Difference between revisions of "Tephrosia hispidula"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| binomial_authority = (Michx.) Pers. | | binomial_authority = (Michx.) Pers. | ||
| range_map = TEPH_HISP_dist.jpg | | range_map = TEPH_HISP_dist.jpg | ||
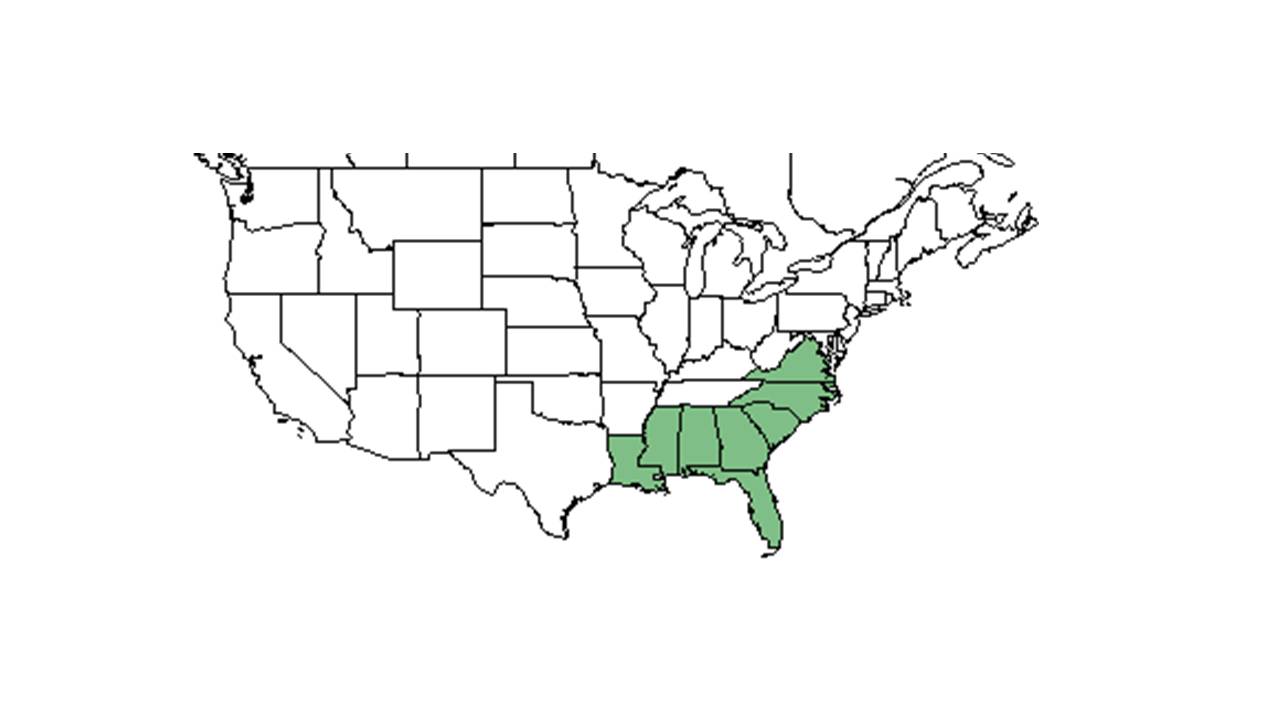
| − | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Tephrosia hispidula'' from USDA NRCS [http:// | + | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Tephrosia hispidula'' from USDA NRCS [http://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=TEHI2 Plants Database]. |
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common name: | + | Common name: Sprawling hoarypea |
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonym: ''Cracca hispidula'' (Michaux) Kuntze.<ref>Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | "Perennial herbs and shrubs with either monopodial or sympodial branching. Leaves odd-pinnate; leaflets 7-29 or rarely 1-41, entire, glabrous or pubescent above and always pubescent beneath, usually with prominent, parallel, secondary veins, estipellate, inflorescences terminal, axillary or apparently opposite a leaf, more or less racemose, with 2-10, papilionaceous, pedicellate flowers at each node with the cluster subtended by a bract and each pedicels subtended, 5-lobed, the lowers the long longest; petals clawed; stamens monadelphous or diadelphous. Legume sessile, linear, straight or slightly curved, usually compressed, nonseptate, dehiscing into 2 separate valves."<ref name="Radford et al 1964">Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 626. Print.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | "Perennial herb from a woody, fusiform taproot; stems decumbent to erct, to 5 dm long, more or less appressed to spreading short-pubescent to short-pilose. Leaves mostly 5-11 cm long; leaflets 9-23, oblong to ovate-lanceolate or narrowly elliptic, 0.7-2.2 cm long, 2-7 mm wide, glabrous to densely short-pubescent above sparsely to densely short-pubescent beneath. Inflorescences opposite the leaves, 5-15 cm long, usually longer than nearest leaf, with a terete or inconspicuously flattened peduncle or rachis and persistent, narrowly lanceolate to linear bracts; pedicels 2-8 mm long. Calyx 3-4 mm long; appressed to spreading short-pubescent; petals at first white, turning pink and then carmine (drying purplish), 1.2-1.5 cm long; stamens diadelphous. Legume 3-4.2 cm long, 4.5-6 cm broad, sparsely to moderately short-pubescent, trichomes 0.6 mm or more long."<ref name="Radford et al 1964"/> | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | + | In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''T. hispidula'' can be found in recently burned longleaf pine/wiregrass communities; pine flatwoods; sandhills; mixed pine and hardwood swamps; edges of pond cypress wetlands; pine-scrub oak-palmetto woodlands; slash pine-wiregrass woodlands; and along the shore of rivers.<ref name="Conde et al. 1983">Conde, L. F., B. F. Swindel, et al. (1983). "Plant species cover, frequency, and biomass: Early responses to clearcutting, burning, windrowing, discing, and bedding in ''Pinus elliottii'' flatwoods." Forest Ecology and Management 6: 319-331.</ref><ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Cecil R Slaughter, R. Kral. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Franklin, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Volusia, Wakulla. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref><ref name="Gliztenstein et al. 2003">Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, et al. (2003). "Fire frequency effects on longleaf pine (''Pinus palustris'', P.Miller) vegetation in South Carolina and northeast Florida, USA." Natural Areas Journal 23: 22-37.</ref> In disturbed habitats it has been found along grassy road margins, sand in open woods by a road, sandy peat of a pine flatwoods ditch, and a recently planted slash pine plantation. Substrate types include rich loamy sand, mucky sands, and dry sands.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> It has been observed to grow with ''Tephrosia chrysophylla.''<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | |
| + | |||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | ===Seed dispersal=== | + | This species has been observed to flower and fruit May through October.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021</ref> |
