Difference between revisions of "Juncus repens"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: none | + | Synonyms: none<ref name=weakley/> |
| − | Varieties: none | + | Varieties: none<ref name=weakley/> |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | The main communities include streams, ponds, lakes, ditches, wet depressions in flatwoods, and cypress savannahs.<ref name= | + | The main communities include streams, ponds, lakes, ditches, wet depressions in flatwoods, and cypress savannahs.<ref name=weakley/> ''J. repens'' has been observed in moist loamy soil of oak-hickory woods, in shallow ditches, in cabbage palm hammocks, in wet muck disturbed sites, and muddy depressions.<ref name= "Herbarium"> Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R. A. Norris, N. Hotchkiss, R. F. Doren, Robert K. Godfrey, Loran C. Anderson, Lisa Keppner, Cecil R. Slaughter, and Floyd Griffith. States and counties: Florida: Volusia, Leon, Washington, Osceola, St Johns, Jackson, and Jefferson. Georgia: Atkinson, Grady, and Thomas. </ref> |
Associated species - ''Taxodium'' spp.<ref name= "Herbarium"/> | Associated species - ''Taxodium'' spp.<ref name= "Herbarium"/> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:31, 2 June 2023
Common names: creeping rush[1]
| Juncus repens | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by the Southeastern Flora Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Juncales |
| Family: | Juncaceae |
| Genus: | Juncus |
| Species: | J. repens |
| Binomial name | |
| Juncus repens Michx. | |
| |
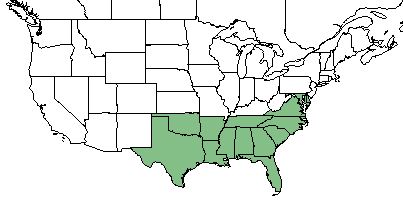
| Natural range of Juncus repens from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: none[1]
Varieties: none[1]
Description
J. repens, also known as lesser creeping rush, is a native annual perennial with a graminoid growth habit that is in the Juncaceae family. It contains rhizomatous growth for rapid clonal reproduction as well. The mature height can reach up to 6.8 feet, yet a short lifespan.[2]
Distribution
J. repens can be found along the Gulf of Mexico coast and Atlantic coast in the Southeast United States, ranging from east Texas to Virginia and Maryland[2] with disjunct populations in western Cuba.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
The main communities include streams, ponds, lakes, ditches, wet depressions in flatwoods, and cypress savannahs.[1] J. repens has been observed in moist loamy soil of oak-hickory woods, in shallow ditches, in cabbage palm hammocks, in wet muck disturbed sites, and muddy depressions.[4]
Associated species - Taxodium spp.[4]
Phenology
Flowering time begins in June and continues into October.[4]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 USDA Plants Database URL: https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=JURE2
- ↑ Sorrie, B. A. and A. S. Weakley 2001. Coastal Plain valcular plant endemics: Phytogeographic patterns. Castanea 66: 50-82.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R. A. Norris, N. Hotchkiss, R. F. Doren, Robert K. Godfrey, Loran C. Anderson, Lisa Keppner, Cecil R. Slaughter, and Floyd Griffith. States and counties: Florida: Volusia, Leon, Washington, Osceola, St Johns, Jackson, and Jefferson. Georgia: Atkinson, Grady, and Thomas. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Herbarium" defined multiple times with different content