Difference between revisions of "Hibiscus aculeatus"
(Created page with "{{italic title}} <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> {{taxobox | name = Hibiscus aculeatus | image = | image_caption = 'Hibiscus aculeatus'' |...") |
|||
| (44 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | Common name: comfort-root; savanna Hibiscus | ||
{{italic title}} | {{italic title}} | ||
<!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| name = Hibiscus aculeatus | | name = Hibiscus aculeatus | ||
| − | | image = | + | | image = File:Hibiscus_aculeatus.jpg|''Hibiscus aculeatus'' Photo by Katelin Stanley |
| − | | image_caption = 'Hibiscus aculeatus'' | + | | image_caption = ''Hibiscus aculeatus'' |
| regnum = Plantae | | regnum = Plantae | ||
| divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | | divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | ||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
| species = '''''H. aculeatus''''' | | species = '''''H. aculeatus''''' | ||
| binomial = ''Hibiscus aculeatus'' | | binomial = ''Hibiscus aculeatus'' | ||
| − | | binomial_authority = | + | | binomial_authority = Walter |
| − | | range_map = | + | | range_map = HIBI_ACUL_dist.jpg |
| − | | range_map_caption = Natural range of '' | + | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Hibiscus aculeatus'' from USDA NRCS [http://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=HIAC Plants Database]. |
}} | }} | ||
| + | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonym: none.<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: none<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | "Shrubs or perennial or annual herbs with stellate pubescence. Leaves unlobed to palmately lobed or dissected; petioles usually long; stipules present, usually caduceus flowers solitary in the upper leaf axils, or in terminal racemes; peduncles and pedicels present or the peduncle obsolete, often elongating in fruit. Involucral bracts 7-15, linear. Sepals 5, widely triangular to triangular-lanceolate, enlarged in fruit; petals oblanceolate to obovate, apex rounded; stamens usually numerous; stigmas 5, capitate, styles free near apex. Capsule 5-locular." <ref name="Radford et al 1964">Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 704-6. Print.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | "Perennial with spreading-ascending or, less frequently erect branches to 1m tall. Trichomes of stems, petioles, leaves and pedicels short, bristly, stellate, scabrous. Leaves palmately 3-5 cleft or lobed, 3-9 cm long, mostly wider than long, coarsely and irregularly serrate, truncate to cleft with an inverted broad, V-shaped sinus; petioles 2-10 cm long. Flowers in leafly-bracteate racemes, bracts less divided than the leaves or entire; peduncles obsolete or to 2 mm long; pedicels 5-12 mm long, elongated slightly in fruit, usually with a few long white trichomes; Involucral bracts 8-10, linear, 1-2 cm long, usually palmately or pinnately cleft at apex. Calyx lobes triangular-lanceolate, 8-12 mm long, acute, elongated in fruit, distinctly keeled to the apex and with a thickened margin resembling the keel, pubescent with long stiff, postulate-based trichomes; petals cream, turning a deeper yellow and finally fading to pink, crimson marked at base, 5-6 cm long. Capsule gradually contracted to a beak, 1.7-2 cm long, pubescent with mixed short and long, bristle-like trichomes. Seeds brown, with fine reticulations and with a few whitish papillate, 3.5-4 mm long." <ref name="Radford et al 1964"/> | ||
| + | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | ''Hibiscus aculeatus'' is found along the southeastern coastal plain, from North Carolina south to Florida and west to Texas.<ref name= "USDA">USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 22 May 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.</ref> Within this distribution, it is found from southeastern North Carolina south to south central peninsular Florida and west to Louisiana and Texas.<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
| + | |||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | + | Generally, ''Hibiscus aculeatus'' can be found in pine savannas and dry loamy or sandy soils found in maritime forests.<ref name=weakley/> Otherwise it is found in plains, prairies, pastures, meadows, and woodland openings or edges. It prefers full sun or partial shade, soil that is slightly acidic, and can withstand winter flooding.<ref name= "lady bird">[[https://www.wildflower.org/plants/search.php?search_field=&newsearch=true]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: May 22, 2019</ref> Also, it has been observed in a variety of habitats including open canopy of pine-wood woodlands, roadbanks and roadsides, ditches, pond and stream margins, flatwoods, sandhills, riverbanks, swales, open and hillside bogs, various low lying areas, and other disturbed areas. Soils include sandy peat, moist and dry loamy sand, calcareous soil, moist sandy loam, and other similar sandy soils.<ref name= "herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2019. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, A. H. Curtiss, J. P. Gillespie, Robert K. Godfrey, Bruce Hansen, C. Jackson, Darren Jackson, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, Gary R. Knight, R. Komarek, Robert Kral, S. W. Leonard, Karen MacClendon, Travis MacClendon, Sidney McDaniel, M. Y. Menzel, Richard S. Mitchell, T. Myint, Leon Neel, R. A. Norris, Kevin Oakes, Gwynn W. Ramsey, P. L. Redfearn, Jr., D. B. Ward, and F. D. Wilson. States and Counties: Alabama: Conecuh. Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Escambia, Franklin, Holmes, Jackson, Lafayette, Leon, Madison, Nassau, Okaloosa, Santa Rosa, Taylor, and Wakulla. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.</ref> It is listed by the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service as a facultative wetland species, where it most often can be found in wetland habitats but can also occasionally occur in non-wetland habitats.<ref name= "USDA"/> One study found ''H. aculeatus'' to be more affected by clearcutting the overstory rather than thinning the overstory.<ref>Brockway, D. G. and C. E. Lewis (2003). "Influence of deer, cattle grazing and timber harvest on plant species diversity in a longleaf pine bluestem ecosystem." Forest Ecology and Management 175: 49-69.</ref> As well, it is considered an indicator species of the north Florida upper panhandle savannas.<ref name= "Carr">Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189.</ref> |
| − | ===Seed dispersal=== | + | |
| − | ===Seed bank and germination=== | + | Associated species includes ''Buchnera floridana'', ''Hypericum opacum'', ''Eryngium integrifolium'', ''Xyris elliottii'', ''Habenaria integra'', ''Polygala ramosa'', ''Polygala lutea'', ''Ctenium aromaticum'', '''''Hibiscus aculeatus''''', and others.<ref name= "herbarium"/> |
| + | |||