| − | ===Seed bank and germination=== | + | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> |
| − | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | + | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> |
| − | ===Pollination=== | + | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> |
| − | === | + | <!--===Pollination===--> |
| − | ===Diseases and parasites=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology=== <!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc.--> |
| − | ==Conservation and | + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> |
| − | == | + | |
| + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
| + | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 12:11, 18 July 2022
| Tephrosia hispidula | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Tephrosia |
| Species: | T. hispidula |
| Binomial name | |
| Tephrosia hispidula (Michx.) Pers. | |
| |
| Natural range of Tephrosia hispidula from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Sprawling hoarypea
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Cracca hispidula (Michaux) Kuntze.[1]
Description
"Perennial herbs and shrubs with either monopodial or sympodial branching. Leaves odd-pinnate; leaflets 7-29 or rarely 1-41, entire, glabrous or pubescent above and always pubescent beneath, usually with prominent, parallel, secondary veins, estipellate, inflorescences terminal, axillary or apparently opposite a leaf, more or less racemose, with 2-10, papilionaceous, pedicellate flowers at each node with the cluster subtended by a bract and each pedicels subtended, 5-lobed, the lowers the long longest; petals clawed; stamens monadelphous or diadelphous. Legume sessile, linear, straight or slightly curved, usually compressed, nonseptate, dehiscing into 2 separate valves."[2]
"Perennial herb from a woody, fusiform taproot; stems decumbent to erct, to 5 dm long, more or less appressed to spreading short-pubescent to short-pilose. Leaves mostly 5-11 cm long; leaflets 9-23, oblong to ovate-lanceolate or narrowly elliptic, 0.7-2.2 cm long, 2-7 mm wide, glabrous to densely short-pubescent above sparsely to densely short-pubescent beneath. Inflorescences opposite the leaves, 5-15 cm long, usually longer than nearest leaf, with a terete or inconspicuously flattened peduncle or rachis and persistent, narrowly lanceolate to linear bracts; pedicels 2-8 mm long. Calyx 3-4 mm long; appressed to spreading short-pubescent; petals at first white, turning pink and then carmine (drying purplish), 1.2-1.5 cm long; stamens diadelphous. Legume 3-4.2 cm long, 4.5-6 cm broad, sparsely to moderately short-pubescent, trichomes 0.6 mm or more long."[2]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, T. hispidula can be found in recently burned longleaf pine/wiregrass communities; pine flatwoods; sandhills; mixed pine and hardwood swamps; edges of pond cypress wetlands; pine-scrub oak-palmetto woodlands; slash pine-wiregrass woodlands; and along the shore of rivers.[3][4][5] In disturbed habitats it has been found along grassy road margins, sand in open woods by a road, sandy peat of a pine flatwoods ditch, and a recently planted slash pine plantation. Substrate types include rich loamy sand, mucky sands, and dry sands.[4] It has been observed to grow with Tephrosia chrysophylla.[4]
Phenology
This species has been observed to flower and fruit May through October.[4][6]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 626. Print.
- ↑ Conde, L. F., B. F. Swindel, et al. (1983). "Plant species cover, frequency, and biomass: Early responses to clearcutting, burning, windrowing, discing, and bedding in Pinus elliottii flatwoods." Forest Ecology and Management 6: 319-331.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Cecil R Slaughter, R. Kral. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Franklin, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Volusia, Wakulla. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, et al. (2003). "Fire frequency effects on longleaf pine (Pinus palustris, P.Miller) vegetation in South Carolina and northeast Florida, USA." Natural Areas Journal 23: 22-37.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021