Difference between revisions of "Phoradendron leucarpum"
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
|||
| (49 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| name = Phoradendron leucarpum | | name = Phoradendron leucarpum | ||
| − | | image = | + | | image = Phor_leuc.jpg |
| − | | image_caption = | + | | image_caption = Photo by Mary Keim, [http://www.florida.plantatlas.usf.edu/Default.aspx Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants] |
| regnum = Plantae | | regnum = Plantae | ||
| divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | | divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| binomial_authority = (Raf.) Reveal & M.C. Johnst. | | binomial_authority = (Raf.) Reveal & M.C. Johnst. | ||
| range_map = phor_leuc_dist.jpg | | range_map = phor_leuc_dist.jpg | ||
| − | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Phoradendron leucarpum'' from USDA NRCS [http:// | + | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Phoradendron leucarpum'' from USDA NRCS [http://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=PHLE14 Plants Database]. |
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common name: | + | Common name: Oak mistletoe<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonyms: ''Phoradendron flavescens'' (Pursh) Nuttall; ''P. leucarpum'' (Rafinesque) Reveal & M.C. Johnston; ''P. serotinum'' (Rafinesque) M.C. Johnston; ''P. serotinum'' (Rafinesque) M.C. Johnston ssp. ''serotinum''.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: none.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The name "mistletoe" comes from the ancient Anglo-Saxon word for dung and twig, which is derived from the observation that mistletoe often sprouts out of bird droppings on branches.<ref name="floridata">[[http://floridata.com/Plants/Loranthaceae/Phoradendron%20leucarpum/595]]Floridata Accessed: February 20, 2016</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | ''P. leucarpum'' is a clumpy, evergreen shrub that can be found growing on branches of broad-leaved trees. The leaves are opposite, thick and leathery, oval to round. Flowers are small and inconspicuous and the fruits are white.<ref name="floridata"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is a hemiparasitic species that has chlorophyll and produces it's own food, but also has modified roots that extracts water and minerals from the host tree's circulatory system.<ref name="floridata"/> It infects more than 105 tree species: broadleaf, evergreen, deciduous, and confiers.<ref name="warnell">[[https://www.warnell.uga.edu/outreach/pubs/pdf/forestry/mistletoe%20monograph%20pub%2008-25.pdf]]Warnell School of Forestry and Natural Resources. Accessed: February 20, 2016</ref> | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | ''P. leucarpum'' can be found on hardwood trees ranging from New Jersey, west to southern Ohio, southern Indiana, and southern Missouri, then south to Florida and Texas.<ref name="floridata"/><ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| + | ''Phoradendron leucarpum'' can be found in mixed hardwoods, cypress swamps, tupelo swamps, floodplain forests, and pine/oak scrubs. It is a parasitic plant that has been observed growing on ''Fraxinus, Liquidambar, Quercus nigra, Carya glabra, Prunus umbellata, Prunus angustifolia, Celtis laevigata, Quercus myrtifolia, Prunus serotina, Planera aquatica, Carya aquatica, Quercus virginiana, Acer, Morus, Populus, Ulmus'' and ''Magnolia.''<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, J. Beckner, Kathy Craddock Burks, J. Carmichael, Nancy Edmonson, Mildred E. Feagle, Angus Gholson Jr., William T. Gillis, Robert K. Godfrey, D.W. Hall, B.K. Holst, Roy N. Jervis, Beverly Judd, Walter S. Judd, Robert L. Lazor, N. Lee, Karen MacClendon, K.M. Meyer, Chas. A. Mosier, C. Morgan, John B. Nelson, Jose Luis Serna, G.K. Small, John K. Small, A. Townesmith, Chris Wall, Randy Wall, D.B. Ward. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Calhoun, Collier, Franklin, Gadsden, Hernando, Highlands, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Marion, Polk, Sarasota, Taylor, Wakulla. Georgia: Decatur, Thomas. Country: Mexico. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| + | ''P. leucarpum'' has been observed fruiting in January, March, November and December, and flowering in January, February, June, September, October, and December.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016</ref> The ripe fruit is a transluscent, pseudo-berry, that contains viscin, which allows the seed to attach to bark.<ref name="warnell"/> | ||
| + | |||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| + | The seeds are primarily dispersed by birds in excrement and regurgitation.<ref name="warnell"/> | ||