| + | ''Hibiscus aculeatus'' is an indicator species for the Upper Panhandle Savannas community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| + | ''H. aculeatus'' generally flowers from June until August, and fruits from July until September.<ref name=weakley/> It has been observed to flower May to September with peak inflorescence in July.<ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016</ref> | ||
| + | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
| + | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| + | |||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | It is a component of ecosystems that are fire-dependent.<ref name= "Carr"/> A study by Kush found ''H. aculeatus'' to benefit most from summer burn regiments rather than winter or spring burn regiments.<ref>Kush, J. S., et al. (2000). Understory plant community response to season of burn in natural longleaf pine forests. Proceedings 21st Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference. Fire and forest ecology: innovative silviculture & vegetation management, Tallahassee, FL, Tall Timbers Research, Inc.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | === | + | Bumble bees have been observed to visit and pollinate this species.<ref>Pitts-Singer, T. L., et al. (2002). "Insect pollinators of three rare plants in a Florida longleaf pine forest." Florida Entomologist 85(2): 308-316.</ref> More specifically, this species has been observed to host bees such as ''Ptilothrix bombiformis'' (family Apidae).<ref>Discoverlife.org [https://www.discoverlife.org/20/q?search=Bidens+albaDiscoverlife.org|Discoverlife.org]</ref> |
| − | ===Diseases and parasites=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> |
| − | ==Conservation and | + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> |
| − | == | + | |
| + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
| + | It is listed as G4 on the global scale due to its distribution and the fact that it is considered critically imperiled in North Carolina.<ref>[[http://explorer.natureserve.org]] NatureServe Explorer. Accessed: May 22, 2019</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | For easy maintenance, this plant can be cut to the base after a frost for successful resprouting.<ref name= "lady bird"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
| + | The roots have been used as a soothing agent leading to the name "comfortroot".<ref>Denhof, Carol. 2017. Plant Spotlight Hibiscus Aculeatus Comfortroot. The Longleaf Leader - Public Lands Restoration. Vol. X. Iss. 2. Page 6</ref><ref>Miller, J.H. and K.V. Miller. Forest Plants of the Southeast and their Wildlife Uses. The University of Georgia Press, Atehns, GA. 454pp.</ref><ref>Xerces Society. 2011. Attracting Native Pollinators-Protecting North America's Bees and Butterflies. Story Publishing, North Adams, MA.</ref><ref>USDA, NRCS. 2017 The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 21 April 2017). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 17:06, 30 May 2023
Common name: comfort-root; savanna Hibiscus
| Hibiscus aculeatus | |
|---|---|
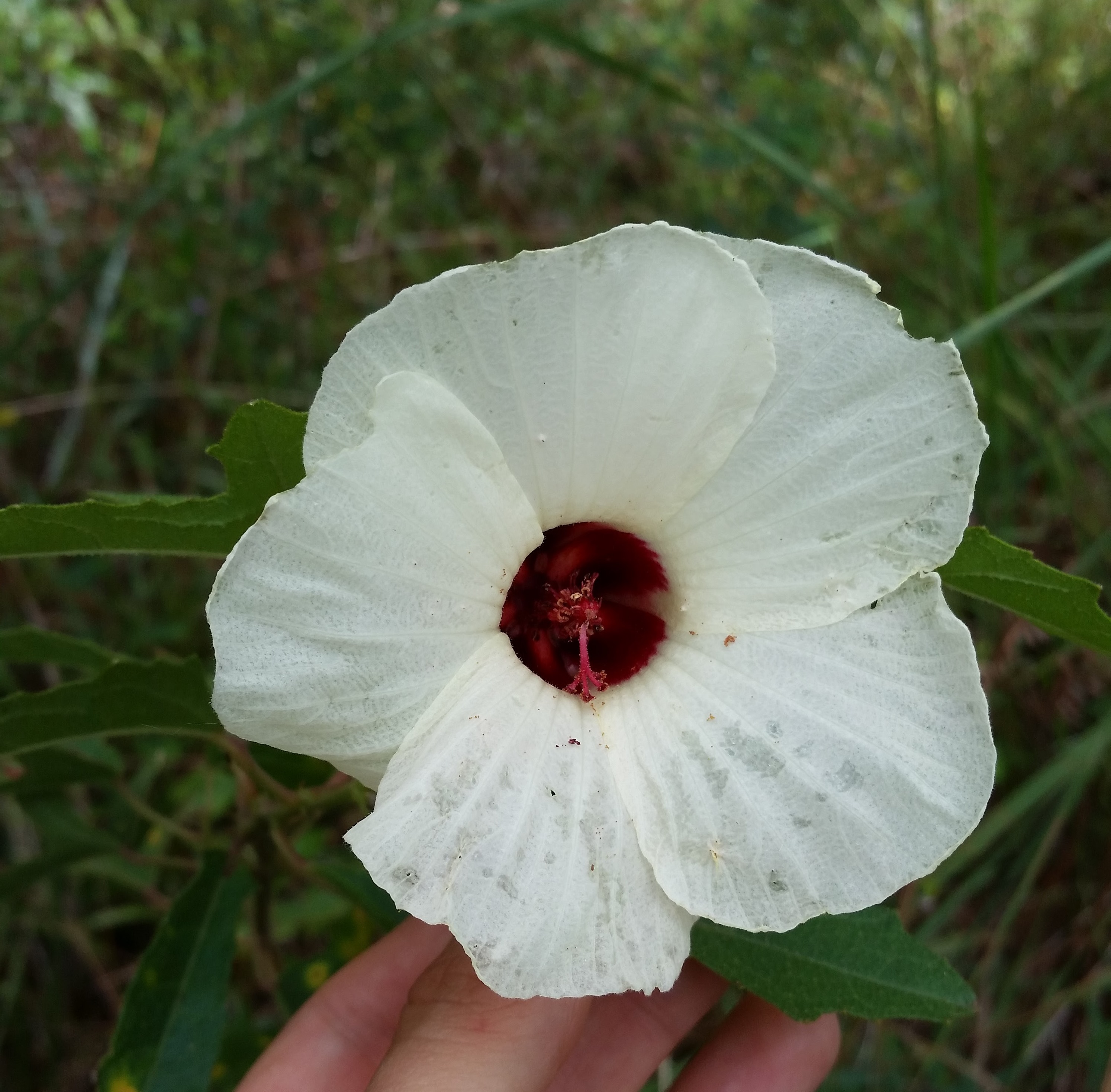

| |
| Hibiscus aculeatus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Dicots |
| Order: | Malvales |
| Family: | Malvaceae |
| Genus: | Hibiscus |
| Species: | H. aculeatus |
| Binomial name | |
| Hibiscus aculeatus Walter | |
| |
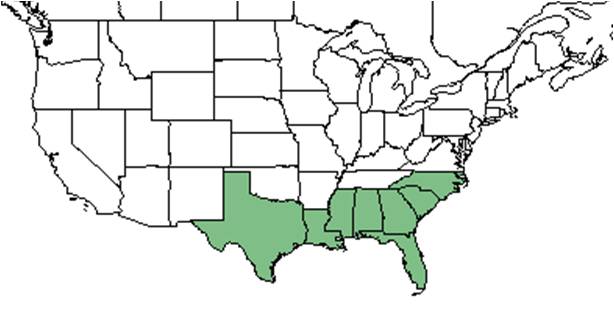
| Natural range of Hibiscus aculeatus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: none.[1]
Varieties: none[1]
