.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016</ref> | |
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| − | + | This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity.<ref>Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> | |
| + | |||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | ===Pollination=== | + | Populations of ''Lithospermum caroliniense'' have been known to persist through repeated annual burns.<ref>Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref> |
| − | === | + | <!--===Pollination===--> |
| − | ===Diseases and parasites=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> |
| − | ==Conservation and | + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> |
| − | == | + | |
| + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
| + | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 17:35, 15 June 2023
| Lithospermum caroliniense | |
|---|---|
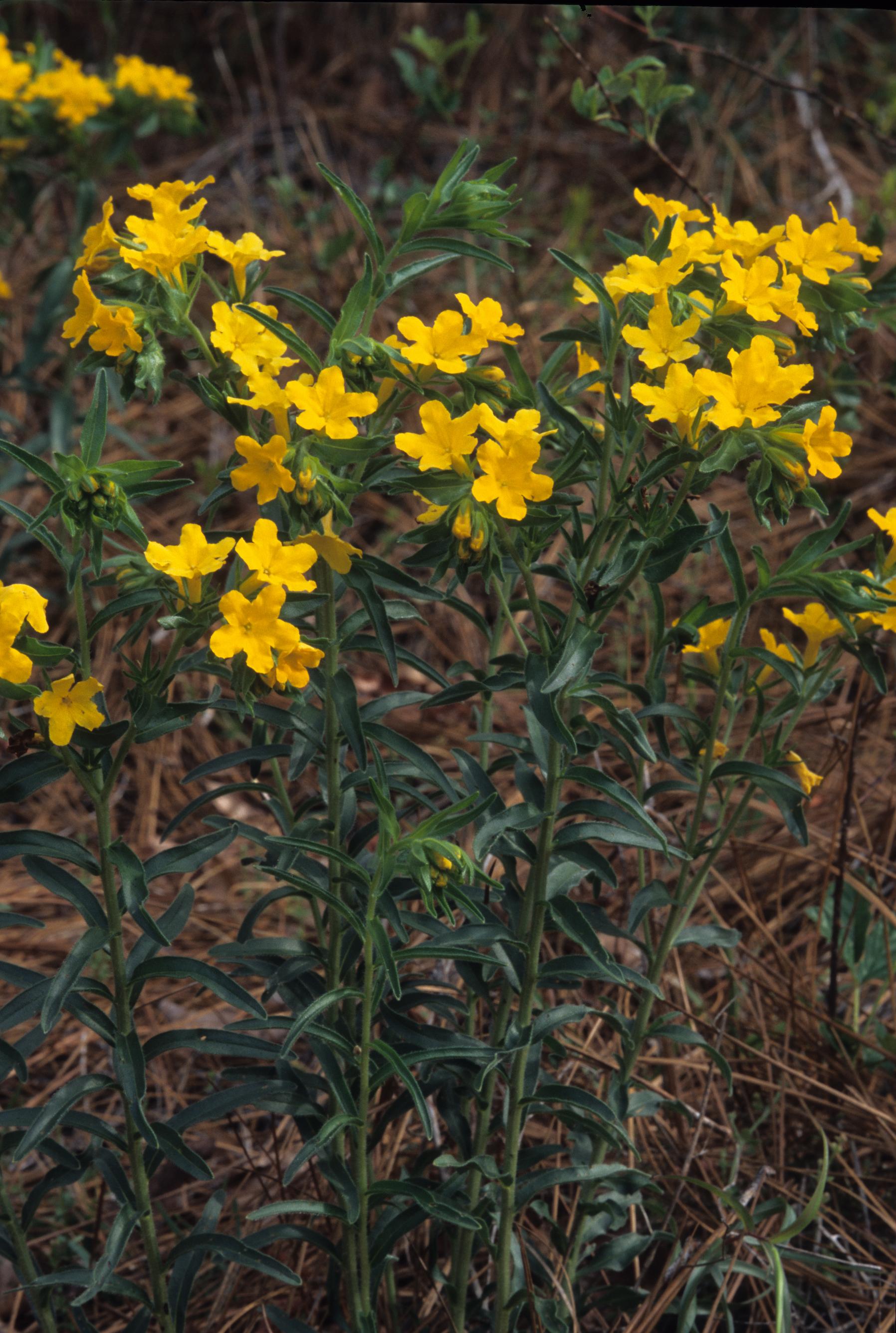

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Boraginaceae |
| Genus: | Lithospermum |
| Species: | L. caroliniense |
| Binomial name | |
| Lithospermum caroliniense Lam. | |
| |
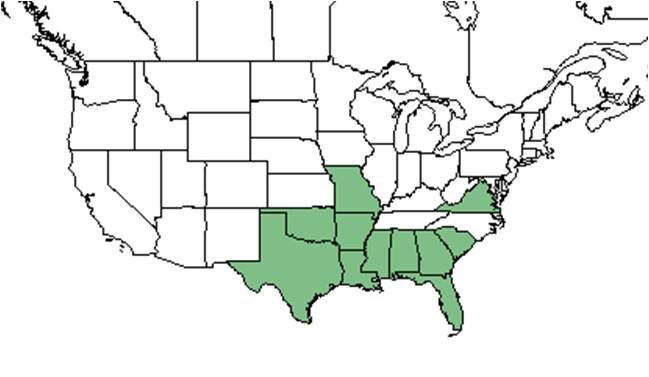
| Natural range of Lithospermum caroliniense from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Carolina puccoon, coastal plain puccoon
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Batschia caroliniensis Walter ex J.F. Gmelin; Lithospermum carolinense ssp. carolinense; L. carolinense var. carolinense[1]
Varieties: none[1]
Description
"Annual or perennial, pubescent or hispid herbs. Leaves usually alternate. Cymes leafy-bracteate, some flowers heterostylic; fruiting pedicels mostly erect or ascending. Calyx cleft into narrow lobes; corolla yellow, yellow-orange, or white (to blue), tubular to funnelform or salverform, throat pubescent, crested or open, lobes spreading and imbricate; anthers included; gynobase flat or depressed. Mericaps 4 or fewer, smooth or wrinkled, with a broad basal attachment scar, the scar often surrounded by a sharp rim."[2]