| + | |||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| + | This species does not exhibit strong seed dormancy. The translucent fruit skin must be pierced or removed to allow for seed germination.<ref name="warnell"/> | ||
| + | |||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | ''Phoradendron leucarpum'' has been observed in recently burned pine forests,<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> and has been known to persist through repeated annual burning.<ref>Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | + | ''Phoradendron leucarpum'' has been observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host wasps such as ''Mischocyttarus cubensis'' (family Vespidae)<ref name="Deyrup 2015">Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> and jumping plant lice such as ''Trioza sp.'' (family Psyllidae).<ref>Discoverlife.org [https://www.discoverlife.org/20/q?search=Bidens+albaDiscoverlife.org|Discoverlife.org]</ref> | |
| − | + | ===Herbivory and toxicology=== <!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc--> | |
| + | The fruit is eaten by birds. This plant is poisonous to humans.<ref name="floridata"/> | ||
| − | |||
===Diseases and parasites=== | ===Diseases and parasites=== | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | This species is hemiparasitic, it has chlorophyll and produces its own food, however, it has modified roots that steal water and minerals from the host tree's circulatory system.<ref name="floridata"/> It causes wood decay, branch death, discoloration and allows for animal and pathogenic entry points into a tree. It is found to infect more than 105 tree species which include broadleaf, evergreen, deciduous, and conifers. It is an obligate parasite and can not grow or survive on dead trees.<ref name="warnell"/> In a study by Panvini and Eickmeier (1993) they found that the nutrients obtained by ''P. leucarpum'' and actively aquired, meaning nutrient acquisition and water flow are not tightly coupled. They also found that ''P. leucarpum'' nutrient status was dependent upon the nutrient condition of the host tree. In another study by Gougherty (2013) it was found that larger trees have a larger mistletoe infestation. This could be due to more perching and foraging of birds. |
| − | == | + | |
| + | There are pests that infect ''P. leucarpum'', these include hickory horned-devil/royal walnut moth (''Citheronia regalis'') and the great blue hairstreak butterfly (''Atlides halesus'').<ref name="warnell"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
| + | There is a custom of kissing underneath the mistletoe. Native Americans have been thought to use infusions of mistletoe roots and berries to induce abortion and externally relieve rheumatism.<ref name="floridata"/> | ||
| + | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
| + | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Gougherty, A. V. (2013). "Spatial distribution of eastern mistletoe phoradendron leucarpum, viscaceae in an urban environment." Journal of the Alabama Academy of Science 84(3-4): 155+. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Panvini, A. D. and W. G. Eickmeier (1993). "Nutrient and Water Relations of the Mistletoe Phoradendron leucarpum (Viscaceae): How Tightly are they Integrated?" American Journal of Botany 80(8): 872-878. | ||
Latest revision as of 12:32, 15 July 2022
| Phoradendron leucarpum | |
|---|---|
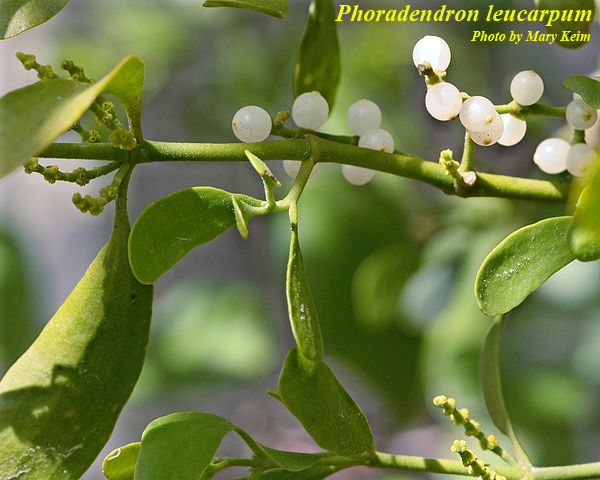

| |
| Photo by Mary Keim, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Santalales |
| Family: | Viscaceae |
| Genus: | Phoradendron |
| Species: | P. leucarpum |
| Binomial name | |
| Phoradendron leucarpum (Raf.) Reveal & M.C. Johnst. | |
| |
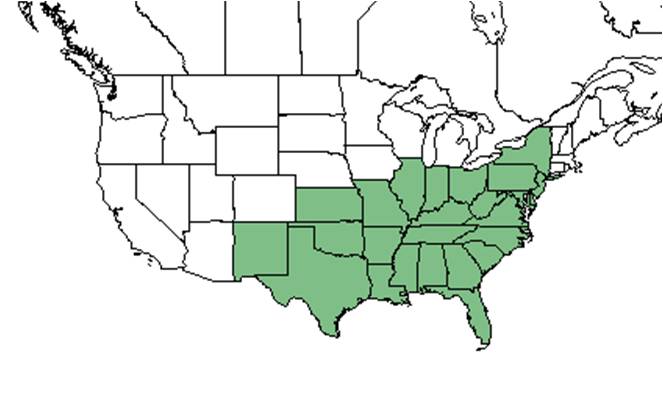
| Natural range of Phoradendron leucarpum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Oak mistletoe[1]
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Phoradendron flavescens (Pursh) Nuttall; P. leucarpum (Rafinesque) Reveal & M.C. Johnston; P. serotinum (Rafinesque) M.C. Johnston; P. serotinum (Rafinesque) M.C. Johnston ssp. serotinum.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
The name "mistletoe" comes from the ancient Anglo-Saxon word for dung and twig, which is derived from the observation that mistletoe often sprouts out of bird droppings on branches.[2]
Description
P. leucarpum is a clumpy, evergreen shrub that can be found growing on branches of broad-leaved trees. The leaves are opposite, thick and leathery, oval to round. Flowers are small and inconspicuous and the fruits are white.[2]