Description
"Shrubs or perennial or annual herbs with stellate pubescence. Leaves unlobed to palmately lobed or dissected; petioles usually long; stipules present, usually caduceus flowers solitary in the upper leaf axils, or in terminal racemes; peduncles and pedicels present or the peduncle obsolete, often elongating in fruit. Involucral bracts 7-15, linear. Sepals 5, widely triangular to triangular-lanceolate, enlarged in fruit; petals oblanceolate to obovate, apex rounded; stamens usually numerous; stigmas 5, capitate, styles free near apex. Capsule 5-locular." [2]
"Perennial with spreading-ascending or, less frequently erect branches to 1m tall. Trichomes of stems, petioles, leaves and pedicels short, bristly, stellate, scabrous. Leaves palmately 3-5 cleft or lobed, 3-9 cm long, mostly wider than long, coarsely and irregularly serrate, truncate to cleft with an inverted broad, V-shaped sinus; petioles 2-10 cm long. Flowers in leafly-bracteate racemes, bracts less divided than the leaves or entire; peduncles obsolete or to 2 mm long; pedicels 5-12 mm long, elongated slightly in fruit, usually with a few long white trichomes; Involucral bracts 8-10, linear, 1-2 cm long, usually palmately or pinnately cleft at apex. Calyx lobes triangular-lanceolate, 8-12 mm long, acute, elongated in fruit, distinctly keeled to the apex and with a thickened margin resembling the keel, pubescent with long stiff, postulate-based trichomes; petals cream, turning a deeper yellow and finally fading to pink, crimson marked at base, 5-6 cm long. Capsule gradually contracted to a beak, 1.7-2 cm long, pubescent with mixed short and long, bristle-like trichomes. Seeds brown, with fine reticulations and with a few whitish papillate, 3.5-4 mm long." [2]
Distribution
Hibiscus aculeatus is found along the southeastern coastal plain, from North Carolina south to Florida and west to Texas.[3] Within this distribution, it is found from southeastern North Carolina south to south central peninsular Florida and west to Louisiana and Texas.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
Generally, Hibiscus aculeatus can be found in pine savannas and dry loamy or sandy soils found in maritime forests.[1] Otherwise it is found in plains, prairies, pastures, meadows, and woodland openings or edges. It prefers full sun or partial shade, soil that is slightly acidic, and can withstand winter flooding.[4] Also, it has been observed in a variety of habitats including open canopy of pine-wood woodlands, roadbanks and roadsides, ditches, pond and stream margins, flatwoods, sandhills, riverbanks, swales, open and hillside bogs, various low lying areas, and other disturbed areas. Soils include sandy peat, moist and dry loamy sand, calcareous soil, moist sandy loam, and other similar sandy soils.[5] It is listed by the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service as a facultative wetland species, where it most often can be found in wetland habitats but can also occasionally occur in non-wetland habitats.[3] One study found H. aculeatus to be more affected by clearcutting the overstory rather than thinning the overstory.[6] As well, it is considered an indicator species of the north Florida upper panhandle savannas.[7]
Associated species includes Buchnera floridana, Hypericum opacum, Eryngium integrifolium, Xyris elliottii, Habenaria integra, Polygala ramosa, Polygala lutea, Ctenium aromaticum, Hibiscus aculeatus, and others.[5]
