Difference between revisions of "Vernonia gigantea"
(→Conservation and Management) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common | + | Common names: Giant ironweed, Common ironweed |
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: '' | + | Synonyms: ''V. altissima'' Nuttal; ''V. altissima'' var. ''taeniotricha''.<ref>Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | In the Coastal Plain, ''V. gigantea'' has been found in loam soil atop of a ravine; loamy sand in mesic hardwoods; river hammocks; marshes; floodplain forests; upland mixed forest; shortleaf pine-post &red oak-mockernut woods; pine-oak-hickory woods in a ravine; annually burned upland pineland; calcareous slopes; sandy loam in mature hardwoods; sandy open live oak hammocks; sand beneath cabbage palm thicket; calcareous mixed flatwoods hammocks; hammock surrounded by marsh; lowland forests habitats; and sandy peat in a clearing of cabbage palm-live oak hammock | + | In the Coastal Plain, ''V. gigantea'' has been found in loam soil atop of a ravine; loamy sand in mesic hardwoods; river hammocks; marshes; floodplain forests; upland mixed forest; shortleaf pine-post &red oak-mockernut woods; pine-oak-hickory woods in a ravine; annually burned upland pineland; calcareous slopes; sandy loam in mature hardwoods; sandy open live oak hammocks; sand beneath cabbage palm thicket; calcareous mixed flatwoods hammocks; hammock surrounded by marsh; lowland forests habitats; and sandy peat in a clearing of cabbage palm-live oak hammock.<ref name="Emery et al. 2011">Emery, S. M., J. Uwimbabazi, et al. (2011). "Fire intensity effects on seed germination of native and invasive Eastern deciduous forest understory plants." Forest Ecology and Management 261: 1401-1408.</ref><ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, Robert L. Lazor, Gary R. Knight, R. Kral, P. L. Redfearn, Jr., R. F. Thorne, R. A. Davidson, Brenda Herring, Don Herring, R. A. Norris, Andre F. Clewell, Sidney McDaniel, R. Komarek, Lisa Keppner, S. W. Leonard, Richard S. Mitchell, D. S. Correll, Grady W. Reinert. States and Counties: Florida: Brevard, Calhoun, Citrus, Dixie, Escambia, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Gilchrist, Gulf, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Nassau, Polk, Putnam, Seminole, St. Johns, Suwannee, Taylor, Wakulla, Washington. Georgia: Thomas. Mississippi: Holmes. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> It is found in disturbed successional areas<ref name="Emery et al. 2011"/> along with moist loam of roadside depressions; loamy sand along edge of channel; open mixed hardwood forest between power-line and road; along powerline corridors; and grassy clearings of pine-palmetto flats. Substrate types include loam, loamy sand, sandy loam, calcareous soils, limestone, sand, and sandy peat.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
| − | Associated species include ''Eupatorium fisulosum, Arnoflossum ovatum, Smilax bona-nox, Morus rubra, Campsis radicans'', and cabbage palm | + | Associated species include ''Eupatorium fisulosum, Arnoflossum ovatum, Smilax bona-nox, Morus rubra, Campsis radicans'', and cabbage palm.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | + | This species has been observed to flower January through November<ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021</ref> and fruits June through November.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | |
| + | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
| − | |||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| − | Heating at low temperatures stimulates germination in ''V. gigantea'' | + | Heating at low temperatures stimulates germination in ''V. gigantea.''<ref name="Emery et al. 2011"/> |
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | It has been observed to thrive after low-intensity fires | + | It has been observed to thrive after low-intensity fires.<ref name="Emery et al. 2011"/> |