It is a hemiparasitic species that has chlorophyll and produces it's own food, but also has modified roots that extracts water and minerals from the host tree's circulatory system.[2] It infects more than 105 tree species: broadleaf, evergreen, deciduous, and confiers.[3]
Distribution
P. leucarpum can be found on hardwood trees ranging from New Jersey, west to southern Ohio, southern Indiana, and southern Missouri, then south to Florida and Texas.[2][1]
Ecology
Habitat
Phoradendron leucarpum can be found in mixed hardwoods, cypress swamps, tupelo swamps, floodplain forests, and pine/oak scrubs. It is a parasitic plant that has been observed growing on Fraxinus, Liquidambar, Quercus nigra, Carya glabra, Prunus umbellata, Prunus angustifolia, Celtis laevigata, Quercus myrtifolia, Prunus serotina, Planera aquatica, Carya aquatica, Quercus virginiana, Acer, Morus, Populus, Ulmus and Magnolia.[4]
Phenology
P. leucarpum has been observed fruiting in January, March, November and December, and flowering in January, February, June, September, October, and December.[4][5] The ripe fruit is a transluscent, pseudo-berry, that contains viscin, which allows the seed to attach to bark.[3]
Seed dispersal
The seeds are primarily dispersed by birds in excrement and regurgitation.[3]
Seed bank and germination
This species does not exhibit strong seed dormancy. The translucent fruit skin must be pierced or removed to allow for seed germination.[3]
Fire ecology
Phoradendron leucarpum has been observed in recently burned pine forests,[4] and has been known to persist through repeated annual burning.[6]
Pollination
Phoradendron leucarpum has been observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host wasps such as Mischocyttarus cubensis (family Vespidae)[7] and jumping plant lice such as Trioza sp. (family Psyllidae).[8]
Herbivory and toxicology
The fruit is eaten by birds. This plant is poisonous to humans.[2]
Diseases and parasites
This species is hemiparasitic, it has chlorophyll and produces its own food, however, it has modified roots that steal water and minerals from the host tree's circulatory system.[2] It causes wood decay, branch death, discoloration and allows for animal and pathogenic entry points into a tree. It is found to infect more than 105 tree species which include broadleaf, evergreen, deciduous, and conifers. It is an obligate parasite and can not grow or survive on dead trees.[3] In a study by Panvini and Eickmeier (1993) they found that the nutrients obtained by P. leucarpum and actively aquired, meaning nutrient acquisition and water flow are not tightly coupled. They also found that P. leucarpum nutrient status was dependent upon the nutrient condition of the host tree. In another study by Gougherty (2013) it was found that larger trees have a larger mistletoe infestation. This could be due to more perching and foraging of birds.
There are pests that infect P. leucarpum, these include hickory horned-devil/royal walnut moth (Citheronia regalis) and the great blue hairstreak butterfly (Atlides halesus).[3]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
There is a custom of kissing underneath the mistletoe. Native Americans have been thought to use infusions of mistletoe roots and berries to induce abortion and externally relieve rheumatism.[2]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Gougherty, A. V. (2013). "Spatial distribution of eastern mistletoe phoradendron leucarpum, viscaceae in an urban environment." Journal of the Alabama Academy of Science 84(3-4): 155+.
Panvini, A. D. and W. G. Eickmeier (1993). "Nutrient and Water Relations of the Mistletoe Phoradendron leucarpum (Viscaceae): How Tightly are they Integrated?" American Journal of Botany 80(8): 872-878.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 [[1]]Floridata Accessed: February 20, 2016
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 [[2]]Warnell School of Forestry and Natural Resources. Accessed: February 20, 2016
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, J. Beckner, Kathy Craddock Burks, J. Carmichael, Nancy Edmonson, Mildred E. Feagle, Angus Gholson Jr., William T. Gillis, Robert K. Godfrey, D.W. Hall, B.K. Holst, Roy N. Jervis, Beverly Judd, Walter S. Judd, Robert L. Lazor, N. Lee, Karen MacClendon, K.M. Meyer, Chas. A. Mosier, C. Morgan, John B. Nelson, Jose Luis Serna, G.K. Small, John K. Small, A. Townesmith, Chris Wall, Randy Wall, D.B. Ward. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Calhoun, Collier, Franklin, Gadsden, Hernando, Highlands, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Marion, Polk, Sarasota, Taylor, Wakulla. Georgia: Decatur, Thomas. Country: Mexico. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [3]