Hibiscus aculeatus is an indicator species for the Upper Panhandle Savannas community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[8]
Phenology
H. aculeatus generally flowers from June until August, and fruits from July until September.[1] It has been observed to flower May to September with peak inflorescence in July.[9]
Fire ecology
It is a component of ecosystems that are fire-dependent.[7] A study by Kush found H. aculeatus to benefit most from summer burn regiments rather than winter or spring burn regiments.[10]
Pollination
Bumble bees have been observed to visit and pollinate this species.[11] More specifically, this species has been observed to host bees such as Ptilothrix bombiformis (family Apidae).[12]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
It is listed as G4 on the global scale due to its distribution and the fact that it is considered critically imperiled in North Carolina.[13]
For easy maintenance, this plant can be cut to the base after a frost for successful resprouting.[4]
Cultural use
The roots have been used as a soothing agent leading to the name "comfortroot".[14][15][16][17]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 704-6. Print.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 22 May 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 [[1]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: May 22, 2019
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2019. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, A. H. Curtiss, J. P. Gillespie, Robert K. Godfrey, Bruce Hansen, C. Jackson, Darren Jackson, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, Gary R. Knight, R. Komarek, Robert Kral, S. W. Leonard, Karen MacClendon, Travis MacClendon, Sidney McDaniel, M. Y. Menzel, Richard S. Mitchell, T. Myint, Leon Neel, R. A. Norris, Kevin Oakes, Gwynn W. Ramsey, P. L. Redfearn, Jr., D. B. Ward, and F. D. Wilson. States and Counties: Alabama: Conecuh. Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Escambia, Franklin, Holmes, Jackson, Lafayette, Leon, Madison, Nassau, Okaloosa, Santa Rosa, Taylor, and Wakulla. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.
- ↑ Brockway, D. G. and C. E. Lewis (2003). "Influence of deer, cattle grazing and timber harvest on plant species diversity in a longleaf pine bluestem ecosystem." Forest Ecology and Management 175: 49-69.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kush, J. S., et al. (2000). Understory plant community response to season of burn in natural longleaf pine forests. Proceedings 21st Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference. Fire and forest ecology: innovative silviculture & vegetation management, Tallahassee, FL, Tall Timbers Research, Inc.
- ↑ Pitts-Singer, T. L., et al. (2002). "Insect pollinators of three rare plants in a Florida longleaf pine forest." Florida Entomologist 85(2): 308-316.
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [2]
- ↑ [[3]] NatureServe Explorer. Accessed: May 22, 2019
- ↑ Denhof, Carol. 2017. Plant Spotlight Hibiscus Aculeatus Comfortroot. The Longleaf Leader - Public Lands Restoration. Vol. X. Iss. 2. Page 6
- ↑ Miller, J.H. and K.V. Miller. Forest Plants of the Southeast and their Wildlife Uses. The University of Georgia Press, Atehns, GA. 454pp.
- ↑ Xerces Society. 2011. Attracting Native Pollinators-Protecting North America's Bees and Butterflies. Story Publishing, North Adams, MA.
- ↑ USDA, NRCS. 2017 The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 21 April 2017). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.