| − | + | ||
| − | <!--=== | + | ===Pollination=== |
| + | ''Vernonia gigantea'' has been observed with bees such as ''Xylocopa virginica'' (family Apidae), leafcutting bees from the Megachilidae family such as ''Megachile brevis, M. latimanus, M. mendica,'' and ''M. perihirta'', and plant bugs such as ''Lygus lineolaris'' (family Miridae).<ref>Discoverlife.org [https://www.discoverlife.org/20/q?search=Bidens+albaDiscoverlife.org|Discoverlife.org]</ref> | ||
| + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology=== <!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc.--> | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| + | |||
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | |||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 17:21, 18 July 2022
| Vernonia gigantea | |
|---|---|
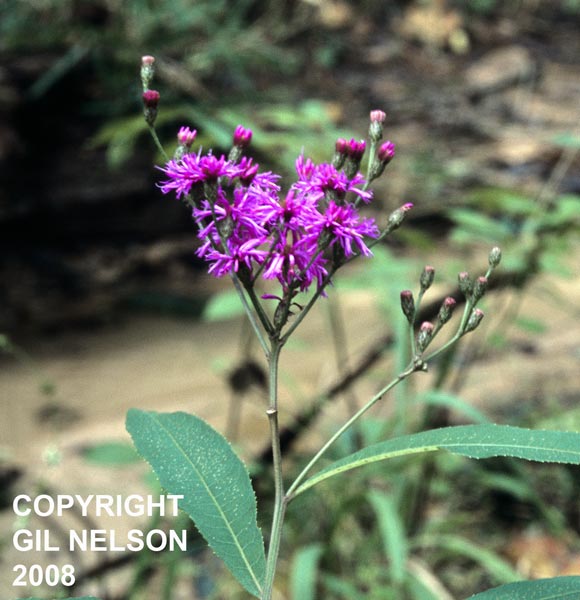

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Vernonia |
| Species: | V. gigantea |
| Binomial name | |
| Vernonia gigantea (Walter) Trel. | |
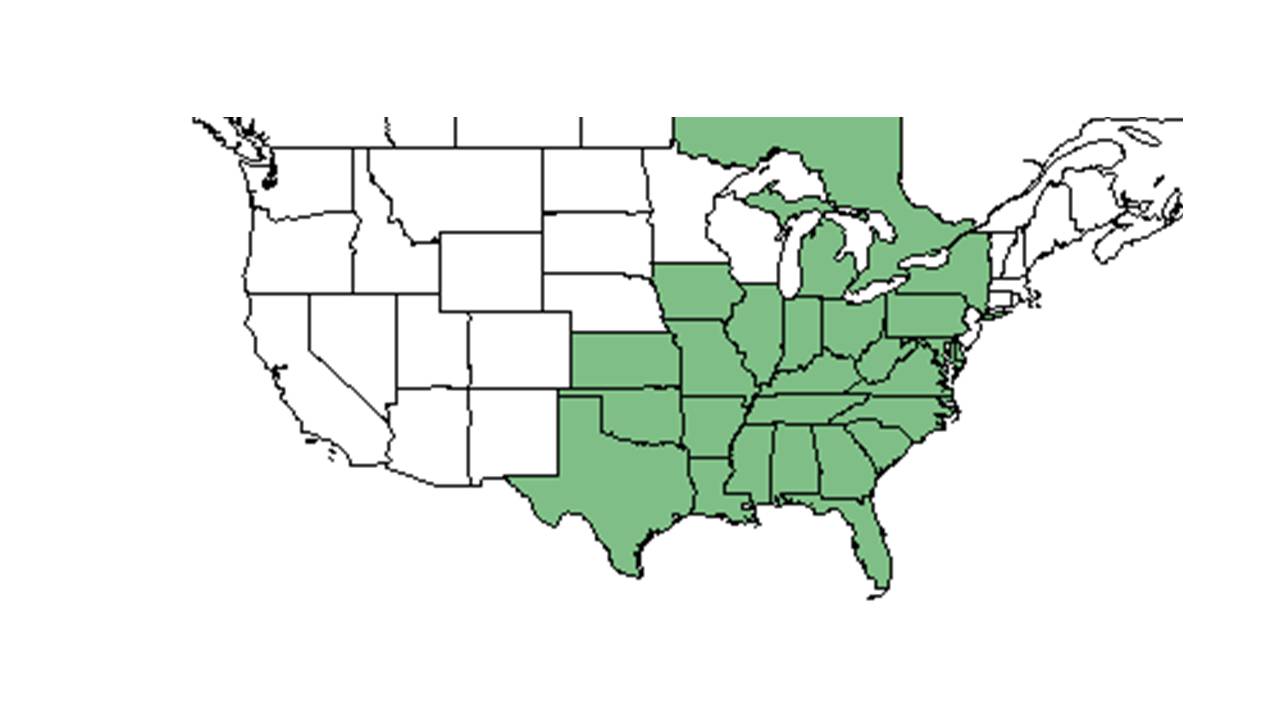
| |
| Natural range of Vernonia gigantea from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Giant ironweed, Common ironweed
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: V. altissima Nuttal; V. altissima var. taeniotricha.[1]
Description
A description of Vernonia gigantea is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain, V. gigantea has been found in loam soil atop of a ravine; loamy sand in mesic hardwoods; river hammocks; marshes; floodplain forests; upland mixed forest; shortleaf pine-post &red oak-mockernut woods; pine-oak-hickory woods in a ravine; annually burned upland pineland; calcareous slopes; sandy loam in mature hardwoods; sandy open live oak hammocks; sand beneath cabbage palm thicket; calcareous mixed flatwoods hammocks; hammock surrounded by marsh; lowland forests habitats; and sandy peat in a clearing of cabbage palm-live oak hammock.[2][3] It is found in disturbed successional areas[2] along with moist loam of roadside depressions; loamy sand along edge of channel; open mixed hardwood forest between power-line and road; along powerline corridors; and grassy clearings of pine-palmetto flats. Substrate types include loam, loamy sand, sandy loam, calcareous soils, limestone, sand, and sandy peat.[3]
Associated species include Eupatorium fisulosum, Arnoflossum ovatum, Smilax bona-nox, Morus rubra, Campsis radicans, and cabbage palm.[3]
Phenology
This species has been observed to flower January through November[4] and fruits June through November.[3]
Seed bank and germination
Heating at low temperatures stimulates germination in V. gigantea.[2]
Fire ecology
It has been observed to thrive after low-intensity fires.[2]
Pollination
Vernonia gigantea has been observed with bees such as Xylocopa virginica (family Apidae), leafcutting bees from the Megachilidae family such as Megachile brevis, M. latimanus, M. mendica, and M. perihirta, and plant bugs such as Lygus lineolaris (family Miridae).[5]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Emery, S. M., J. Uwimbabazi, et al. (2011). "Fire intensity effects on seed germination of native and invasive Eastern deciduous forest understory plants." Forest Ecology and Management 261: 1401-1408.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, Robert L. Lazor, Gary R. Knight, R. Kral, P. L. Redfearn, Jr., R. F. Thorne, R. A. Davidson, Brenda Herring, Don Herring, R. A. Norris, Andre F. Clewell, Sidney McDaniel, R. Komarek, Lisa Keppner, S. W. Leonard, Richard S. Mitchell, D. S. Correll, Grady W. Reinert. States and Counties: Florida: Brevard, Calhoun, Citrus, Dixie, Escambia, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Gilchrist, Gulf, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Nassau, Polk, Putnam, Seminole, St. Johns, Suwannee, Taylor, Wakulla, Washington. Georgia: Thomas. Mississippi: Holmes. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [1]