Difference between revisions of "Vaccinium corymbosum"
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | + | ''Vaccinium corymbosum'' has been observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host bees from the Apidae family such as ''Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens,'' and ''Habropoda laboriosa'', plasterer bees such as ''Hylaeus confluens'' (family Colletidae), sweat bees from the Halictidae family such as ''Augochlorella gratiosa, Augochloropsis anonyma, A. sumptuosa,'' and ''Lasioglossum placidensis'', wasps from the Leucospididae family such as ''Leucospis robertsoni,'' and ''L. slossonae'', and thread-waisted wasps from the Vespidae family such as ''Pachodynerus nasidens, Polistes bahamensis, Stenodynerus histrionalis rufustus, S. lineatifrons,'' and ''Zethus slossonae''.<ref name="Deyrup 2015">Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> Additionally, ''V. corymbosum'' has been observed with ground-nesting bees from the Andrenidae family such as ''Andrena bradleyi, A. carolina, A. forbesii, A. imitatrix, A. nasonii, A. rufosignata'' and ''A. vicina,'' bees from the Apidae family such as ''Bombus auricomus, B. bimaculatus, B. griseocollis, Nomada xanthura'' and ''Xylocopa virginica'', sweat bees from the Halictidae family such as ''A. sericeus, A. virescens, Augochlorella aurata, A. metallica, Halictus confusus, L bruneri, L. cressonii, L. leucozonium, L. oceanicum, L. tegulare, L. timothyi, L. versans, L. versatum,'' and ''Sphecodes aroniae,'' and leafcutting bees from the Megachilidae family such as ''Osmia lignaria'' and ''O. sandhouseae''.<ref>Discoverlife.org [https://www.discoverlife.org/20/q?search=Bidens+albaDiscoverlife.org|Discoverlife.org]</ref> | |
| − | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology=== <!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc.--> | |
| − | Apidae | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Halictidae | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <!--=== | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:14, 18 July 2022
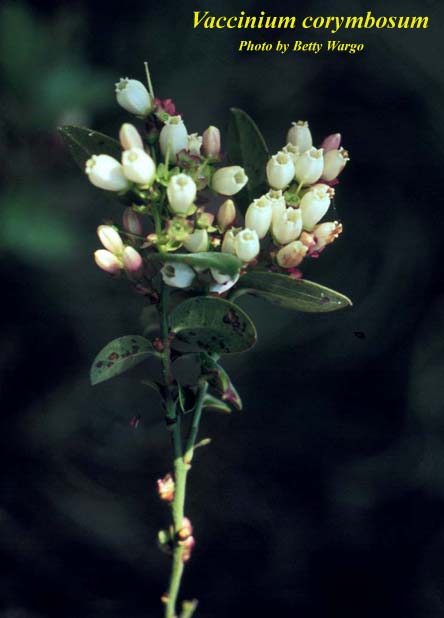
| Vaccinium corymbosum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Betty Wargo, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ericaceae |
| Genus: | Vaccinium |
| Species: | V. corymbosum |
| Binomial name | |
| Vaccinium corymbosum L. | |
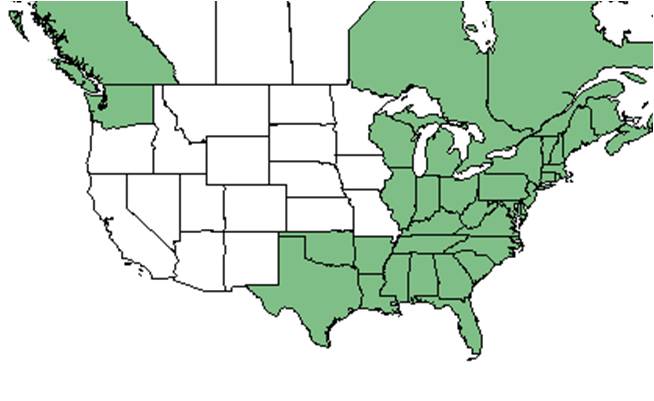
| |
| Natural range of Vaccinium corymbosum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Highbush blueberry
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Cyanococcus corymbosus (Linnaeus) Rydberg; V. constablaei A. Gray.[1]
Varieties: V. corymbosum var. albiflorum (Hooker) Fernald; V. corymbosum var. glabrum.[2]
Description
A description of Vaccinium corymbosum is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