"Plant 3-10 dm tall, arising from a strong-staining taproot; stems simple or branched, very leafy, hirsute. Cymes dense, leafy-bracteate, elongate at maturity and loosely flowered; flowers heterostylic, all subtended by a bract. Calyx 6-8 mm long at anthesis, 8-10 mm long at maturity; corolla orange-yellow, funnelform, 13-25 mm long; anthers in short-styled flowers at the top of the corolla tube and just below the appendages at the throat, style extending only to the middle of tube; anther in long-styled flowers near the middle of the corolla tube, the long style reaching to and beyond the top of the tube, the appendages weakly developed at the throat; corolla nectary 1-0lobed, villous at the base of tube; stigma terminal, minutely villosulous, bilobed. Mericaps white, smooth, often pitted, 3-3.5 mm long."[2]
Distribution
This plant is a southeastern coastal plain endemic. It's found from southeastern South Carolina to Panhandle Florida, and west to Texas.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, L. caroliniense has been found in pinewoods and sand dunes. In human-disturbed areas it has occurred in cut over secondary sandhill forest and along highways.[3] Associated species include Berlandiera pumila, Chrysopsis, Licania michauxii, Cnidoscolus stimulosus, Phlox pilosa, Rubus cuneifolius, and Solidago door.[3] Soils include sand and loamy sand.[3]
Phenology
L. caroliniense flowers from April through June.[3][4]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity.[5]
Fire ecology
Populations of Lithospermum caroliniense have been known to persist through repeated annual burns.[6]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 882. Print.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Bill Anderson, Loran C. Anderson, Pam Anderson, R. Komarek, T. MacClendon, K. MacClendon, Sidney McDaniel, R. A. Norris. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Jackson, Liberty Georgia: Decatur, Dougherty. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.