V. corymbosum has been found on stands of slash pine, bald cypress swamps, mixed hardwood swamps, pine-oak woodlands, prairies, wet flatwoods, and sand ridges.[3] It is also found in disturbed areas including burned pinewoods, along roadsides, and burned pine savannahs.[3]
Associated species: Gaylussocia spp., Acer rubrum, Liquidambar styraciflua, Pinus virginiana, and V. myrsinites.[3][4]
Phenology
V. corymbosum has been observed to flower January to April and in December.[5]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by consumption by vertebrates.[6]
Pollination
Vaccinium corymbosum has been observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host bees from the Apidae family such as Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens, and Habropoda laboriosa, plasterer bees such as Hylaeus confluens (family Colletidae), sweat bees from the Halictidae family such as Augochlorella gratiosa, Augochloropsis anonyma, A. sumptuosa, and Lasioglossum placidensis, wasps from the Leucospididae family such as Leucospis robertsoni, and L. slossonae, and thread-waisted wasps from the Vespidae family such as Pachodynerus nasidens, Polistes bahamensis, Stenodynerus histrionalis rufustus, S. lineatifrons, and Zethus slossonae.[7] Additionally, V. corymbosum has been observed with ground-nesting bees from the Andrenidae family such as Andrena bradleyi, A. carolina, A. forbesii, A. imitatrix, A. nasonii, A. rufosignata and A. vicina, bees from the Apidae family such as Bombus auricomus, B. bimaculatus, B. griseocollis, Nomada xanthura and Xylocopa virginica, sweat bees from the Halictidae family such as A. sericeus, A. virescens, Augochlorella aurata, A. metallica, Halictus confusus, L bruneri, L. cressonii, L. leucozonium, L. oceanicum, L. tegulare, L. timothyi, L. versans, L. versatum, and Sphecodes aroniae, and leafcutting bees from the Megachilidae family such as Osmia lignaria and O. sandhouseae.[8]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
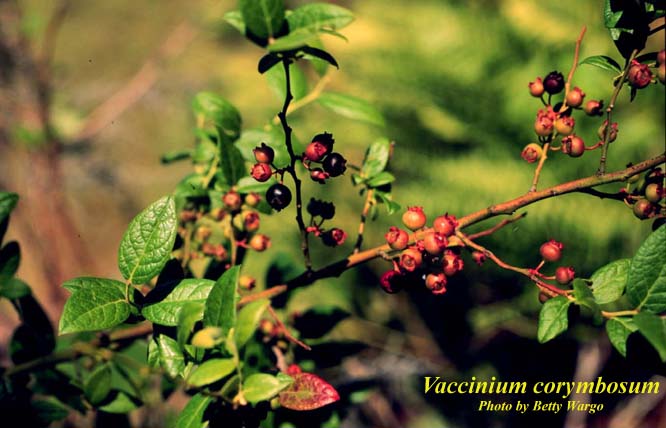
Vaccinium corymbosum produces a berry that can be eaten raw or cooked into goods such as jellies or pies.[9]
Photo Gallery
Flowers & Fruit of Vaccinium corymbosum Photos by Betty Wargo, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Florida State University Herbarium Database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: L.C. Anderson, R.K. Godfrey, B. K. Holst, Cecil R Slaughter, and Birgit Wiedwald. States and counties: Florida: Liberty, Marion, Nassau, Sarasota, Wakulla, and Walton.
- ↑ Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University accessed using Southeastern Regional Network of Expertise and Collections (SERNEC) data portal. URL: http://sernecportal.org/portal/collections/index.php Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Stevens Heckscher. States and Counties: New Jersey: Cumberland.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 14 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [1]
- ↑ Hardin, J.W., Arena, J.M. 1969. Human Poisoning from Native and Cultivated Plants. Duke University Press, Durham, North Carolina.

